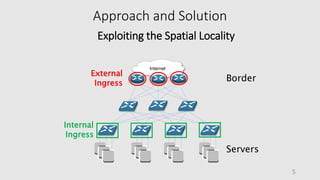
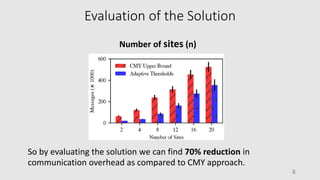
This document presents a novel approach for network-wide heavy-hitter detection, aiming to identify significant outliers in network traffic to enhance performance diagnostics while minimizing communication overhead. The proposed method utilizes adaptive local thresholds and exploits spatial locality, achieving a 70% reduction in communication compared to previous techniques focused on single switches. Future improvements include reducing state storage in switches, supporting distinct counts, and scaling for a larger number of sites.