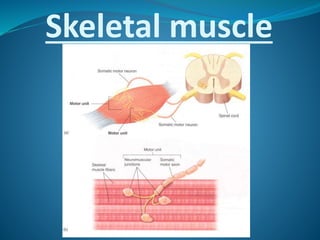
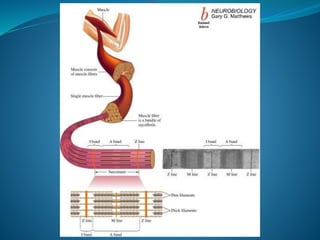
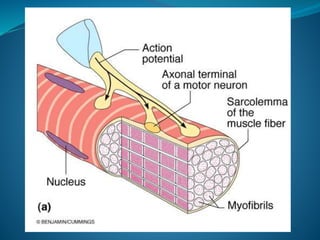
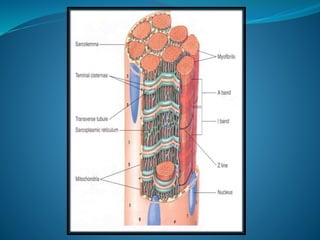
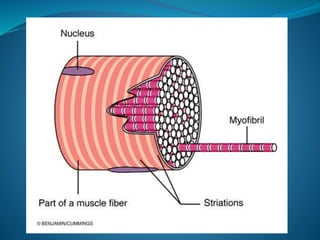
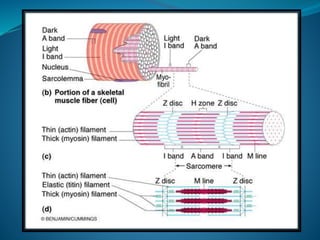
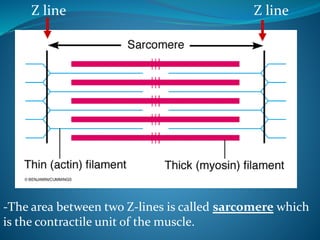
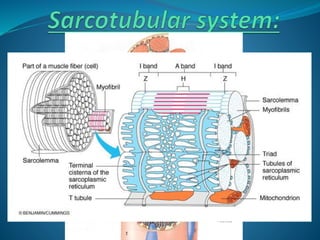
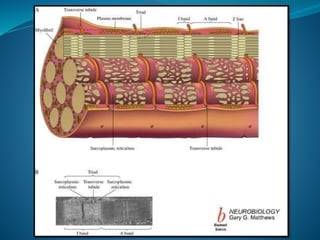
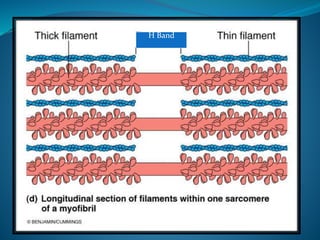
Skeletal muscle consists of cylindrical, multinucleated fibers that contain myofibrils made up of actin and myosin filaments, which form striations visible under a microscope. The sarcotubular system, including T-tubules and the sarcoplasmic reticulum, plays a crucial role in spreading action potentials and releasing calcium ions necessary for muscle contraction. Key muscle proteins include myosin, actin, tropomyosin, and troponin, which regulate the contraction process.











![* Muscle proteins:
[A] Contractile proteins:
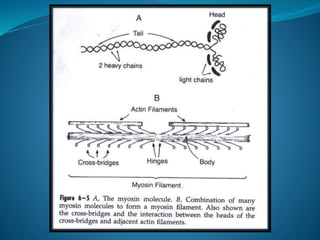
1-Myosin:
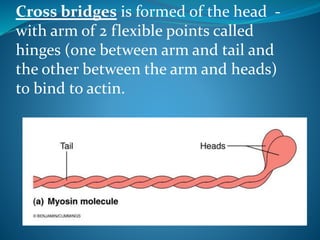
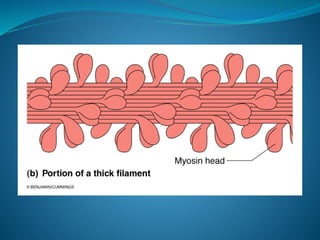
- Myosin is complex protein with M.W. 480,000.
- Composed of 6 polypeptide chains (2 heavy
chains and 4 light chains).
- The 2 heavy chains wrap spirally around each
other as double helix forming long tail, while the
terminal part combine with the 4 light chains
forming 2 globular heads, the head contains
actin-binding sites and ATP-ase enzyme (help
ATP hydrolysis).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/musclenaglaalecture1-140921072042-phpapp02/85/Physiology-Muscle-21-320.jpg)

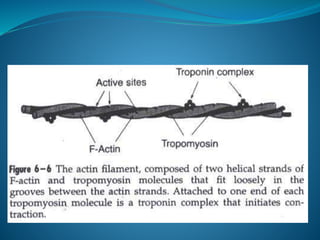
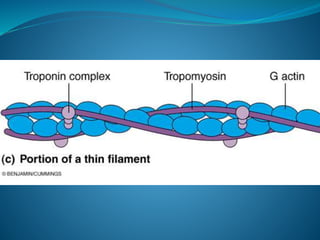
![[B] Regulatory protein:
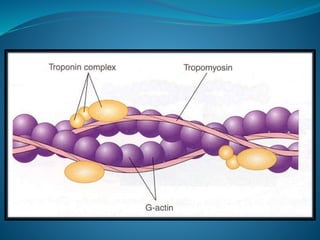
1- Tropomyosin:
It is long filament of two polypeptide
chains twisting on each other and
located between the 2 chains of
actin covering its active sites which
combine to myosin.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/musclenaglaalecture1-140921072042-phpapp02/85/Physiology-Muscle-28-320.jpg)