Nanomaterials are materials that have at least one dimension sized between 1 to 100 nanometers. They have unique properties compared to larger materials due to increased surface area to volume ratio and quantum effects. Nanomaterials can be synthesized through top-down methods that break down bulk materials or bottom-up techniques that build up atoms and molecules. They have a variety of applications including in electronics, energy storage, medicine and more due to their small size and novel characteristics.



![12/4//2015
7
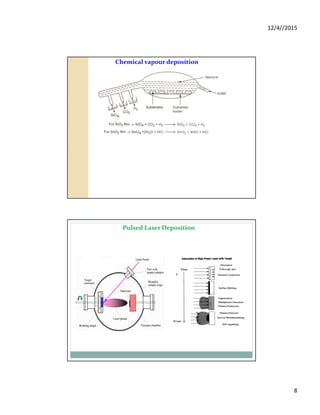
Synthesis of nanomaterials
Bulk
Powder
Nanoparticles
Top Down method Bottom Up method
Nanoparticles
Clusters
Atoms
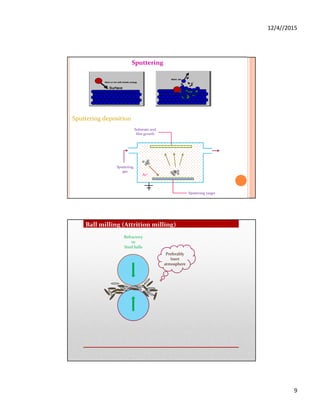
Sol-gel technique
Zr[OCH(CH3)]4.(CH3)2COOH Zirconium chloride
TOPO
60oC, Argon Atm.
340oC
Stirring
Cooled 60oC
Zirconia Nanoparticle
Precipitation
Washing
Calcination
800oC
Acetone](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nanomaterials-220208051556/85/Nanomaterials-7-320.jpg)
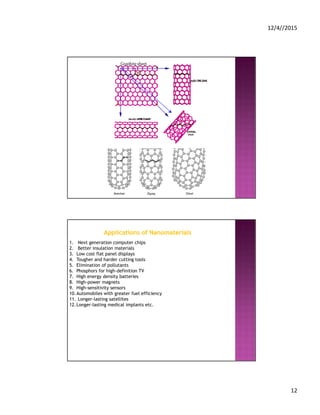
![12/4//2015
16
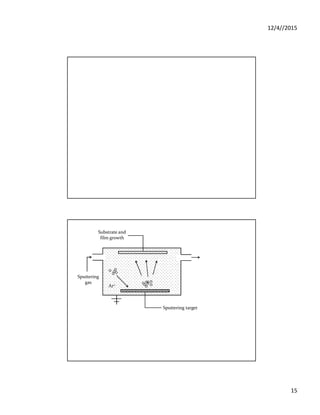
Sol-gel technique
Zr[OCH(CH3)]4.(CH3)2COOH Zirconium chloride
TOPO
60oC, Argon Atm.
340oC
Stirring
Cooled 60oC
Zirconia Nanoparticle
Precipitation
Washing
Calcination
800oC
Acetone
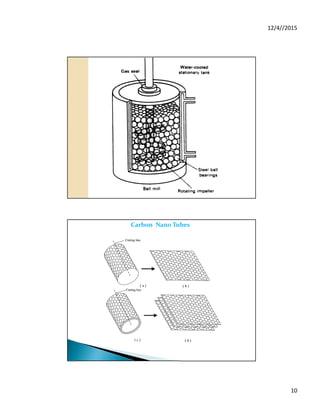
Refractory
or
Steel balls
Preferably
Inert
atmosphere](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nanomaterials-220208051556/85/Nanomaterials-16-320.jpg)