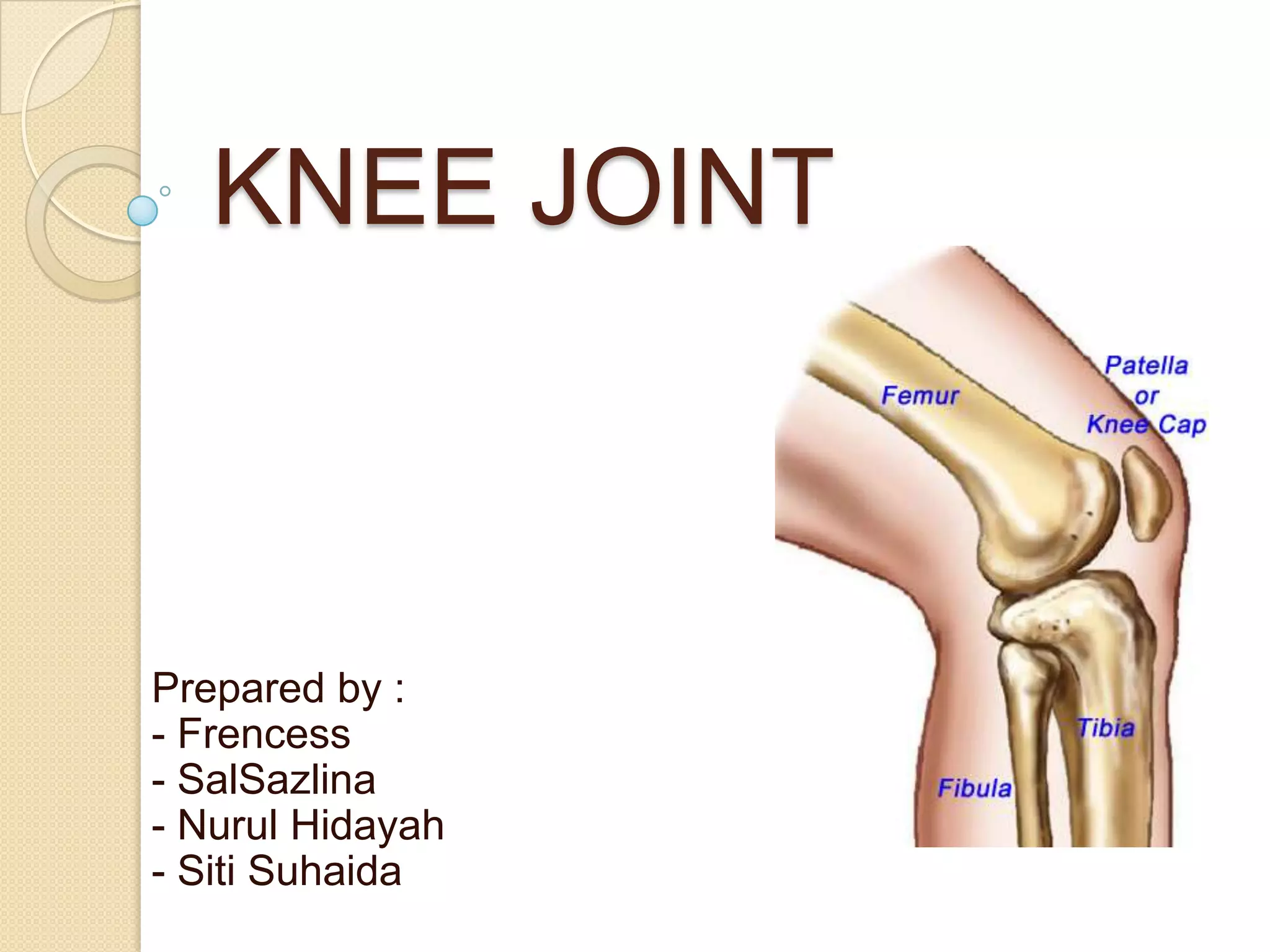
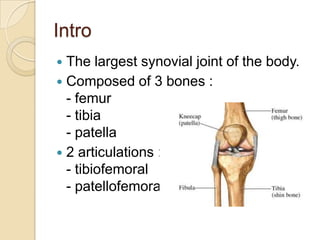
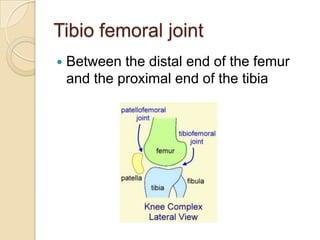
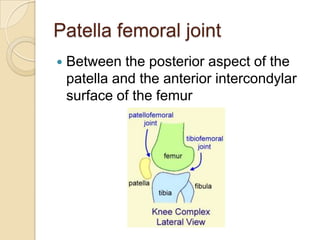
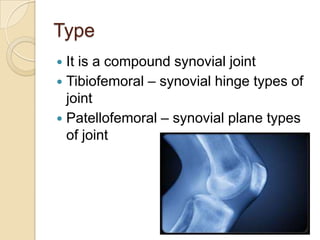
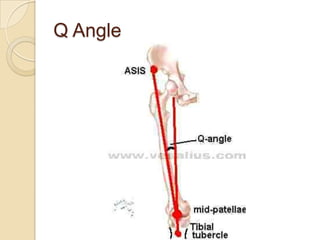
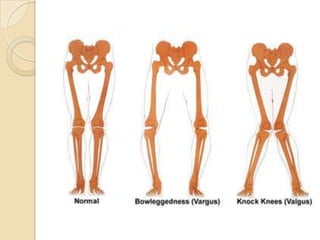
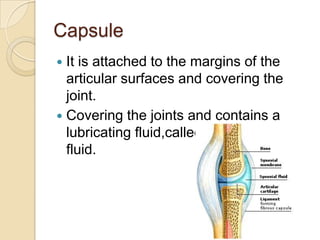
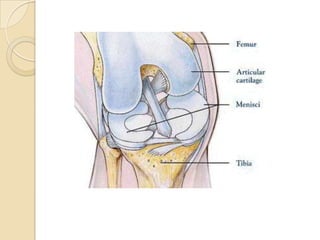
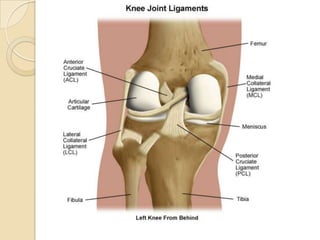
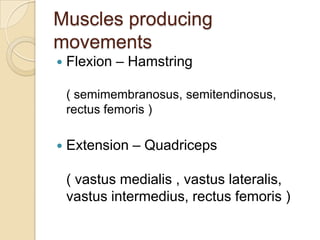
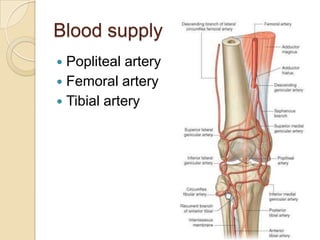
The knee joint is the largest synovial joint in the body. It is composed of three bones: the femur, tibia, and patella. The knee joint has two articulations: the tibiofemoral joint between the femur and tibia, and the patellofemoral joint between the patella and femur. The knee joint is a compound synovial joint, with the tibiofemoral joint being a hinge type and the patellofemoral joint being a plane type. The knee joint is surrounded by ligaments such as the ACL and PCL, and contains a synovial fluid within its capsule. It also contains menisci that act as cushions and increase stability.