Embed presentation
Downloaded 48 times








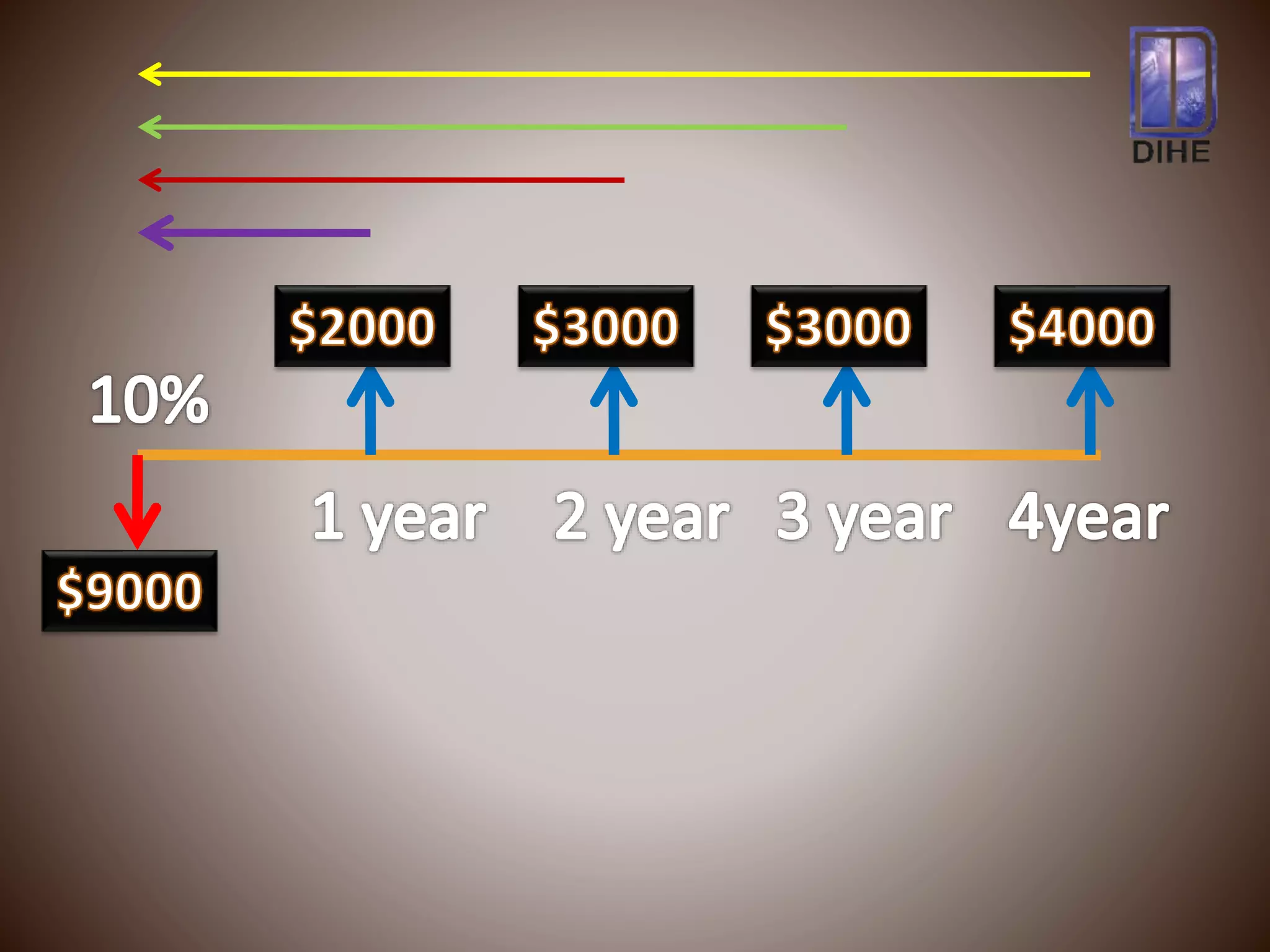



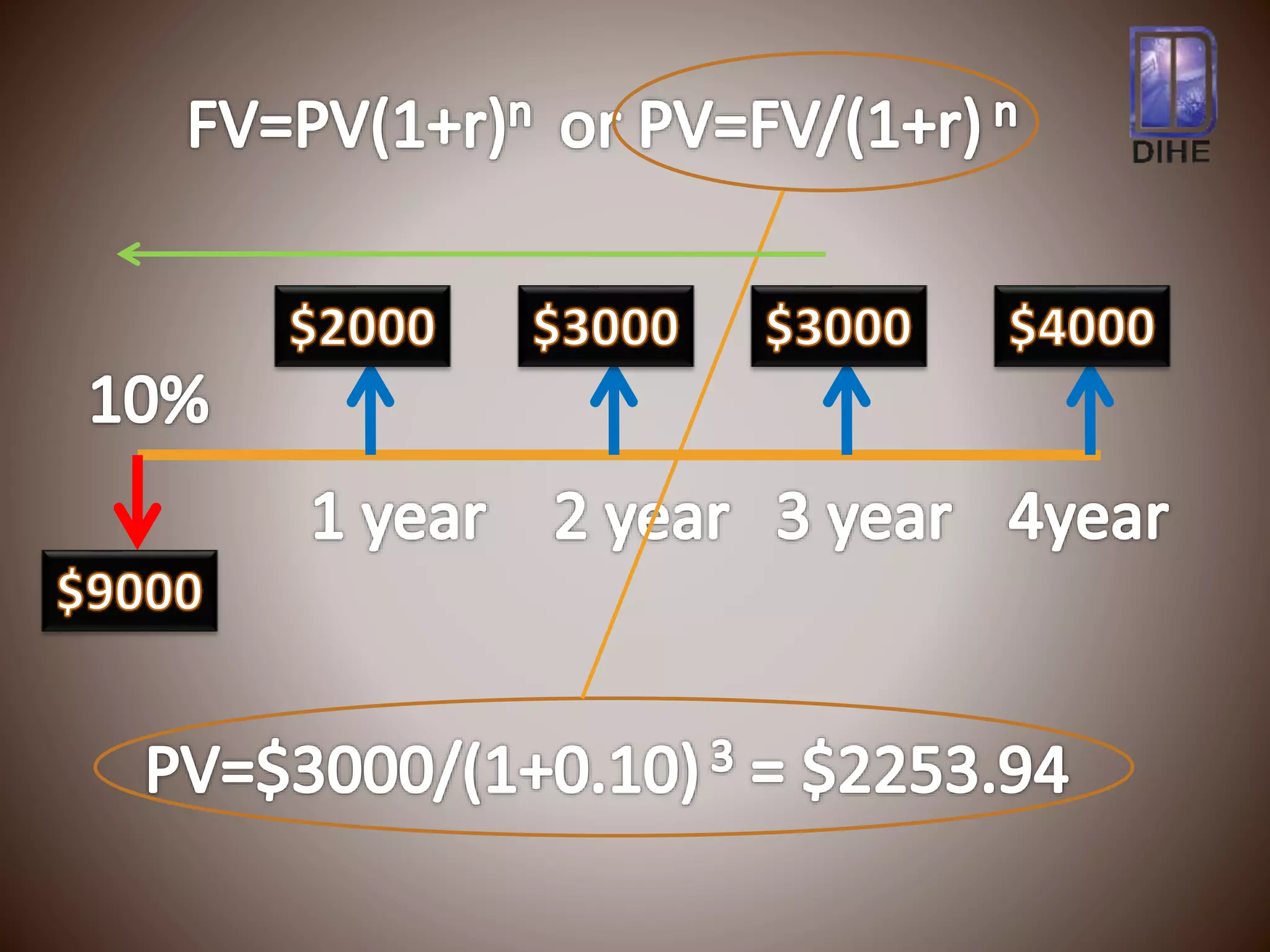

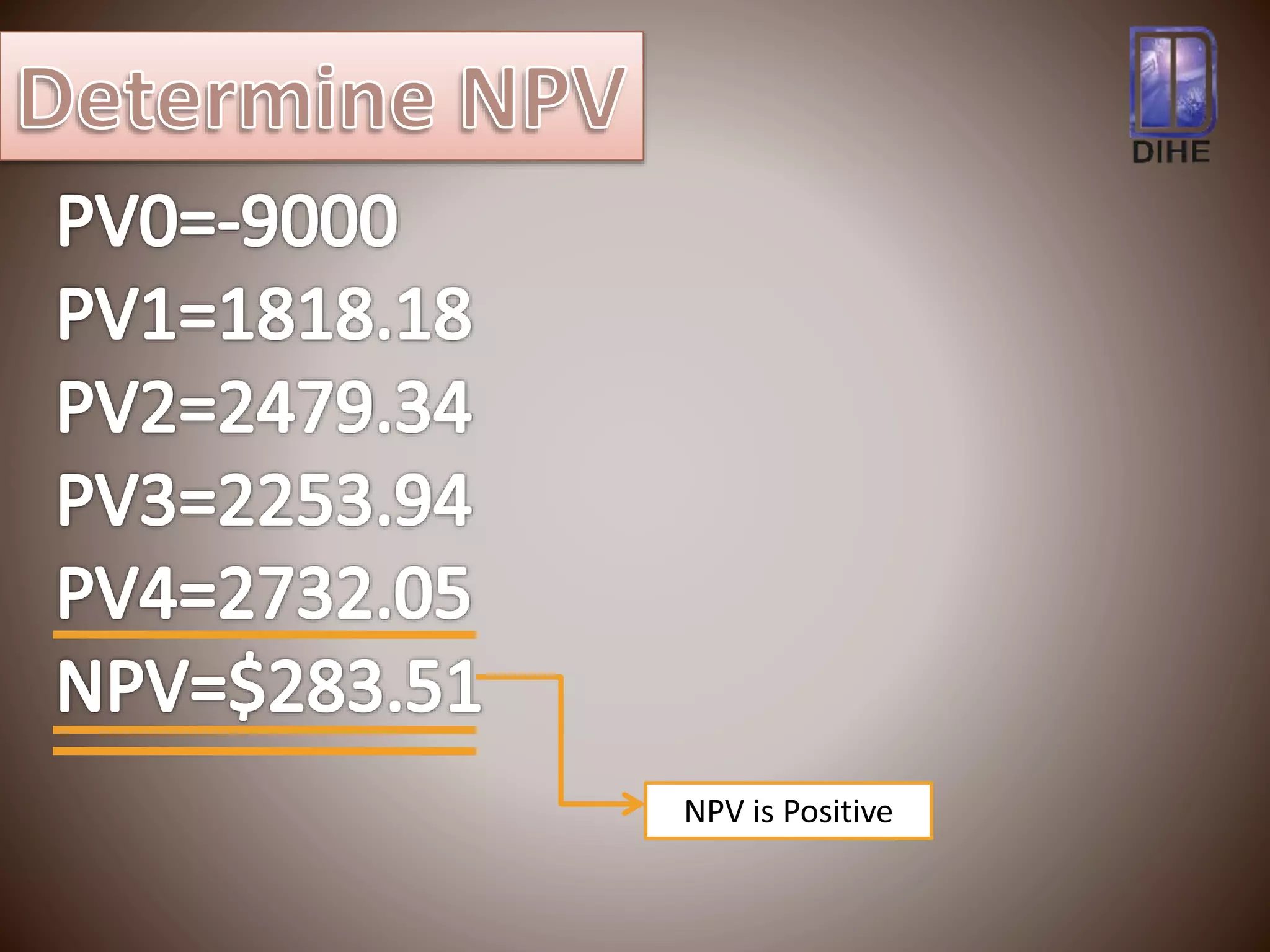



The document discusses net present value (NPV) as a capital budgeting technique that discounts cash inflows and outflows to account for the time value of money. NPV is calculated as the present value of cash inflows minus the present value of cash outflows. If NPV is positive, the investment proposal is acceptable as it adds value. If NPV is negative, the proposal is rejected. The example calculates NPV of $283.51 for an investment of $9,000 with expected cash flows over four years, indicating it is a positive NPV and acceptable project.

















