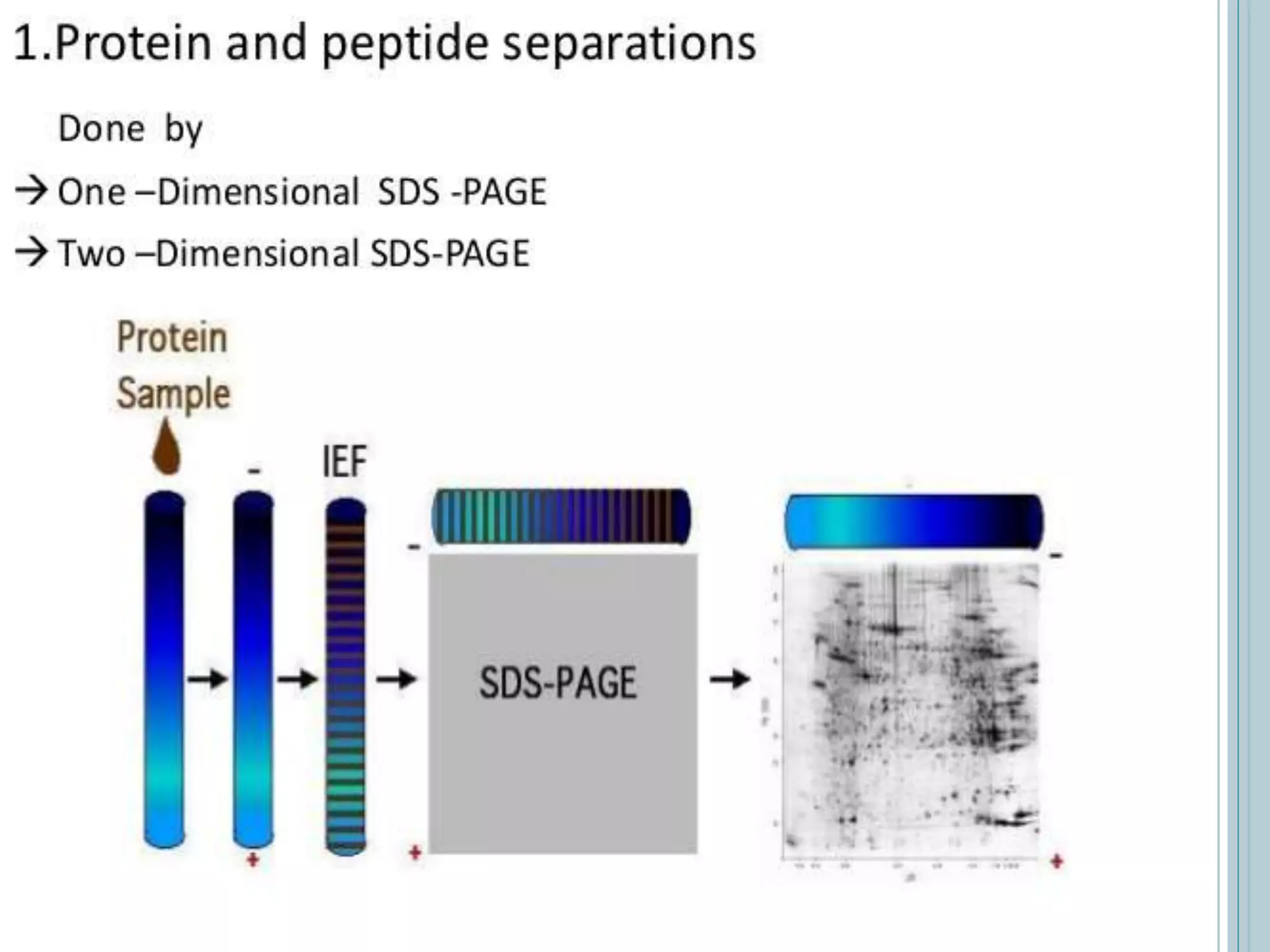
Proteomics aims to identify all proteins in a cell or organism, including post-translational modifications, localization, functions, and interactions. Understanding the proteome allows for protein characterization, identification of protein interactions, and disease biomarkers. The main types of proteomics are expression proteomics, which studies qualitative and quantitative protein expression under different conditions; structural proteomics, which determines protein structure; and functional proteomics, which elucidates protein functions and interactions. Proteomics provides information that cannot be obtained from genomics alone and benefits areas like protein expression studies, modifications, functions, and interactions.