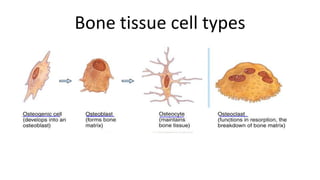
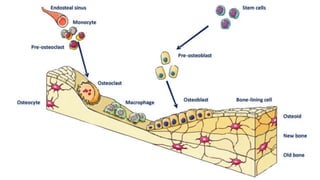
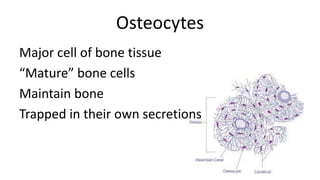
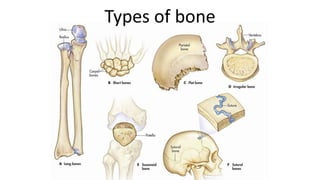
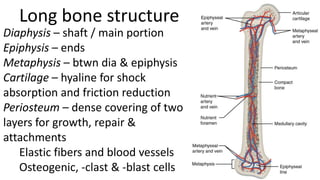
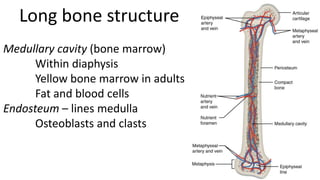
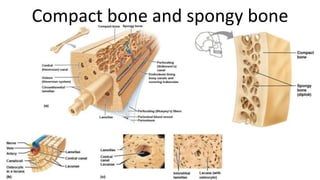
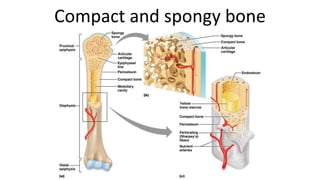
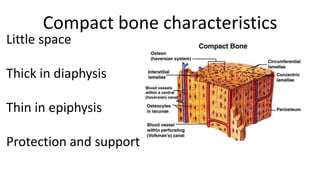
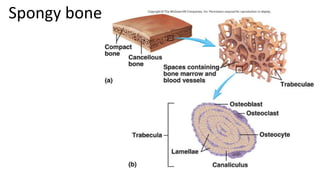
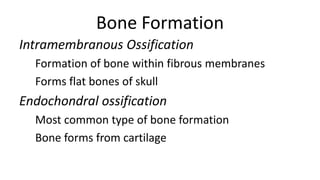
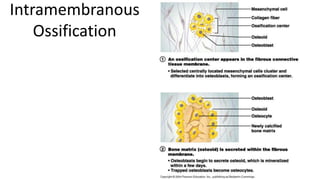
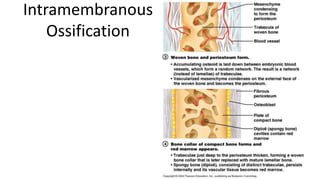
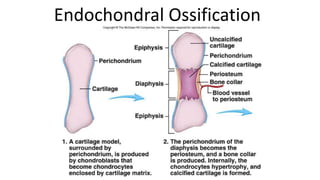
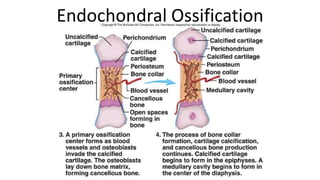
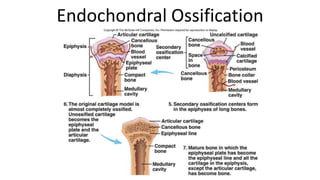
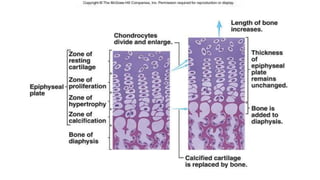
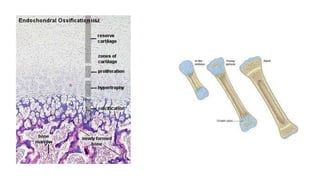
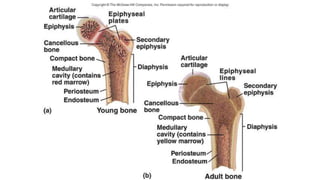
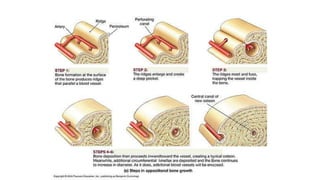
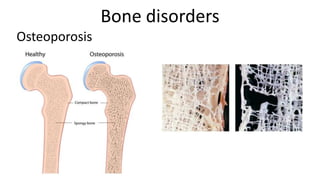
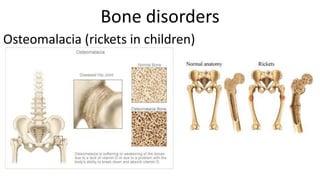
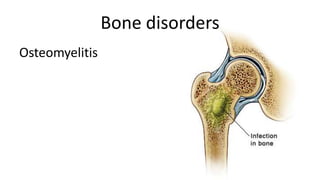
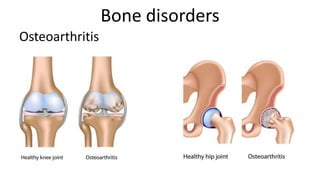
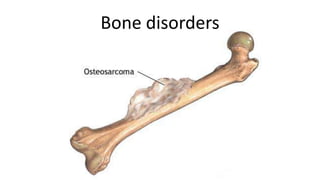
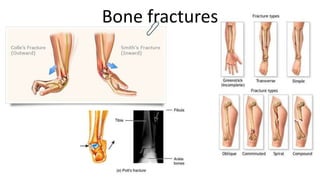
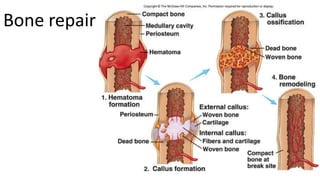
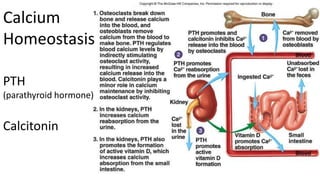
The skeletal system includes bones and cartilage that provide structure, allow for movement, and protect organs. The medical specialty of orthopedics focuses on treating the skeleton and joints. Skeletal tissue includes cartilage and bone, which are types of dense connective tissue. Bones have important functions like support, protection, movement, mineral storage, and blood cell production. Bone is made up of osteogenic cells, osteoblasts that form bone, osteocytes embedded in bone matrix, and osteoclasts that resorb bone. There are different types of bones like long bones with a diaphysis, epiphyses, and metaphysis. Bone formation occurs through intramembranous ossification or endochondral ossification. Common bone