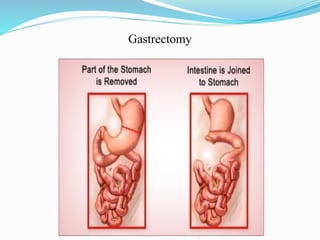
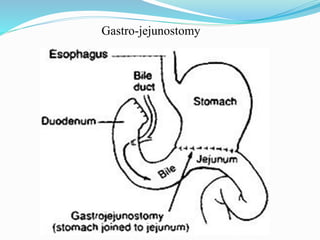
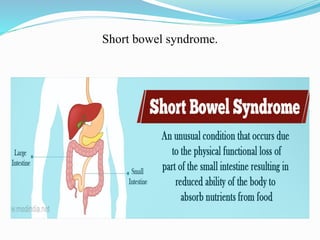
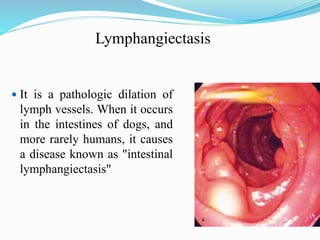
Malabsorption syndrome is characterized by ineffective nutrient absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, leading to malnutrition and various anemias. Common causes include bile salt insufficiency, infections, pancreatic diseases, and intestinal structural defects, with symptoms such as chronic diarrhea, weight loss, and failure to thrive. Management involves dietary modifications, fluid replacement, and treatment of underlying conditions, while nursing care focuses on monitoring patient status and providing education to families.