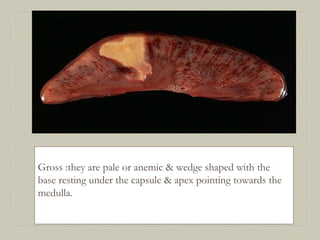
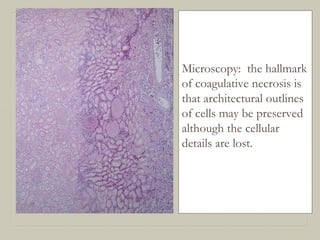
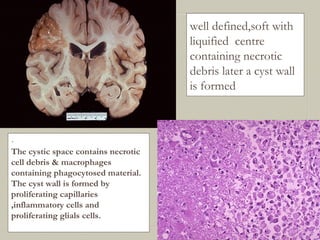
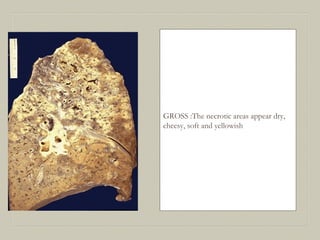
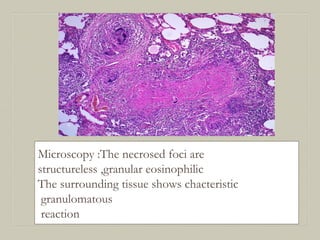
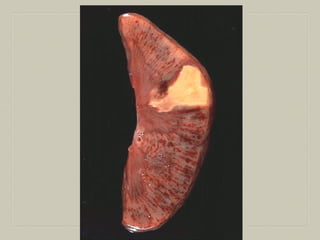
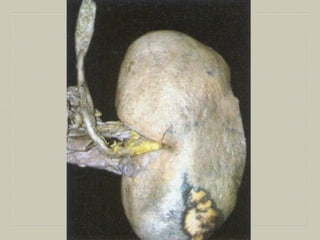
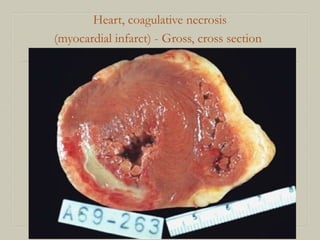
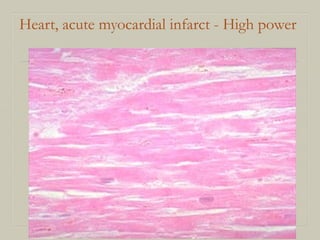
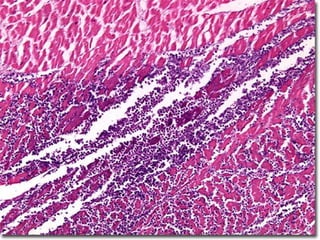
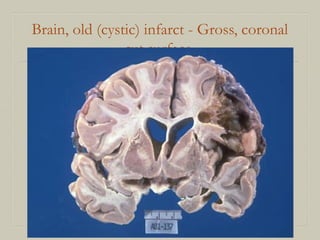
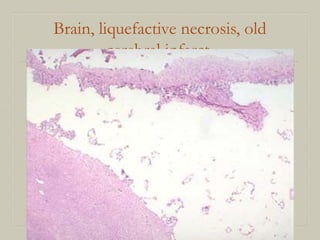
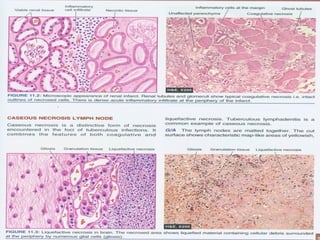
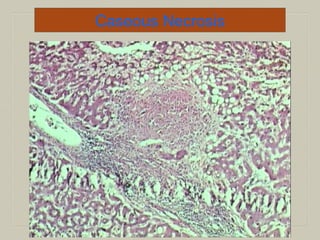
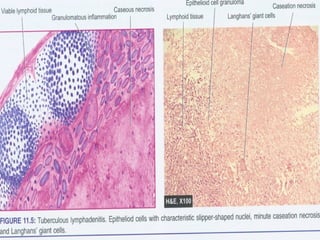
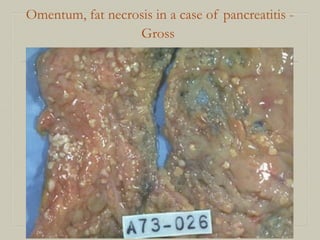
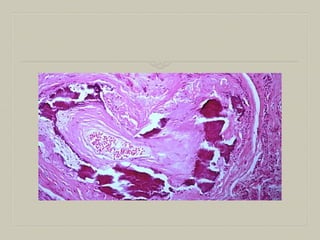
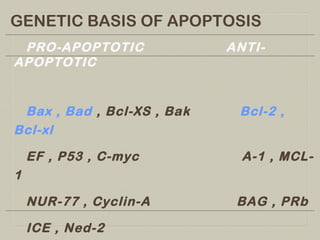
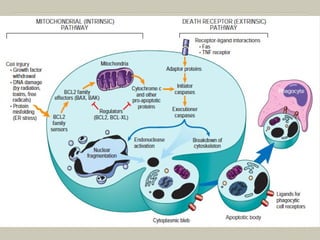
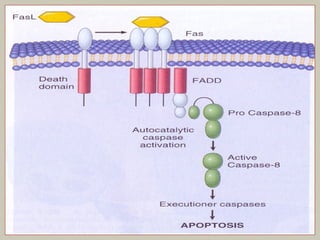
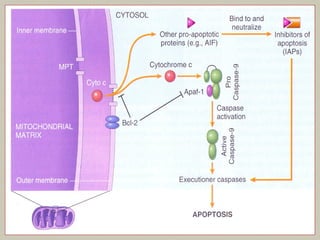
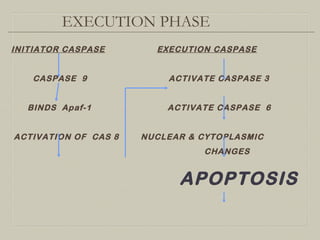
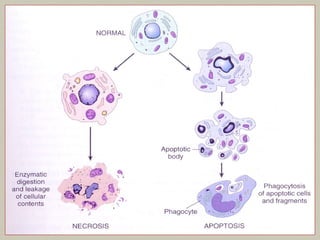
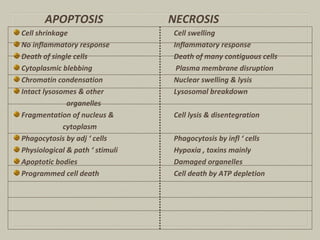
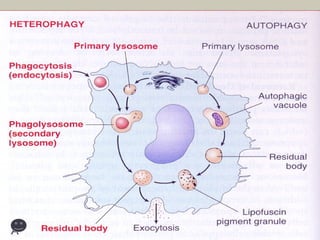
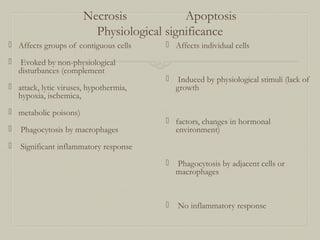
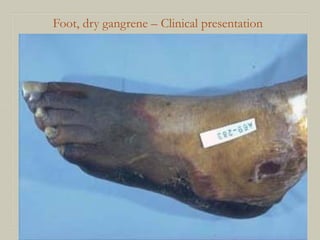
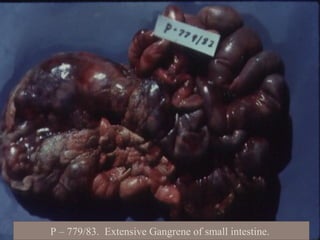
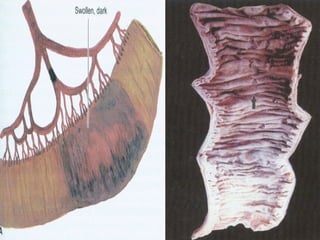
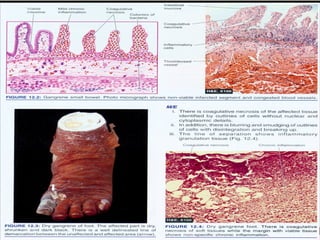
This document defines and describes various pathological processes including degeneration, necrosis, apoptosis, gangrene, and calcification. It discusses four main types of degenerative cell changes: cellular swelling, fatty change, hyaline change, and mucoid change. It also describes five types of necrosis: coagulative, liquefactive, caseous, fat, and fibrinoid necrosis. Apoptosis is defined as a genetically programmed form of cell death. Gangrene is described as necrosis with superadded putrefaction. Pathologic calcification can be either dystrophic or metastatic.



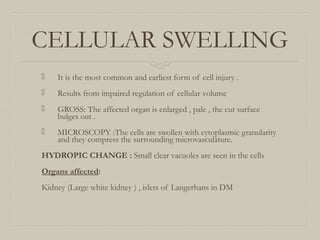
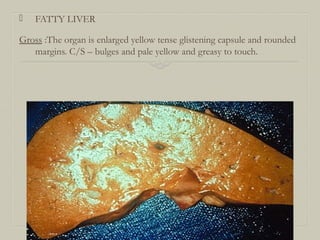
![FATTY CHANGE
Occurs due to intracellular accumulation of neutral
fats.
CAUSES:
Excess alcohol consumption,obesity malnutrition
,starvation ,diabetes mellitus, chronic ilnesses , late
pregnancy, hypoxia , hepatotoxins [ carbontetra
chloride , chloroform , ether,aflatoxins ] certain
drugslike estrogen steroids tetracycline etc.
Liver is the most common organ affected . Other
organs affected are heart, kidney and skeletal muscle.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/necrosisgangrene-170421144523/85/Necrosis-gangrene-pathology-calcification-6-320.jpg)
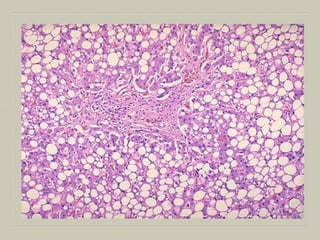
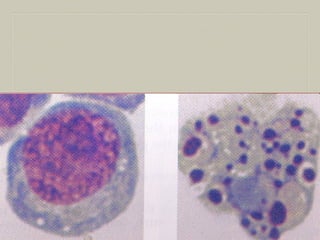
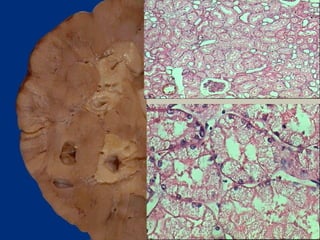
![MICROSCOPY
Fat in the cytoplasm of the hepatocytes is seen as
clear area which may vary from minute droplets in the
cytoplasm of a few hepatocytes [microvesicular] to
distension of the entire cytoplasm of most cells by
coaslesced droplets [macrovesicular] pushing the
nucleus to the periphery of the cell.
Occ. the adjacent cell containing fat, rupture
producing fatty cysts
Special stains such Sudan III & IV,Sudan black Oil
red O can be employed to demonstrate fat in the
tissue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/necrosisgangrene-170421144523/85/Necrosis-gangrene-pathology-calcification-8-320.jpg)