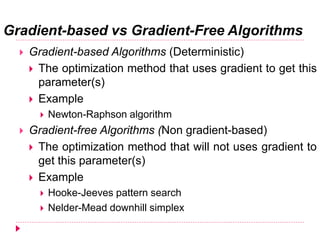
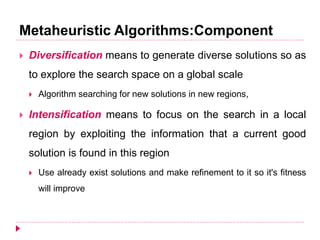
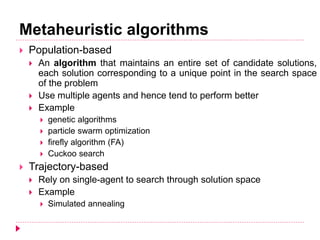
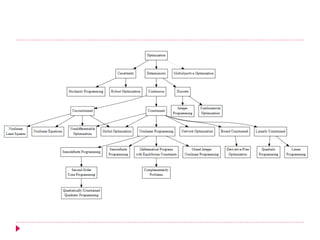
The document discusses different types of nature-inspired metaheuristics used for optimization problems. It describes deterministic methods like hill-climbing that always produce the same output for a given input, and stochastic methods like genetic algorithms that can produce different outputs for the same input due to randomness. Gradient-based methods use gradients to find optimal parameters, while gradient-free methods do not. Metaheuristics employ intensification to exploit good solutions locally and diversification to explore globally. Population-based metaheuristics maintain a set of candidate solutions, while trajectory-based methods rely on a single agent. Examples of various metaheuristics are provided.