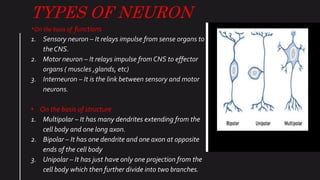
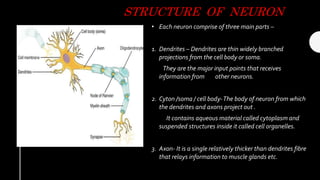
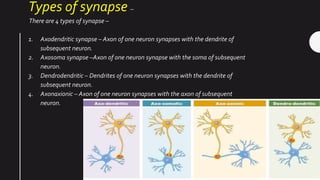
Neurons are electrically excitable cells that communicate with each other and the body. The human nervous system contains around 100 billion neurons. There are three main types of neurons - sensory neurons relay signals from sense organs to the central nervous system, motor neurons relay signals from the CNS to effector organs, and interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons. Each neuron has a cell body, dendrites that receive signals, and an axon that transmits signals. When a neuron is stimulated, it generates an action potential down its axon via changes in membrane potential. Neurotransmitters are released at synapses to transmit signals between neurons.