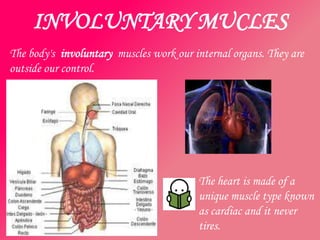
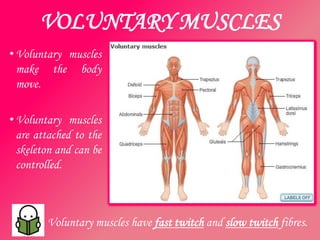
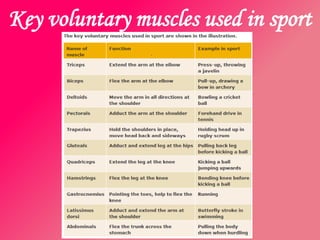
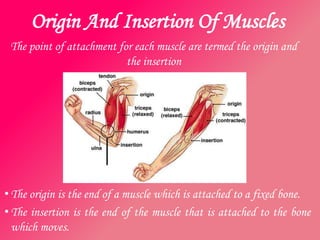
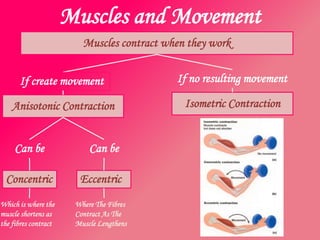
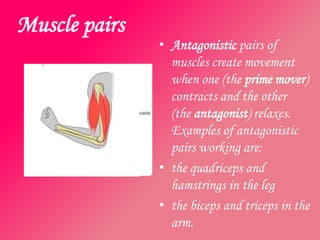
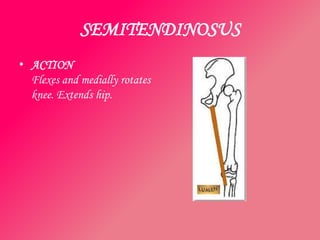
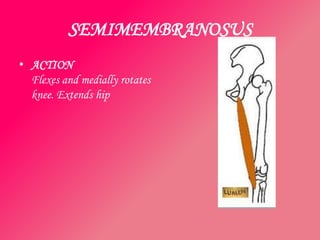
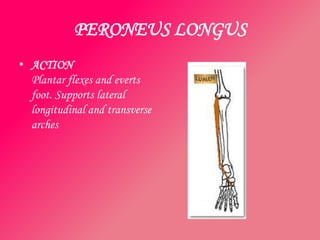
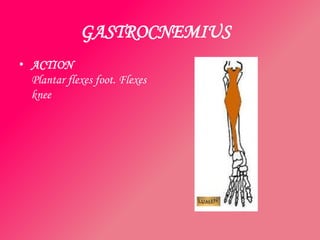
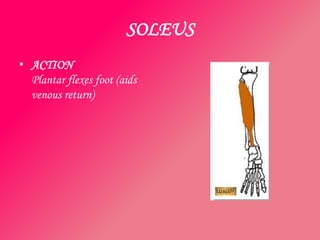
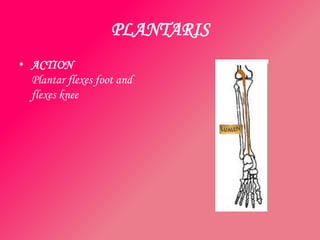
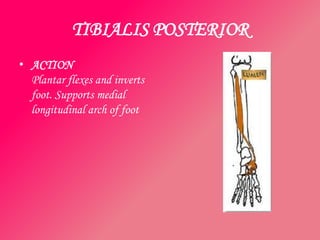
The document discusses the different types of muscles in the body, including voluntary muscles that are attached to the skeleton and can be controlled to enable movement, and involuntary muscles like the heart that work internal organs automatically. It provides details on muscle fiber types, how muscles contract and create movement through antagonistic pairs, and the benefits of good muscle tone for posture, performance, and confidence.