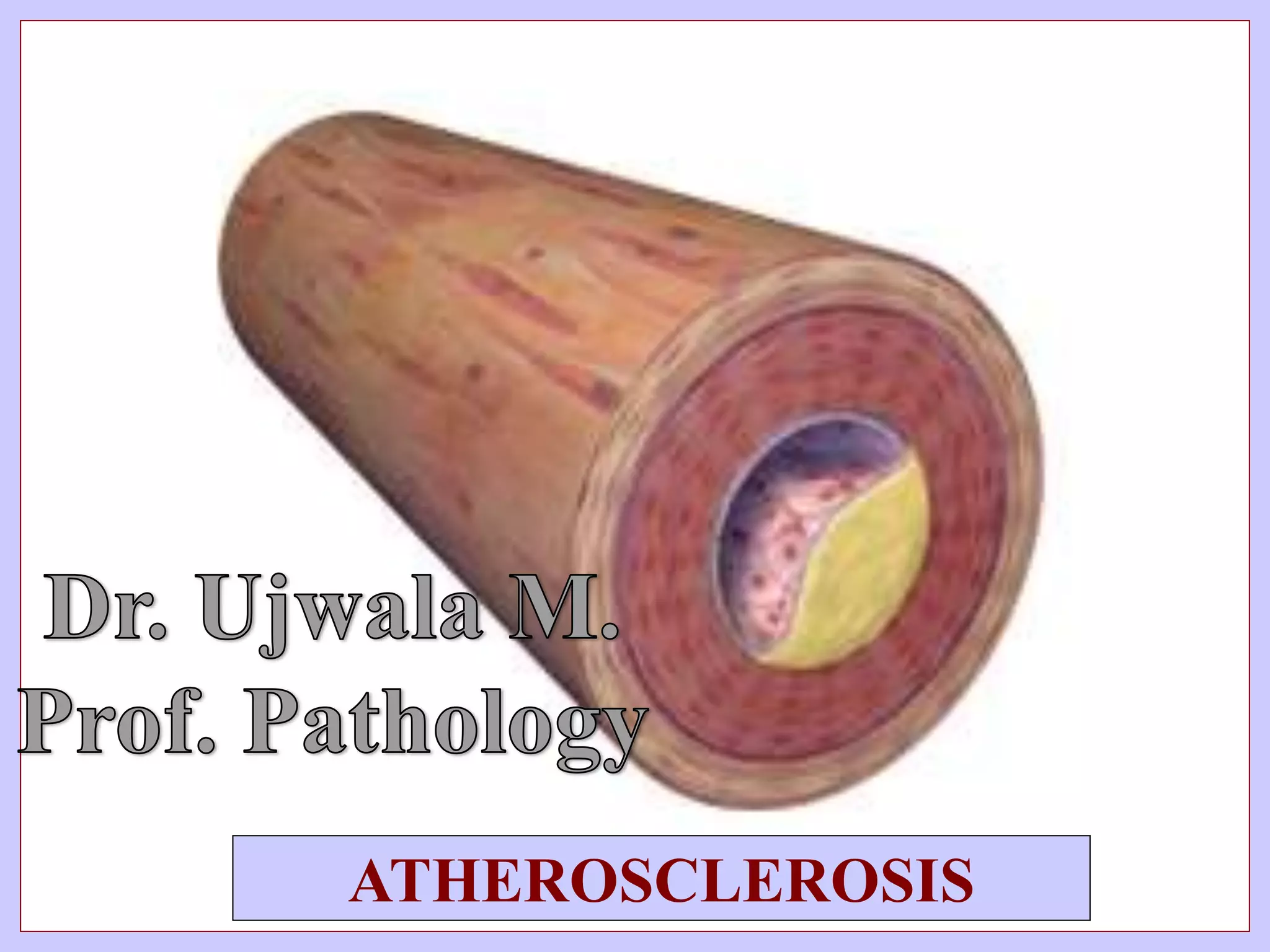
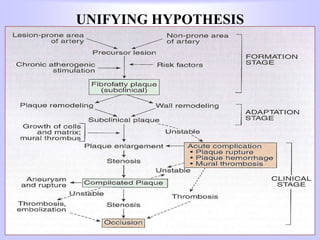
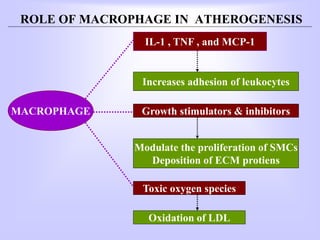
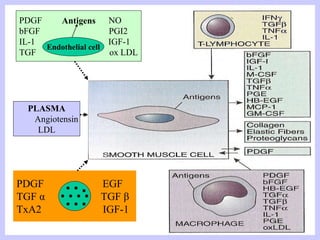
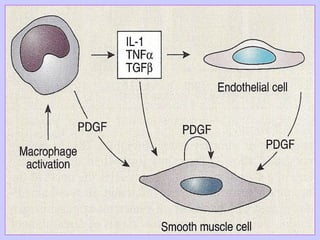
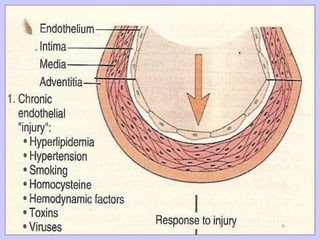
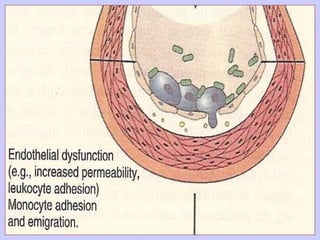
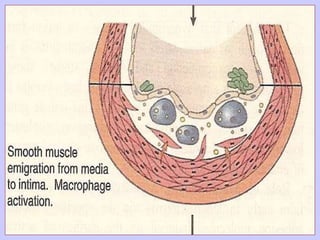
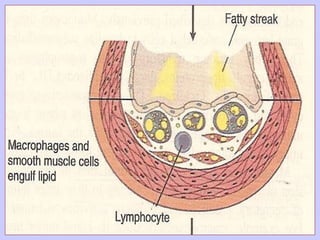
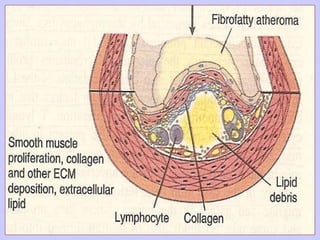
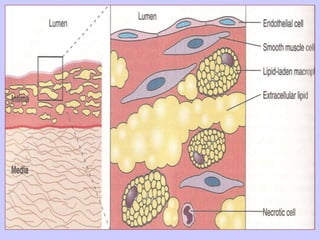
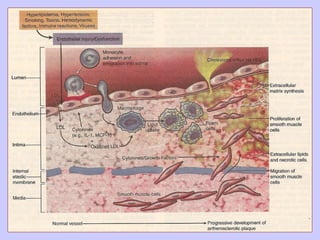
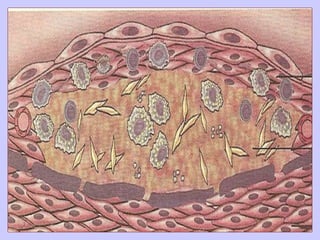
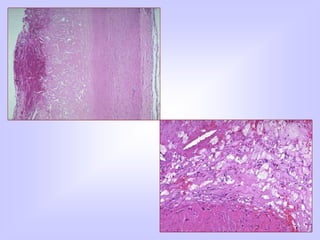
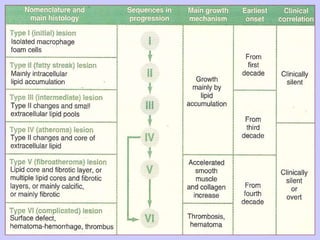
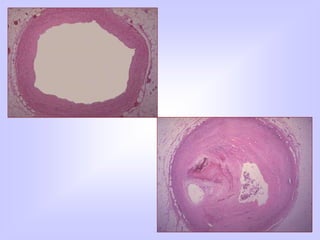
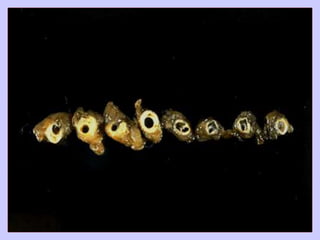
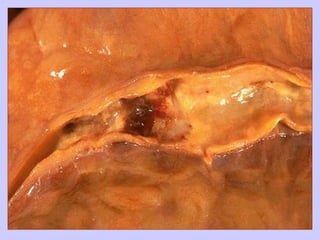
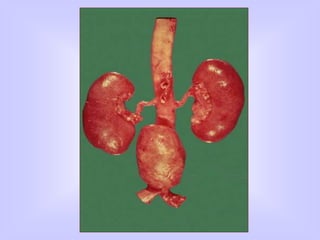
The document discusses atherosclerosis and its risk factors and various hypotheses about its pathogenesis. It describes the roles of oxidized LDL, macrophages, and endothelial cells in driving atherosclerosis. It outlines the progression from fatty streaks to more advanced atheromatous plaques and complicated lesions. Fatty streaks are the earliest subclinical lesions while atherosclerosis refers to lesions that are clinically significant. Complications can arise from processes like calcification, ulceration, rupture, hemorrhage, and thrombosis.