Embed presentation


![char str[] ="Happy";
char *p=str;
printf("%sn",str);
printf("%sn",str);
printf("%sn", p);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-210511045736/85/12-string-and-pointer-4-320.jpg)
![for(i = 0; str[i]; i++)
printf("%cn",str[i]);
for(i = 0; str[i]!='0'; i++)
printf("%cn",*(str+i));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-210511045736/85/12-string-and-pointer-5-320.jpg)
![char *ptr; ptr=str;
for( i=0;str[i];i++)
printf("%ct",*(ptr+i));
ptr=str;
for( i=0;str[i]!='0';i++)
printf("%ct",*ptr++);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-210511045736/85/12-string-and-pointer-6-320.jpg)


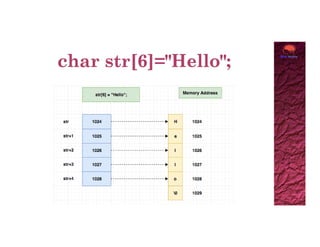
The document discusses how strings in C act as pointers, with examples illustrating the usage of string variables and character traversal. It provides code snippets to demonstrate different methods to print characters of a string. Overall, it highlights the relationship between string names and their memory addresses.



![char str[] ="Happy";
char *p=str;
printf("%sn",str);
printf("%sn",str);
printf("%sn", p);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-210511045736/85/12-string-and-pointer-4-320.jpg)
![for(i = 0; str[i]; i++)
printf("%cn",str[i]);
for(i = 0; str[i]!='0'; i++)
printf("%cn",*(str+i));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-210511045736/85/12-string-and-pointer-5-320.jpg)
![char *ptr; ptr=str;
for( i=0;str[i];i++)
printf("%ct",*(ptr+i));
ptr=str;
for( i=0;str[i]!='0';i++)
printf("%ct",*ptr++);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-210511045736/85/12-string-and-pointer-6-320.jpg)
