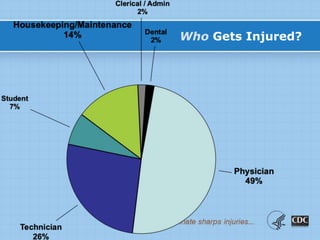
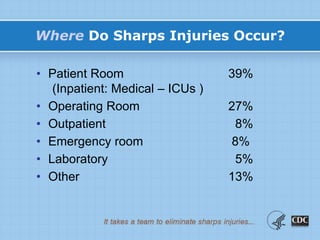
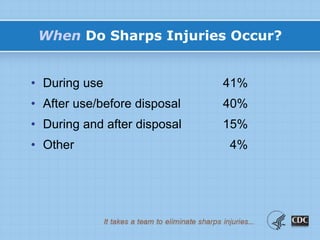
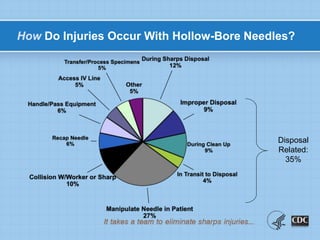
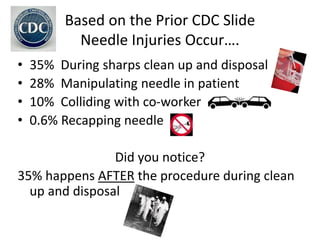
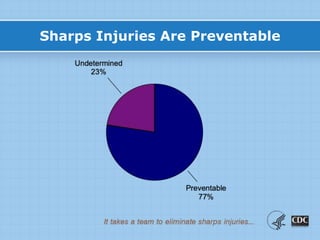
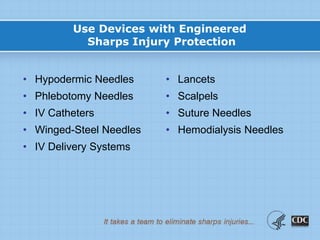
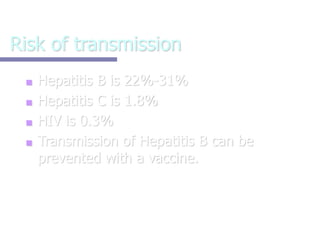This document provides information on preventing and reporting needlestick and sharps injuries. It discusses who is most at risk, where injuries typically occur, when they happen, and which devices are most commonly involved. The six devices that account for 78% of injuries are identified. Strategies for prevention include eliminating unnecessary needle use, using safer sharps devices with safety features, and following safe work practices around preparation, awareness during procedures, and proper clean up and disposal. Not following these practices can lead to exposure to bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV. It is important to report any exposures immediately to facilitate testing and post-exposure prophylaxis if needed.