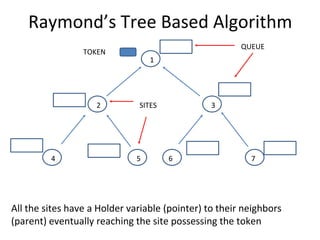
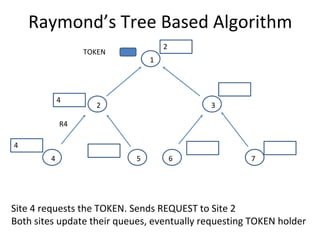
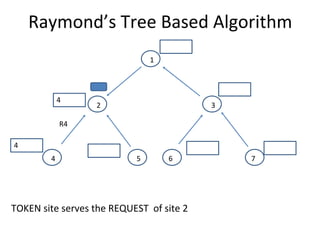
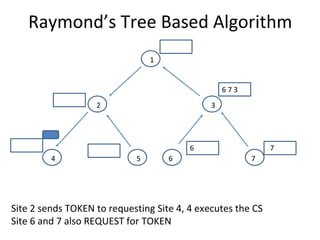
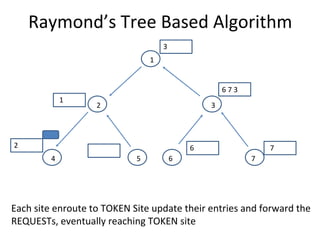
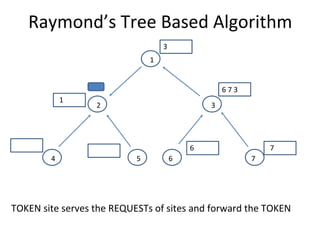
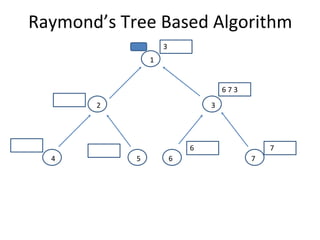
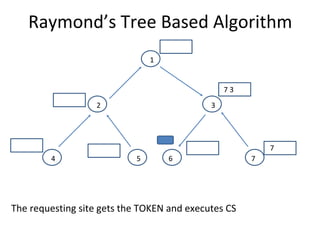
The document discusses mutual exclusion algorithms for distributed systems, focusing on both non-token and token-based methods such as Lamport’s, Ricart-Agrawala’s, and Raymond’s tree-based algorithm. It explores the state transitions, request handling, and token management necessary for ensuring mutual exclusion while avoiding deadlock and starvation. Performance metrics are examined, including message overhead and response time, with the goal of optimizing efficiency in distributed systems.


![System
SV [1…..N] : System State
SN [1…..N] : Highest Seq. No.
Token
TSV [1…..N] : System State
TSN [1…..N] : Highest Seq. No.
Singhal’s Heuristic Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-3-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ H N N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R N N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R R N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
TSV [ N N N N ]
TSN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-4-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ H N N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R R N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
TSV [ N N N N ]
TSN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
S2 is Requesting
Token
REQUEST Only “HRE”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-5-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ H N N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R R N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
TSV [ N N N N ]
TSN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
RQ (2,1)
S2 sends Request to S1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-6-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ H N N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R R N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
TSV [ N N N N ]
TSN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
RQ (2,1)
S1 updates itself and
Token(if reqd)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-7-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ H N N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R R N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
TSV [ N N N N ]
TSN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
S1 updates itself and
Token(if reqd)
RQ (2,1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-8-320.jpg)

![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ N R N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R R N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
TSV [ N R N N ]
TSN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
Token Updated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-10-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ N R N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R E N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R R N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
TSV [ N R N N ]
TSN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
S1 completes CS
Sends Token to S2 S2 sets status to E and
Executes CS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-11-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ N R N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R N N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R R N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
TSV [ N N N N ]
TSN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
S2 comes out of CS
Sets status to N
Token
Updated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-12-320.jpg)

![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ N R N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R N N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R R N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
TSV [ N N N N ]
TSN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
S2 updates itself](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-14-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ N R N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ N N N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R R N N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
SV [ R R R N ]
SN [ 0 0 0 0 ]
TSV [ N N N N ]
TSN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
S2 updates itself](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-15-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
TSV [ N N N N ]
TSN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
S2 sets its status to H
All systems are updated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-16-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ N H R N ]
SN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
TSV [ N N N N ]
TSN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
Contd.. S3 makes a REQUEST
REQUEST Only “HRE”
R(3,1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-17-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ N H R N ]
SN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
SV [ N H R N ]
SN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
TSV [ N N R N ]
TSN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
S2 sets S3’s status to R
S2 then updates the TOKEN for S3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-18-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ N N R N ]
SN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
SV [ N N E N ]
SN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
TSV [ N N R N ]
TSN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
S2 sets its own status to N
Sends TOKEN to S3
S3 sets status to E
Executes CS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-19-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ N N R N ]
SN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
SV [ N H N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
TSV [ N N R N ]
TSN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
S3 comes out of CS
Looks for any other ‘R’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-20-320.jpg)
![S1
S2
S3
S4
SV [ N N H N ]
SN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
SV [ N N H N ]
SN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
SV [ N N H N ]
SN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
SV [ N N H N ]
SN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
TSV [ N N N N ]
TSN [ 0 1 1 0 ]
STATES
R : REQUESTING A TOKEN
H : HOLDING IDLE TOKEN
E : EXECUTING IN CRITICAL SECTION
N:NONE OF THE ABOVE
S2 sets its own status to H
All sites are then updated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-21-320.jpg)
![DeadLock and Starvation
Request sent to only those
systems who possess the Token or
will get Token in near future : E, R,
or H
If RQ is sent to any other system
if ‘N’ systems send
requests to each other : Deadlock
if a system sends request
to N system : Starvation
S1
S2
SV [ H N N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
SV [ R N N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]
S3
SV [ R N N N ]
SN [ 0 1 0 0 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaymutualexclusionindistributedsystems-191208184257/85/Mutual-exclusion-in-distributed-systems-22-320.jpg)