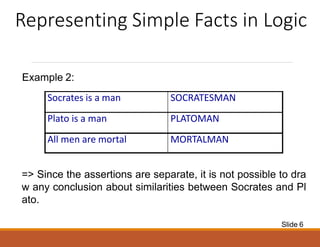
This document discusses representing knowledge in predicate logic and artificial intelligence. It explains how predicate logic can represent objects, relationships, and quantification which allows more complex knowledge representation compared to propositional logic. The document provides examples of representing facts about individuals like Socrates and classes in predicate logic using predicates like man and mortal. It also discusses representing class-instance relationships and property inheritance using the predicates "instance" and "isa".