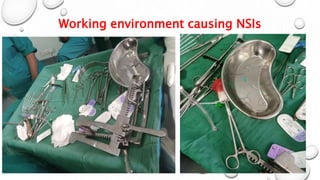
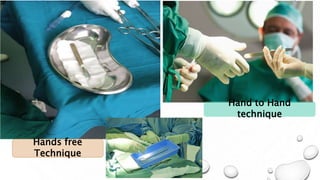
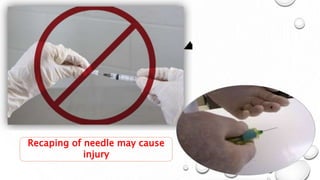
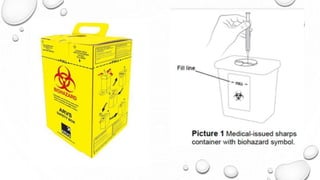
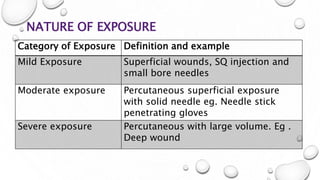
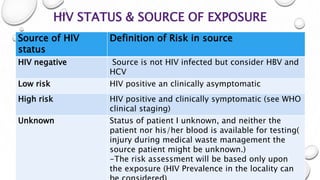
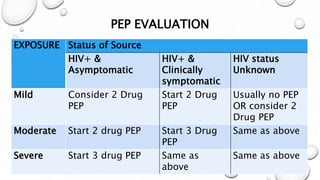
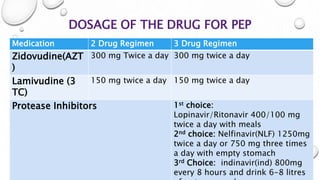
This document provides guidance on proper sharps handling and needlestick injury prevention. It defines sharps and needlestick injuries, identifies causes and risks. Guidelines are provided for safe sharps use, disposal and handling of occupational exposures, including immediate first aid, evaluation for post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), and follow up testing. Case scenarios demonstrate appropriate vs inappropriate responses to needlestick injuries. Overall the document aims to educate on preventing needlestick injuries and properly managing incidents to reduce disease transmission risk among healthcare workers.