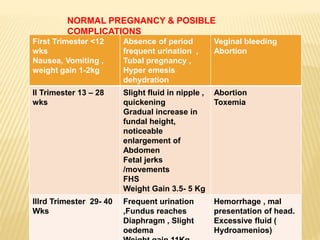
This document discusses maternal health care for paramedics. It covers topics like obstetrics, management of pregnancy and labor under normal and abnormal circumstances, social obstetrics, social pediatrics, maternal and child health services, the need for specialized primary health services for mothers and children, national programs, targets populations, assessing needs, identifying high-risk pregnancies, normal pregnancy and possible complications by trimester, the role of trained birth attendants, and warning signs during pregnancy and labor.