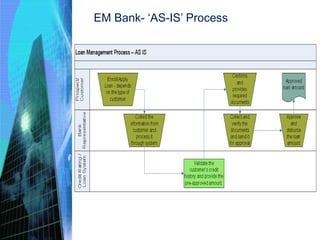
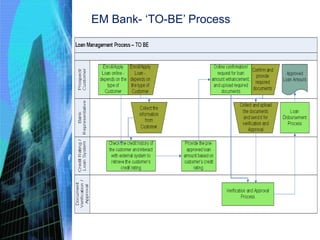
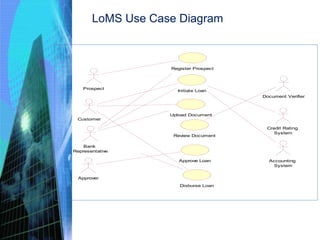
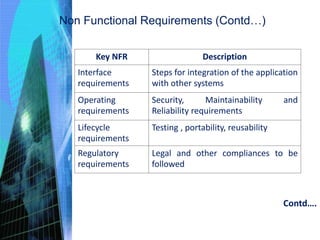
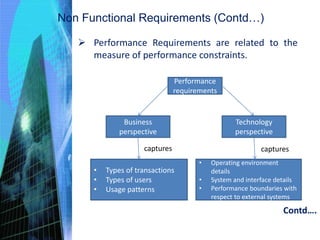
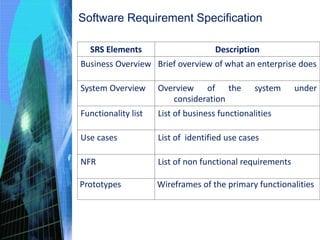
This document discusses the key activities involved in incepting an enterprise application, including enterprise analysis, business modeling, requirements elicitation and analysis, requirements validation, and planning and estimation. Enterprise analysis involves identifying business opportunities and stakeholders. Business modeling helps understand business processes and includes creating AS-IS and TO-BE models. Requirements elicitation captures functional and non-functional requirements through use cases and prototypes. Requirements validation ensures requirements meet business needs. Planning and estimation prepares project plans and estimates costs and effort based on techniques like use case points and function points.