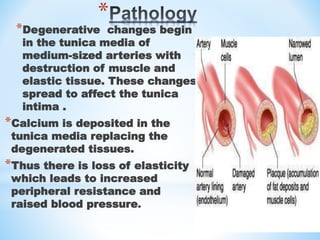
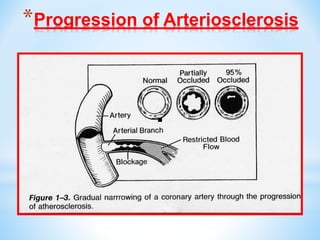
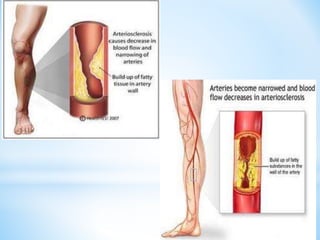
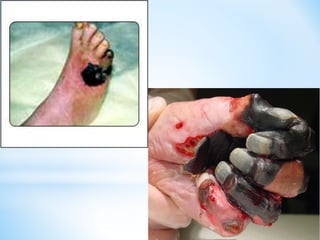
Arteriosclerosis is hardening and loss of elasticity of medium and large arteries due to thickening of arterial walls and deposition of calcium. It results from degeneration of elastic and muscle tissues in the arteries. Symptoms vary depending on the location of affected arteries and can include chest pain, impaired vision, dizziness, leg pain with walking, and skin changes in the legs. Risk factors include age, family history, smoking, high cholesterol, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Diagnostic tests include Doppler ultrasound, MRI, CT scans, and angiography. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes and medication to control symptoms and risk factors.