Embed presentation


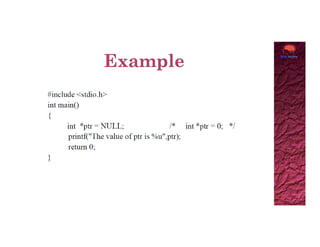




A null pointer points to nothing or nowhere and is initialized to NULL or 0. Pointers must be initialized to NULL to indicate no memory is allocated yet. Functions returning pointers may need to indicate errors by returning a null pointer. Passing NULL to a function avoids passing an invalid memory address. Dereferencing a null pointer will cause a program to abort, so pointers should be checked against NULL before accessing their value.





