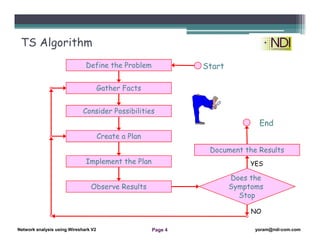
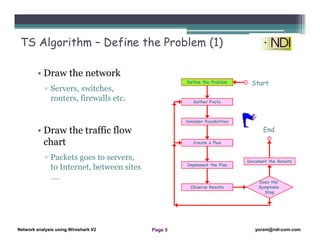
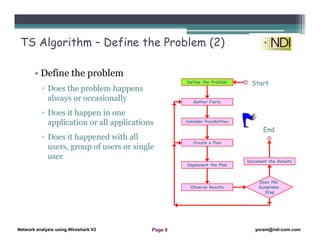
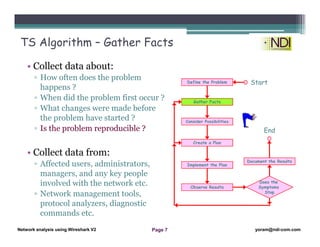
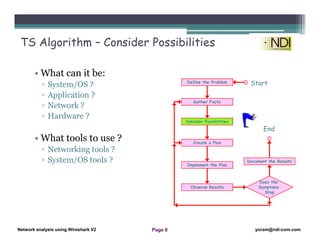
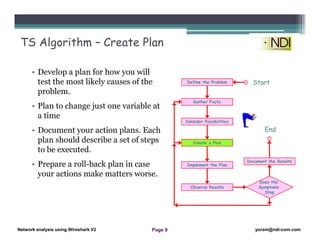
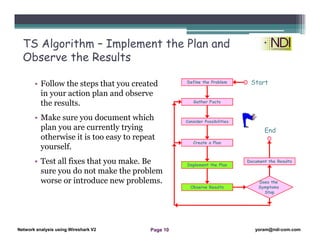
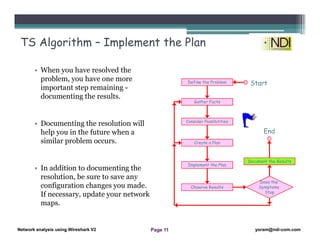
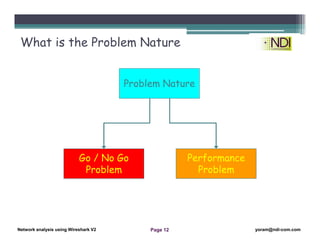
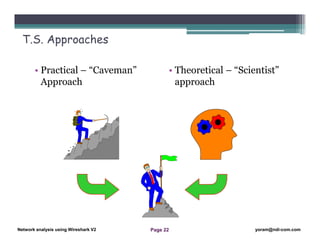
This document serves as a lesson on network analysis using Wireshark, outlining key concepts and methodologies for troubleshooting network problems. It introduces the troubleshooting process through specific algorithms and emphasizes the importance of gathering facts, testing hypotheses, and documenting results. Additionally, it discusses different approaches to troubleshooting, advocating for a comprehensive and systematic examination of the network while considering user-related issues.