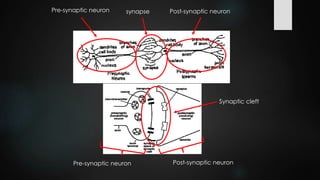
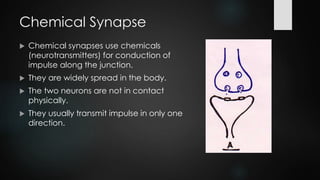
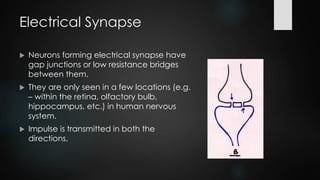
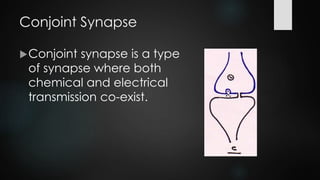
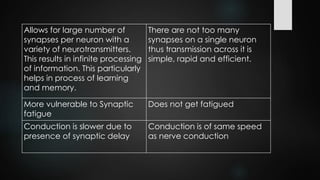
This document discusses and compares chemical and electrical synapses. It defines a synapse as a junction between two neurons. There are three types of synapses: chemical, electrical, and conjoint. Chemical synapses use neurotransmitters for impulse transmission across the synaptic cleft in one direction, while electrical synapses have direct connections through gap junctions that allow for faster two-way transmission. Key differences are that chemical synapses exhibit synaptic properties and delay, while electrical synapses do not.