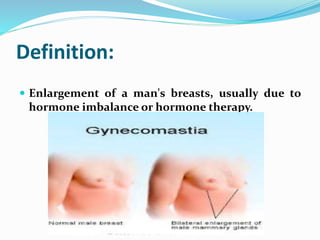
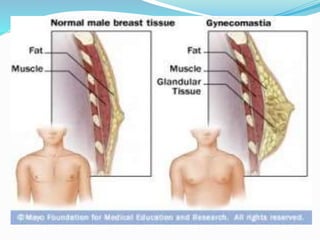
Gynecomastia is a condition where breast tissue swells in boys and men, causing enlarged breasts. It is usually caused by an imbalance of male and female hormones. Gynecomastia commonly occurs during adolescence, older age, and can be caused by certain medications, diseases, or substance abuse. Evaluation may involve blood tests, imaging scans, and biopsies to determine the cause. Treatment options include antiestrogen medications, surgery to remove breast tissue or fat, and lifestyle changes to prevent future occurrence.