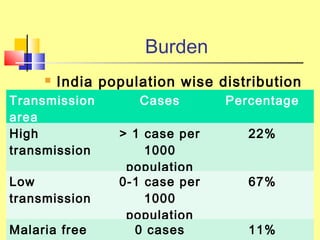
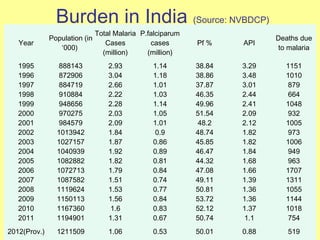
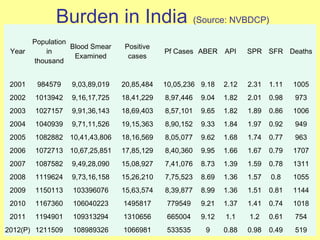
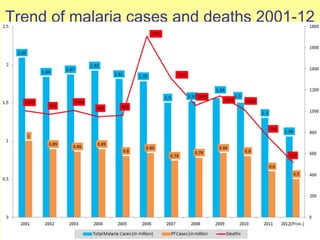
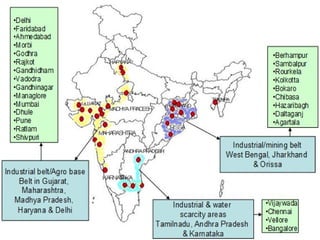
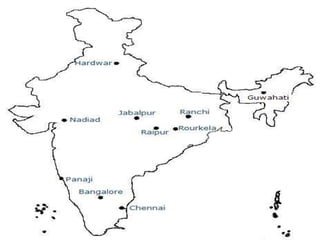
The document discusses the burden and history of malaria control efforts in India. It notes that in 2012, India reported over 1 million malaria cases and over 500 deaths. It outlines the various national malaria control programs from the Bhore Committee in 1946 to the current National Vector Borne Disease Control Program. Key strategies have included insecticide spraying, surveillance, diagnosis and treatment. Urban areas pose ongoing challenges, with the Urban Malaria Scheme currently covering 131 high burden towns.