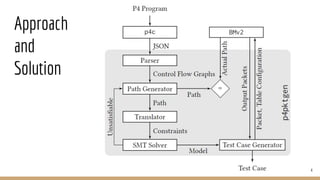
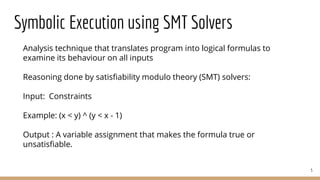
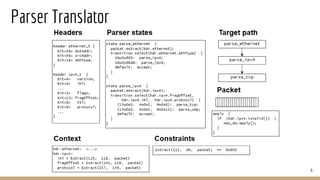
The document discusses p4pktgen, a tool for automated test case generation for P4 programs which addresses the bugs introduced by the flexibility of programmable network devices. It utilizes symbolic execution with SMT solvers to effectively generate test cases and has successfully identified and fixed multiple issues within the P4 toolchain. Future work includes enhancing support for additional P4 features and improving test case generation techniques.