1) The document discusses India's National Leprosy Eradication Programme, including its history, strategies, infrastructure, and treatment protocols.
2) Key statistics provided include that India accounts for 60.9% of global leprosy cases, with a prevalence rate of 5.0 per 10,000 people.
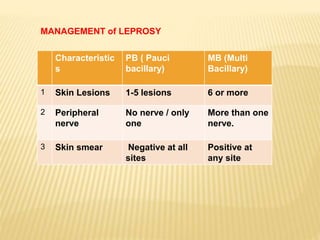
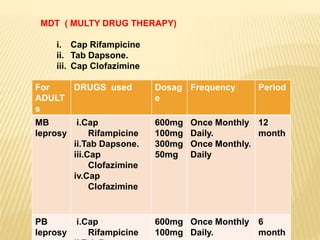
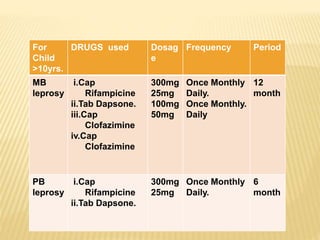
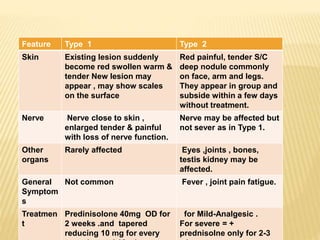
3) The program's objectives are to eliminate leprosy through early case detection, short-term multidrug therapy, health education, and rehabilitation. Treatment involves multidrug regimens administered monthly or daily depending on the type of leprosy.