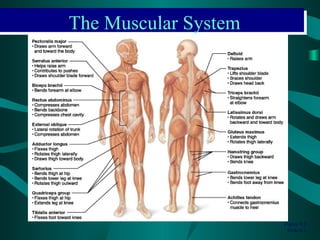
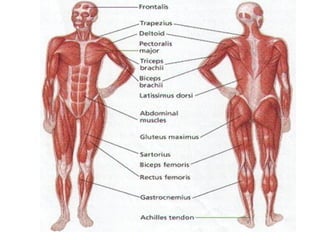
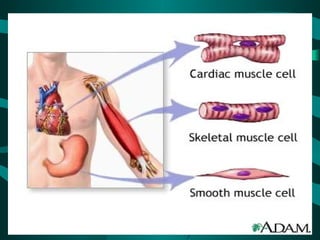
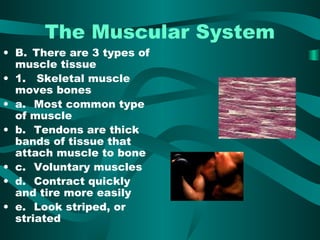
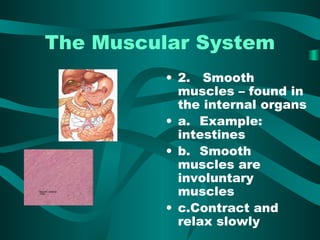
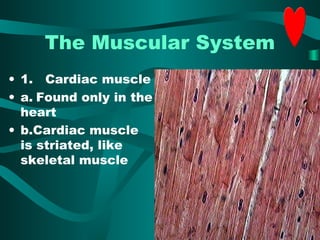
The document discusses the three types of muscle tissue in the human body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscle is voluntary muscle that moves bones and is attached to bones via tendons. Smooth muscle is involuntary and found in internal organs. Cardiac muscle is only located in the heart. The document provides examples of the smallest, largest, longest, and strongest muscles as well as muscle facts about facial expressions and blinking. Diagrams identify major muscles in the arms, legs, and trunk.