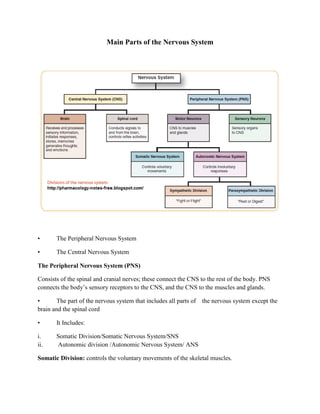
The nervous system is comprised of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS contains the brain and spinal cord, and is responsible for processing sensory information and coordinating voluntary and involuntary actions. The highly complex brain is the control center and consists of different regions that perform specialized functions like memory, vision, and motor control. The PNS connects the CNS to the rest of the body and includes the autonomic nervous system which regulates involuntary body functions. Neurons are the basic functional units that transmit electrochemical signals throughout the nervous system, enabling it to coordinate all activities and maintain homeostasis.