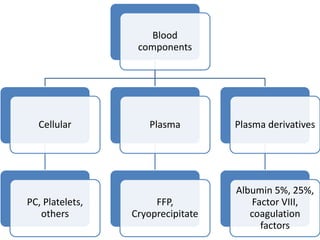
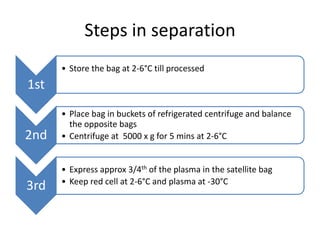
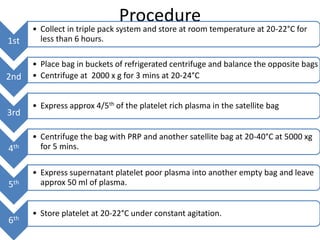
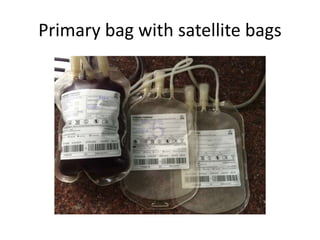
1) Blood components like packed red cells, platelet concentrates and fresh frozen plasma can be prepared by separating whole blood into its components using centrifugation and expressors.
2) Optimal storage conditions and times allow individual components to be stored and transfused separately as needed rather than transfusing whole blood.
3) The document outlines the equipment, procedures and quality indicators for preparing the main blood components from a single donor to benefit multiple recipients.