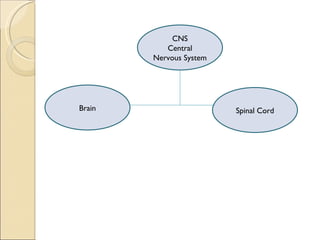
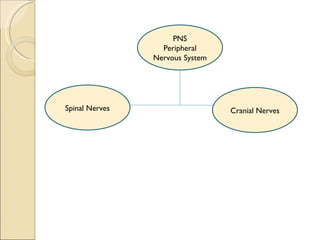
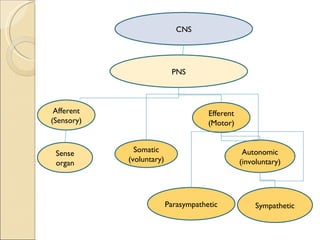
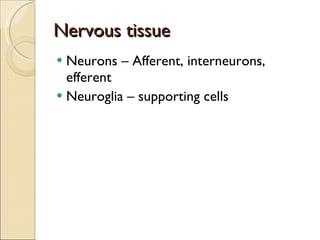
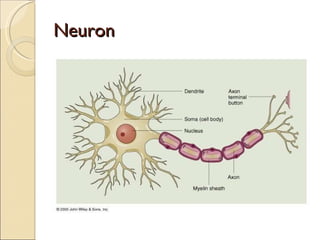
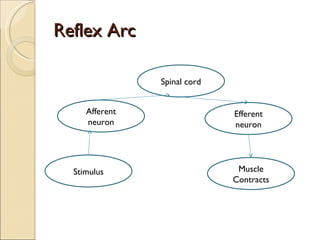
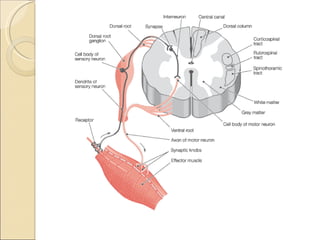
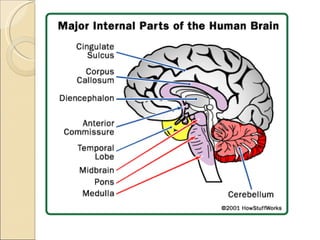
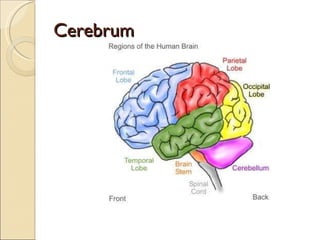
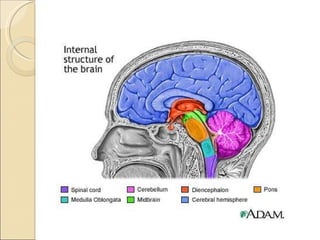
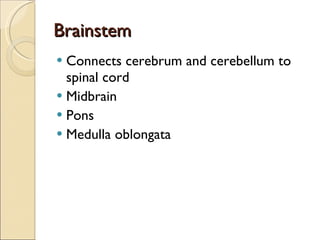
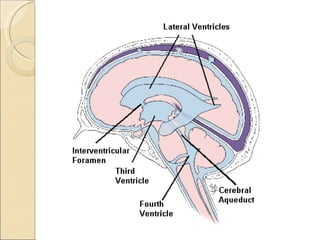
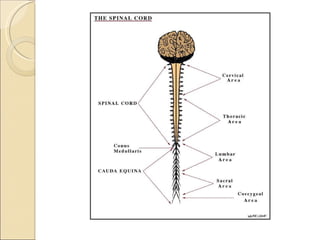
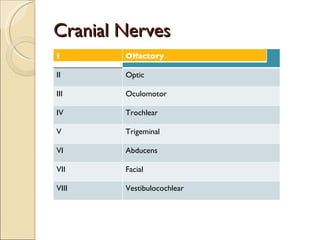
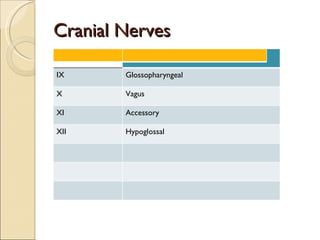
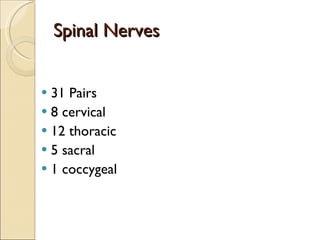
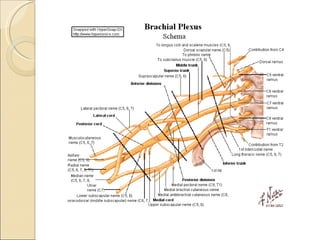
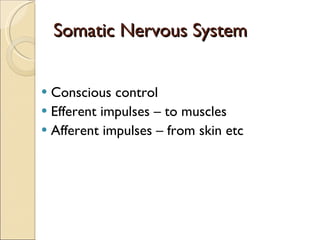
The document summarizes the main components and functions of the human nervous system. It describes the central nervous system including the brain and spinal cord. It also describes the peripheral nervous system including cranial nerves and spinal nerves. Finally, it discusses the different types of neurons, their functions, and how they transmit signals in the body.