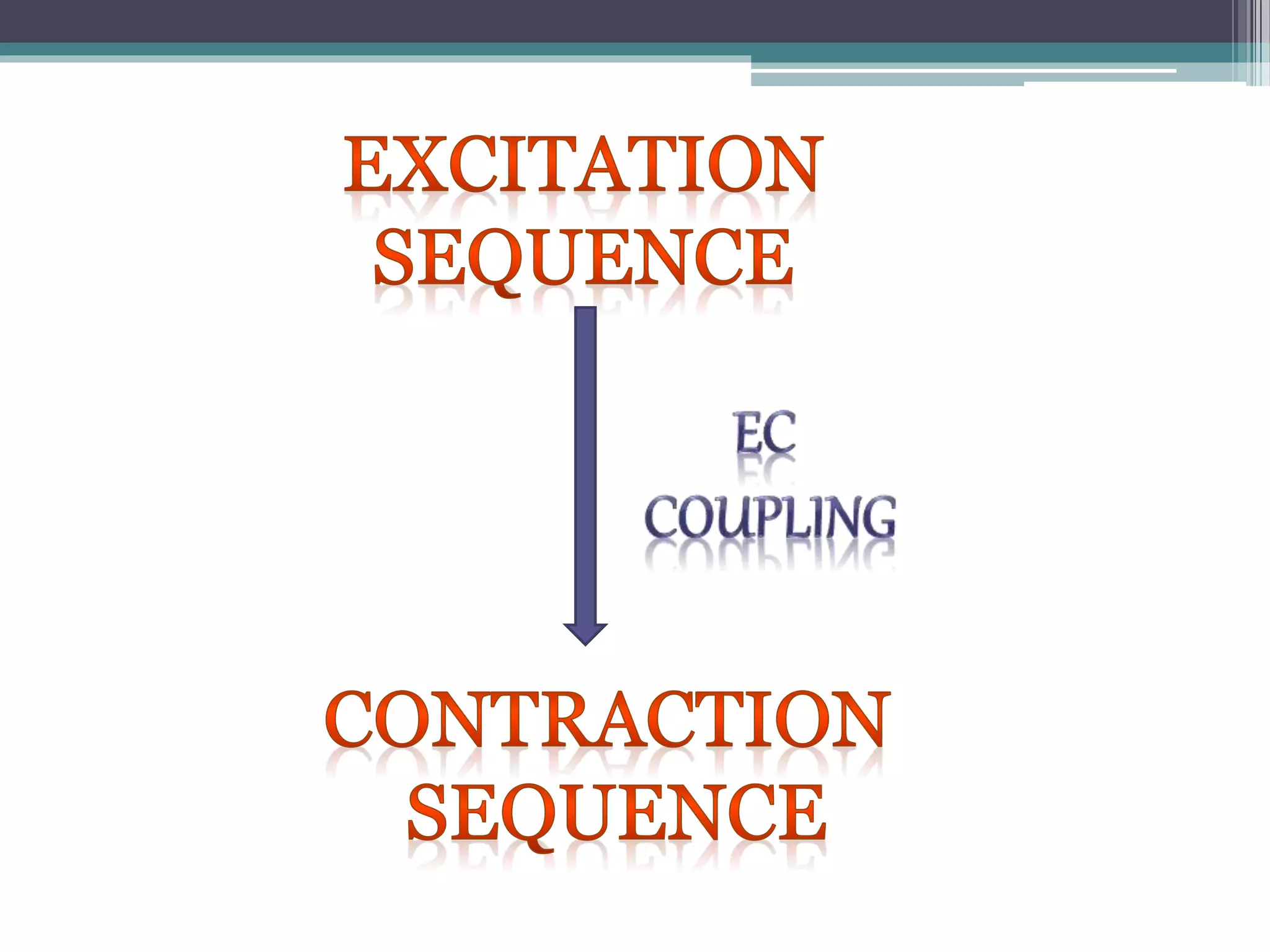
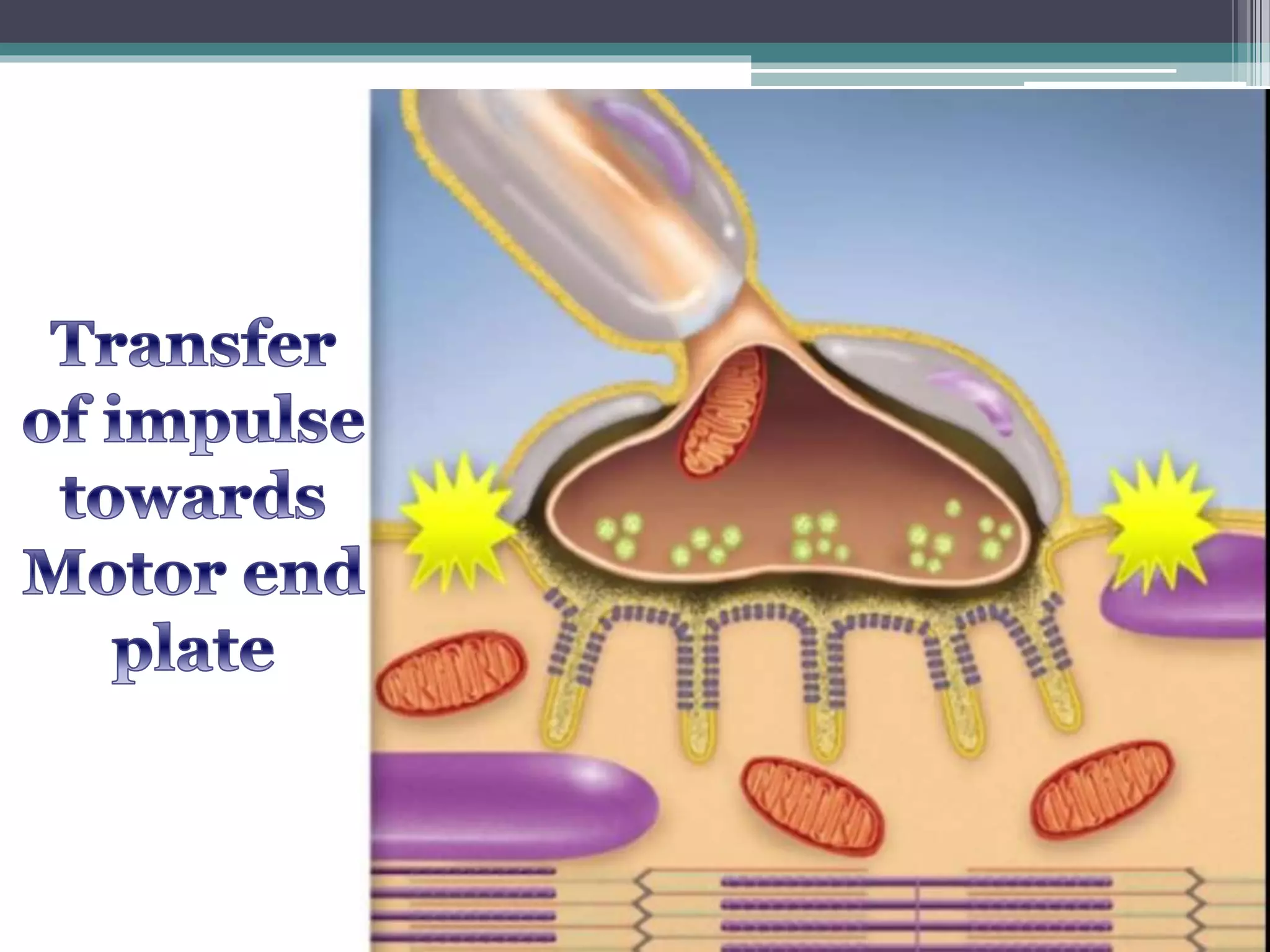
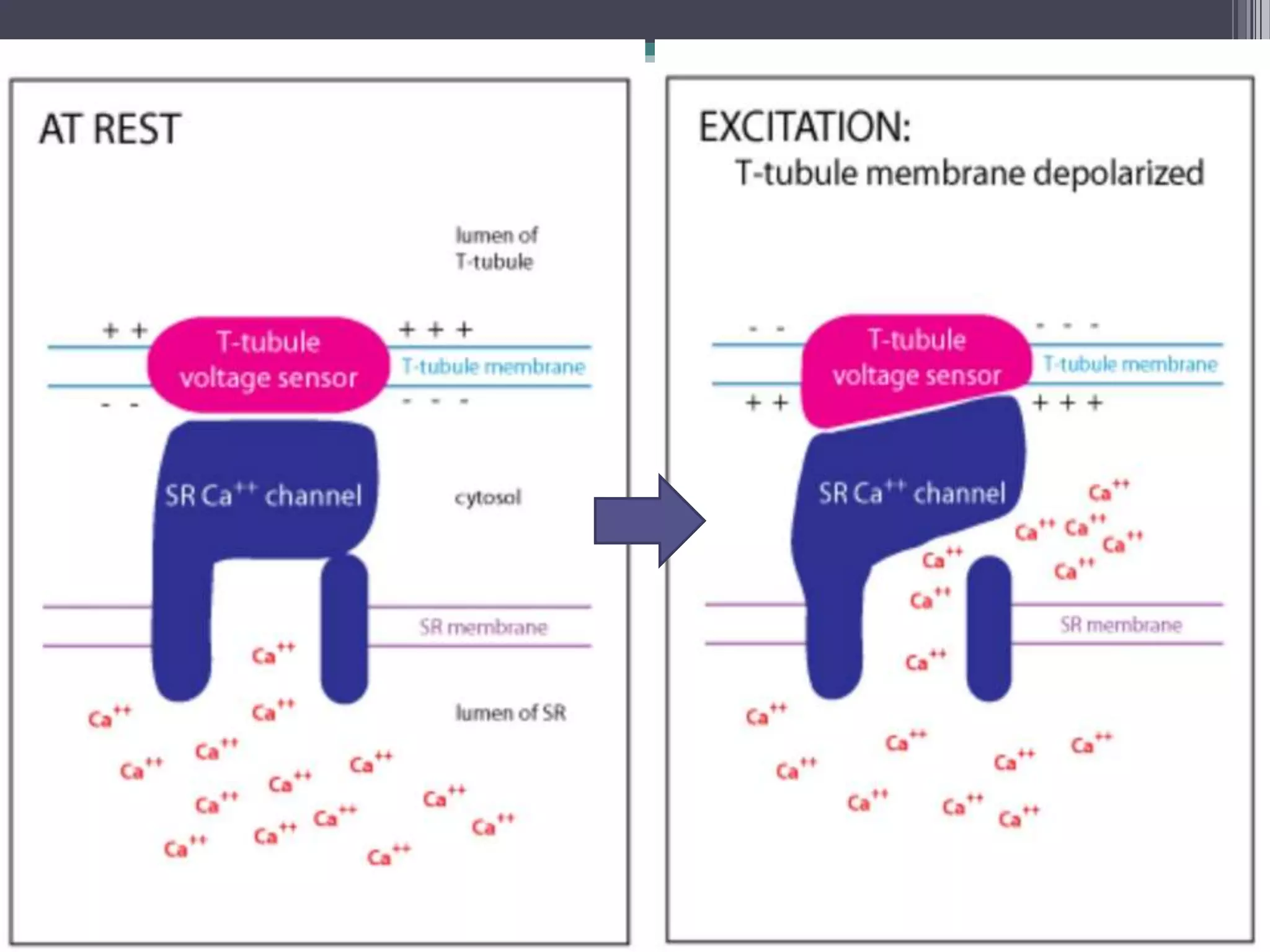
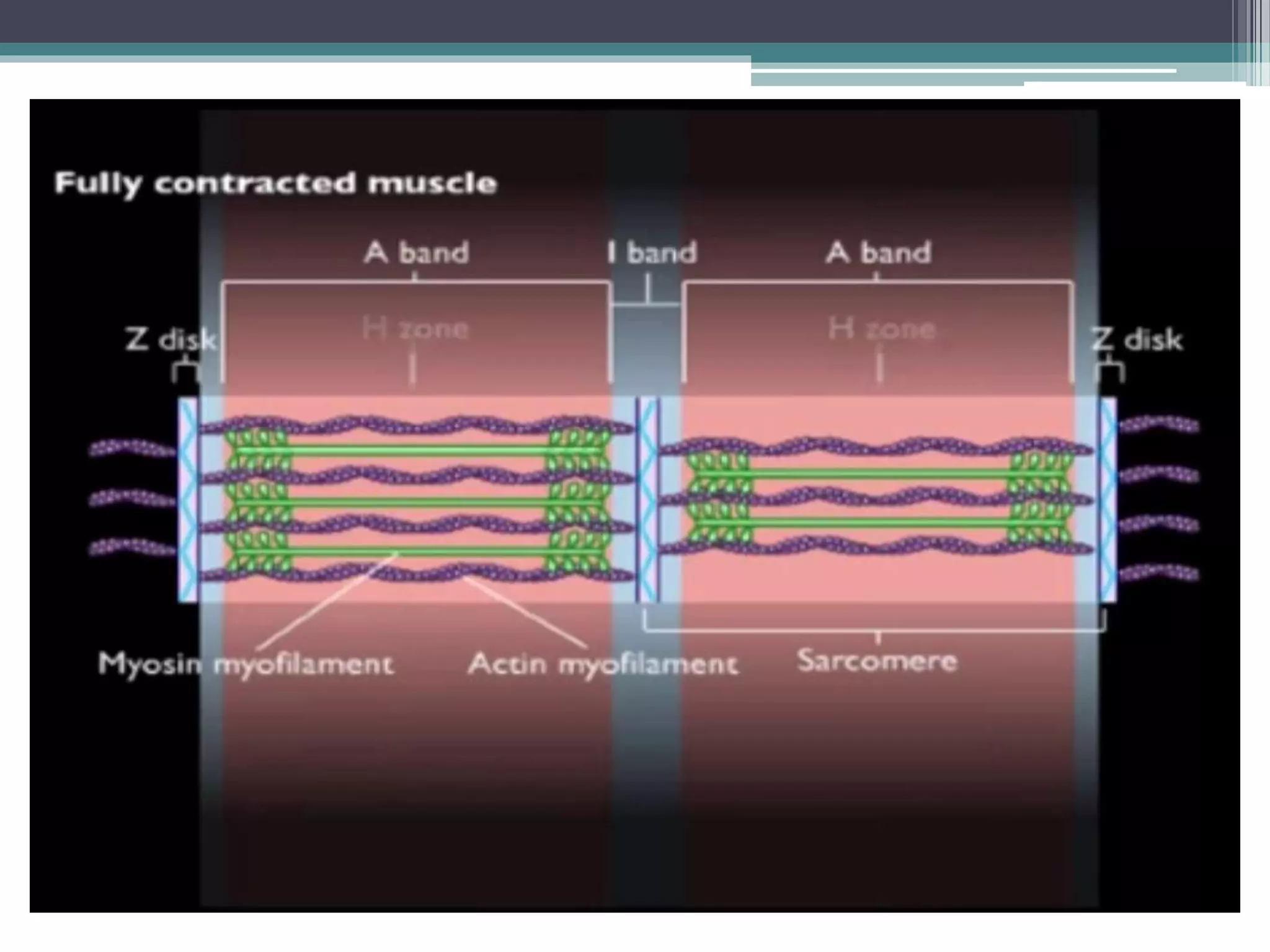
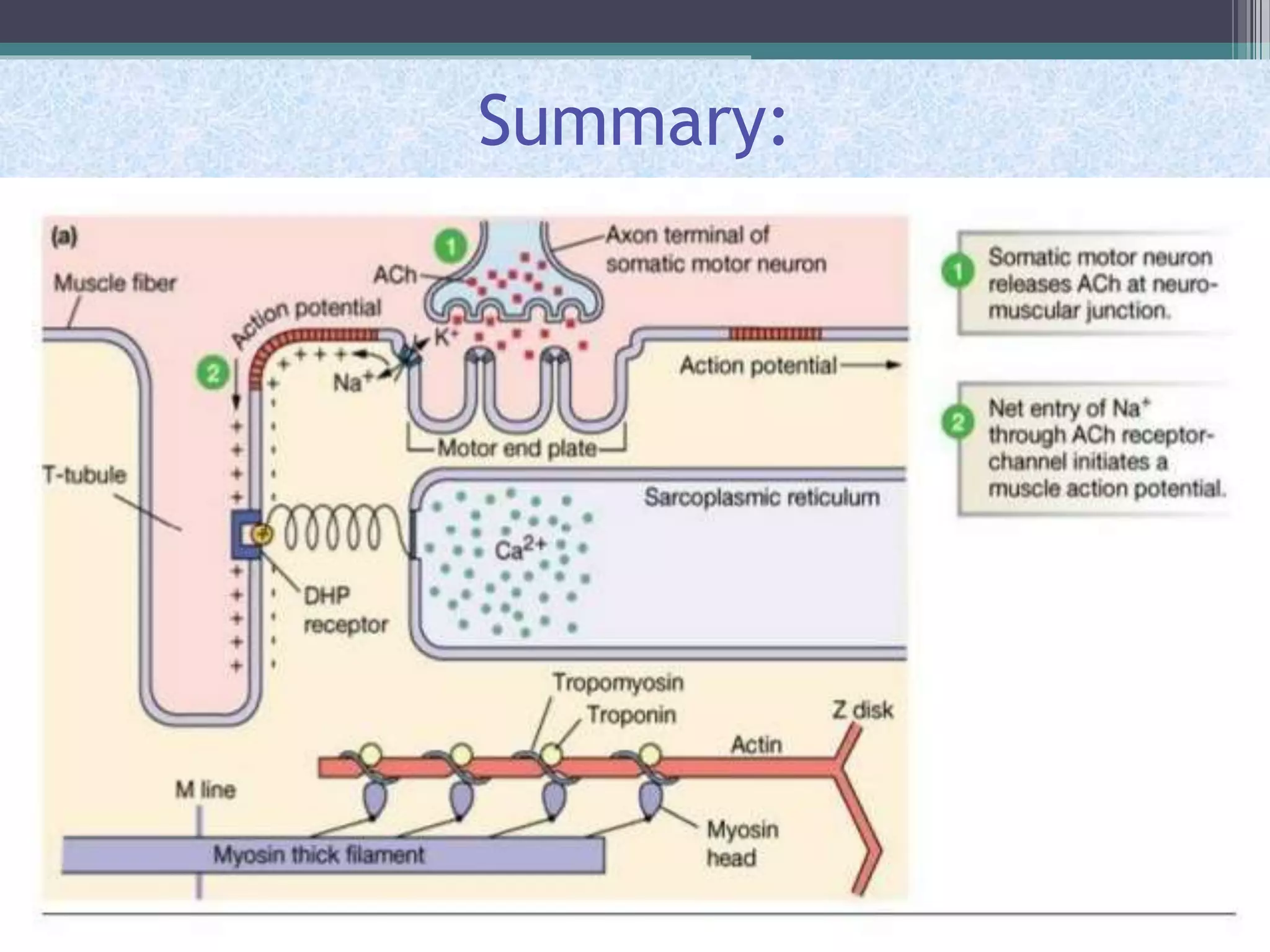
This document discusses excitation-contraction coupling (EC coupling) in skeletal muscle. It begins by defining EC coupling as the process by which an action potential triggers muscle contraction through calcium ion release. It then describes how the action potential spreads through the T-tubule system and activates the dihydropyridine and ryanodine receptors, causing calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. This triggers the contraction sequence and binding of calcium to troponin. Relaxation occurs via reuptake of calcium into the sarcoplasmic reticulum by SERCA pumps. Differences in smooth and cardiac muscle EC coupling are also summarized.