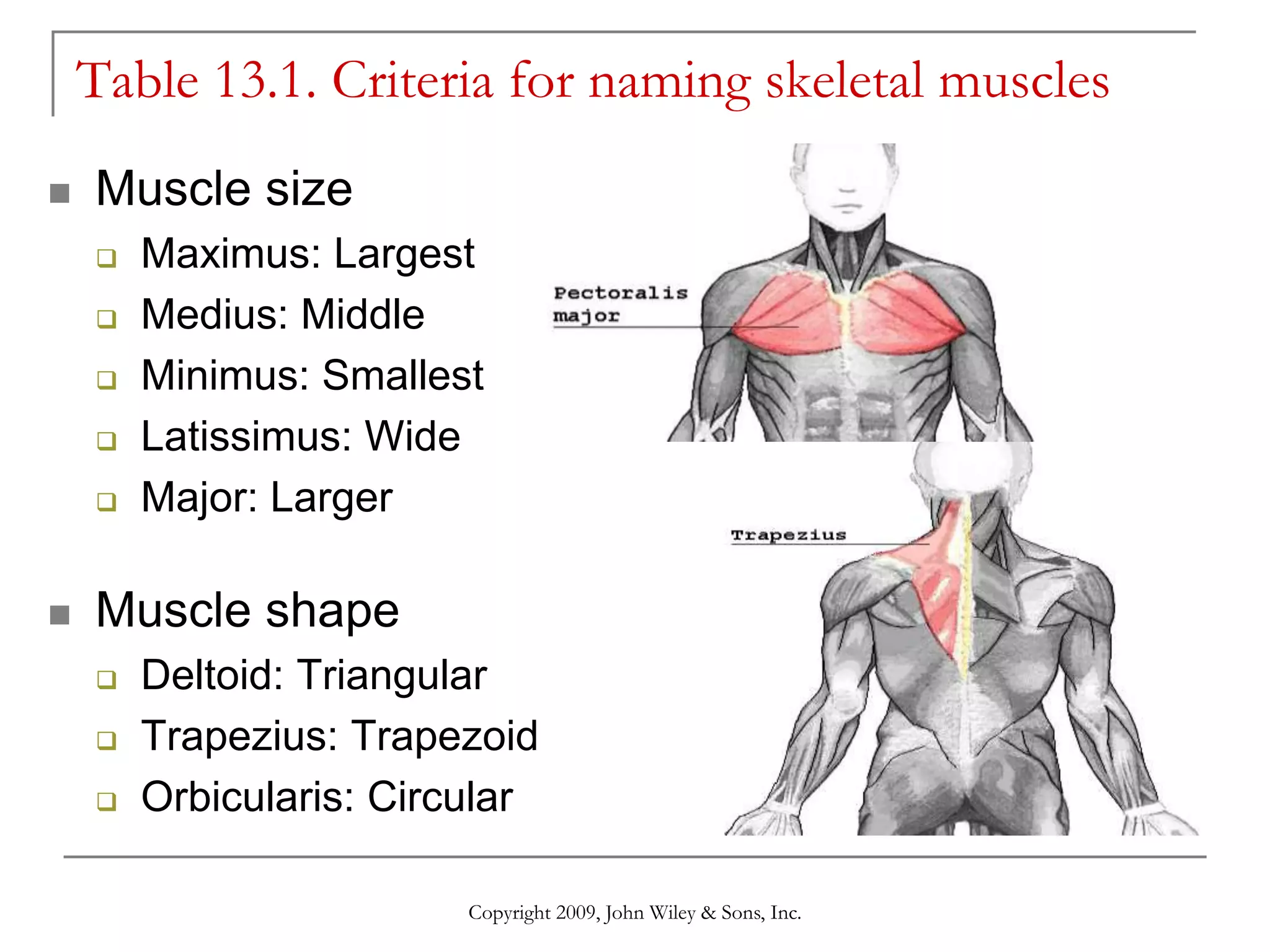
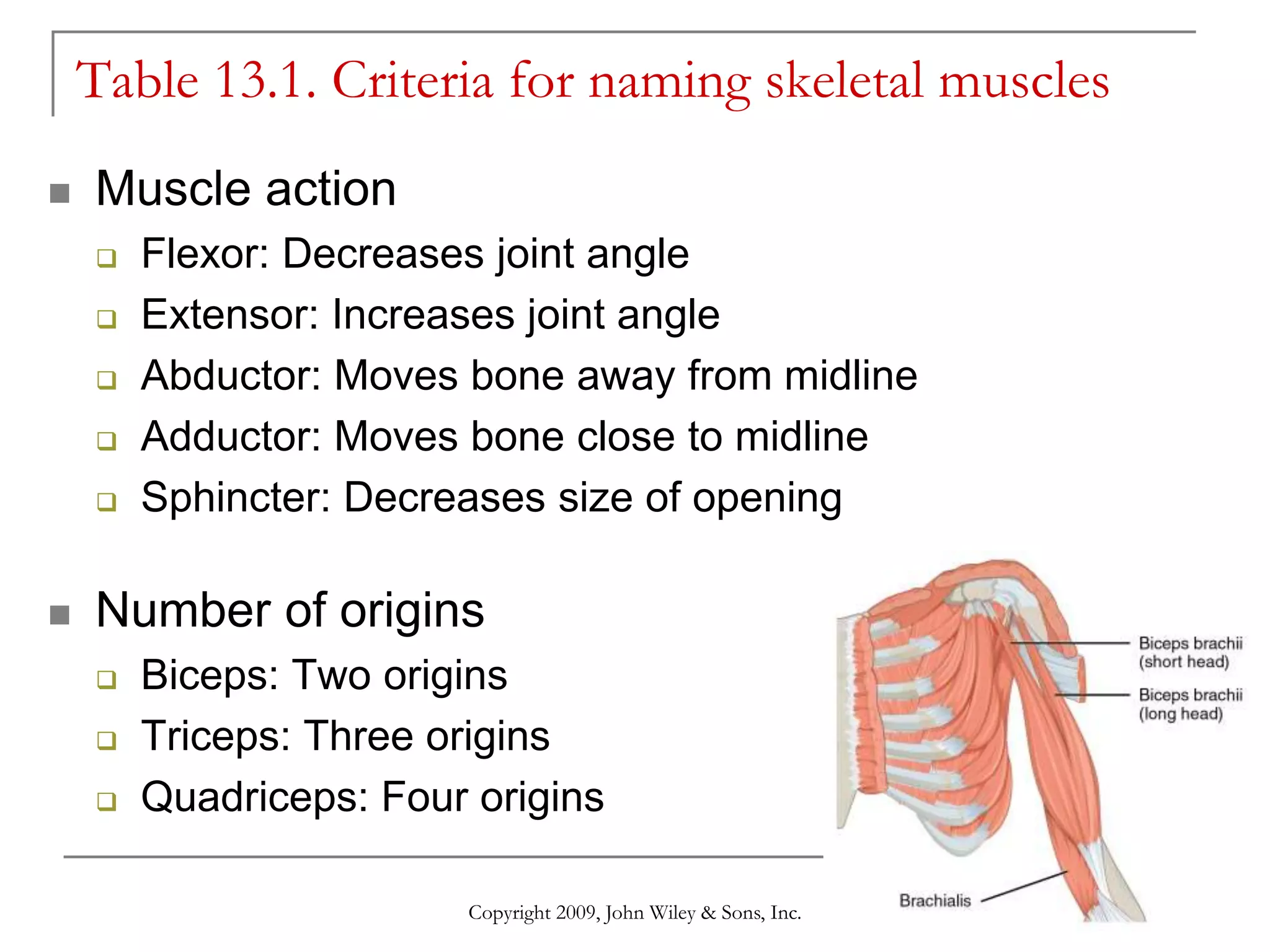
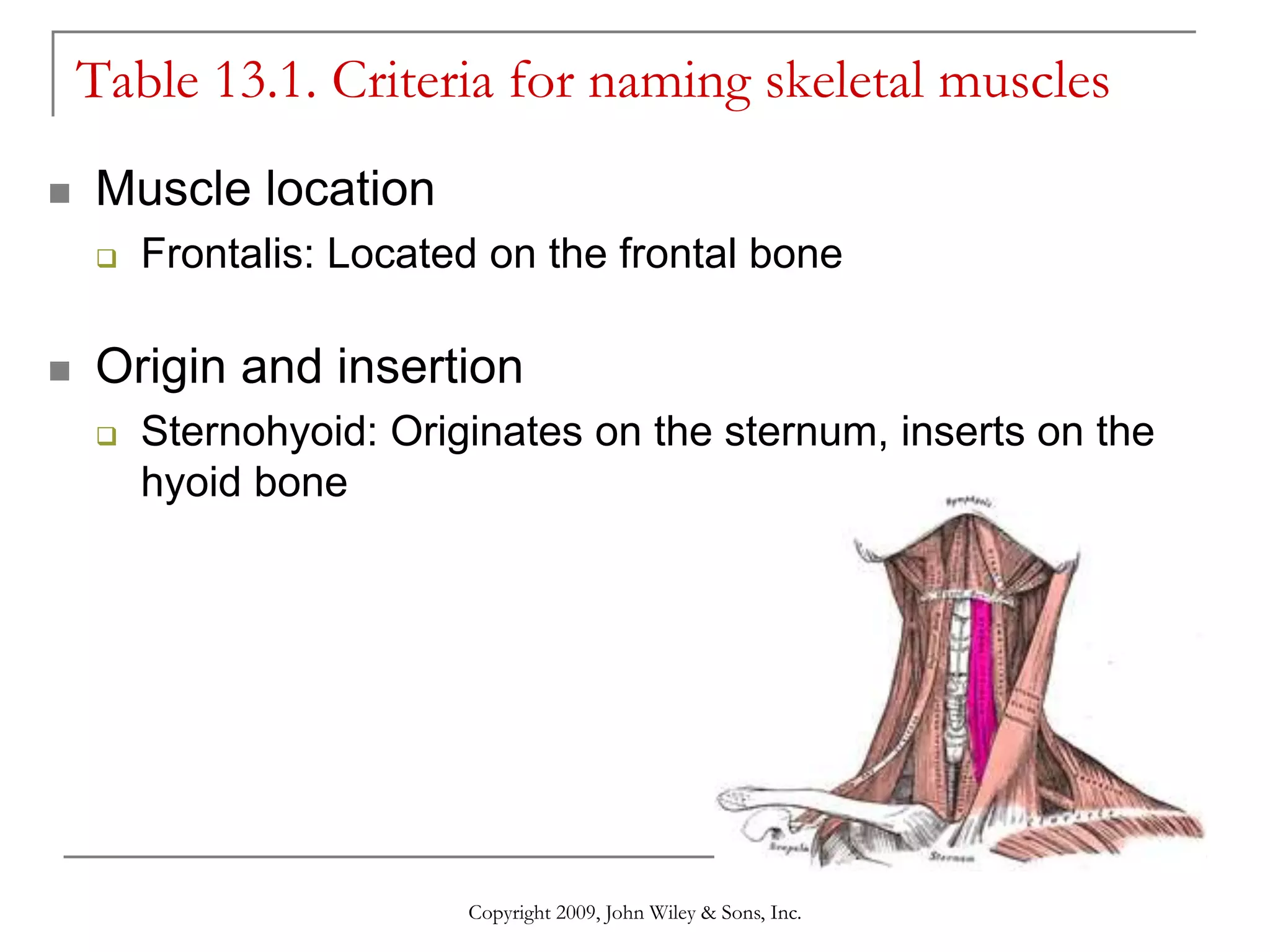
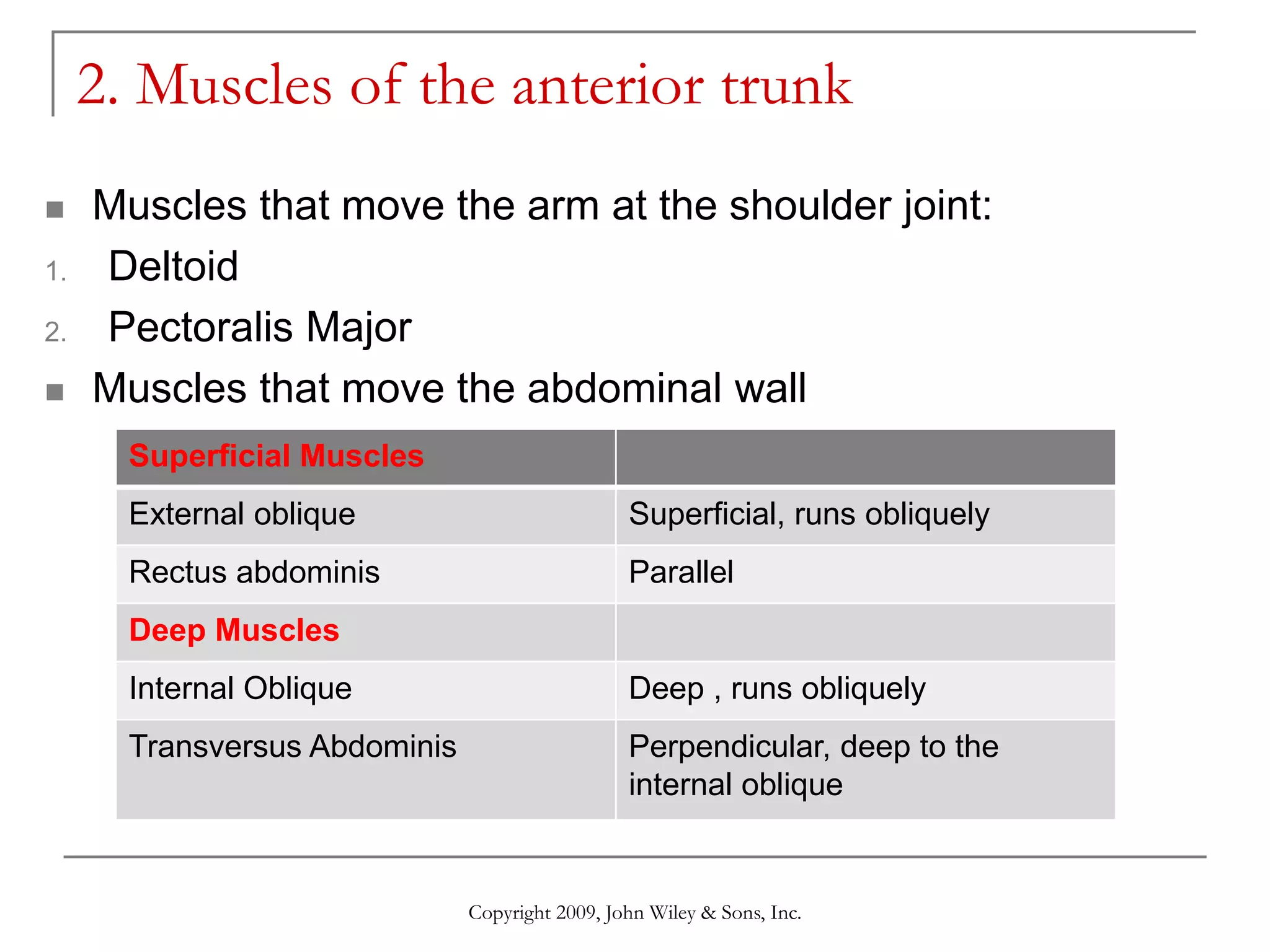
This document provides information about skeletal muscles, including their naming criteria, identification, and actions. It discusses the major muscles in the head and neck, anterior and posterior trunk, arm, forearm, thigh, leg, and foot. For each body region, the muscles are grouped based on their location and functions, such as muscles of facial expression, mastication, and neck movement. Accompanying illustrations and tables show the skeletal muscles and provide further details.