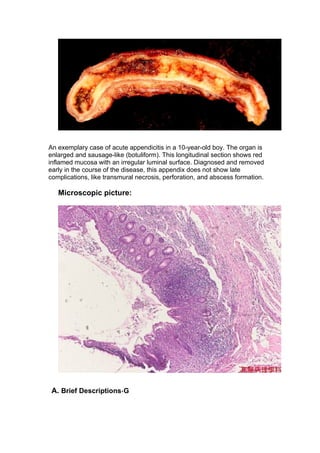
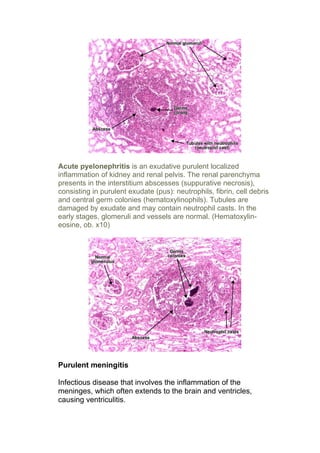
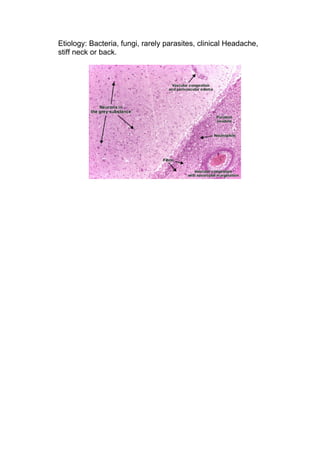
Purulent inflammation, also known as suppurative inflammation, results from bacterial infection and is characterized by large amounts of pus consisting of neutrophils, dead cells, and fluid. Abscesses form when pus accumulates in enclosed tissue spaces. Examples given include suppurative appendicitis, pyelonephritis, and purulent meningitis. Suppurative appendicitis specifically involves obstruction of the appendix leading to bacterial infection, swelling, and eventual rupture and abscess formation. Pyelonephritis is a urinary tract infection of the kidneys that can cause interstitial abscesses and suppuration if severe. Purulent meningitis is an infectious inflammation of the meninges often involving the brain and