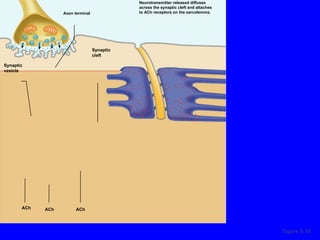
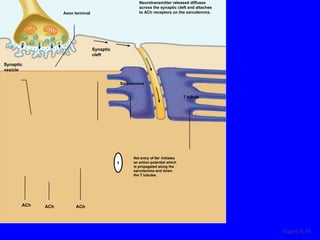
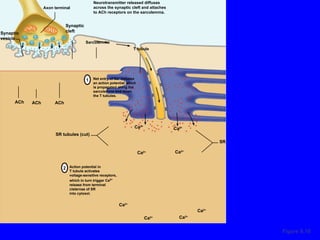
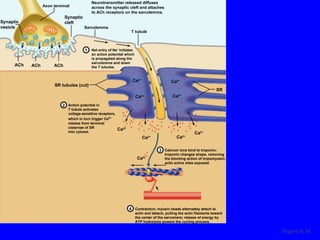
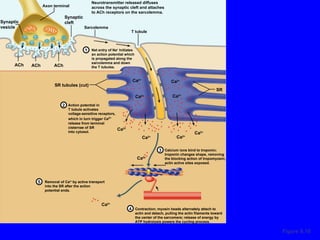
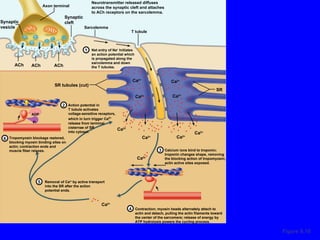
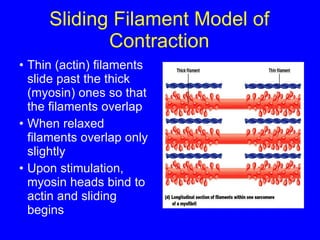
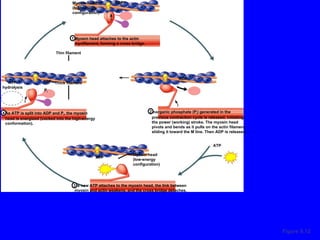
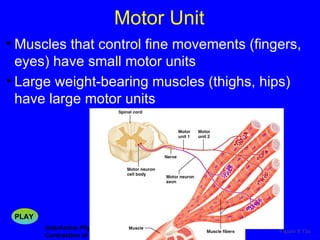
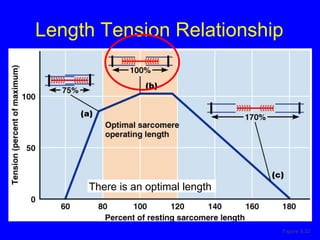
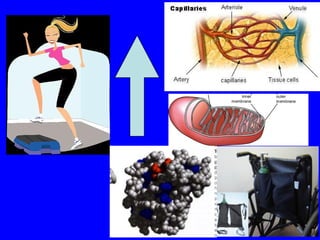
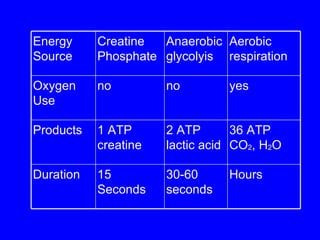
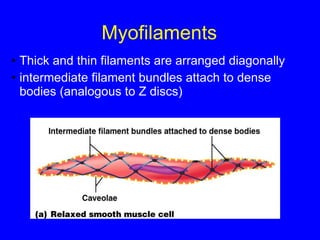
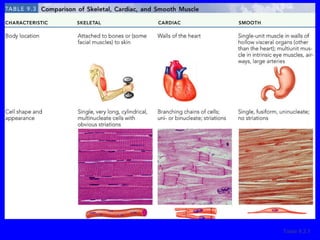
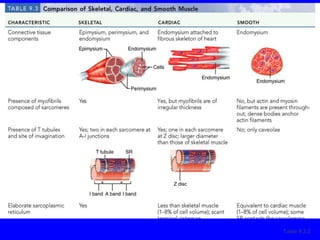
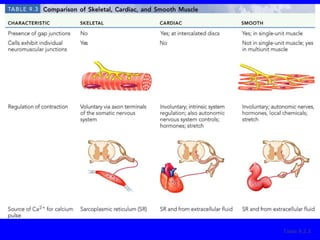
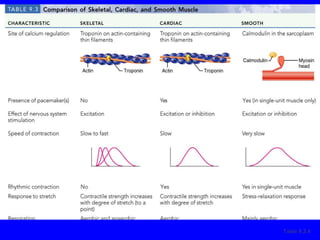
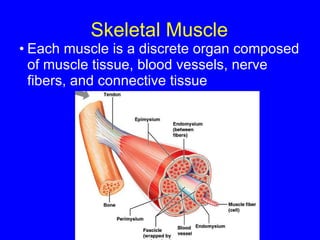
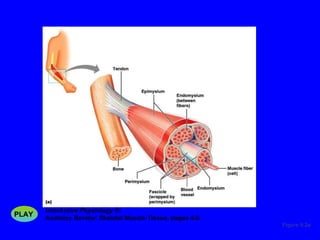
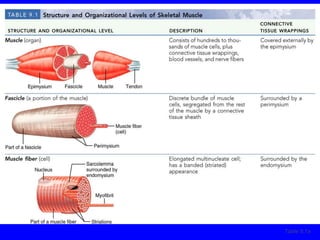
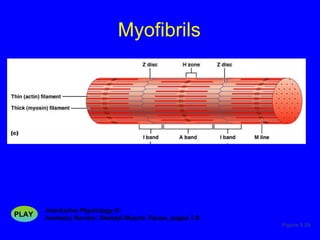
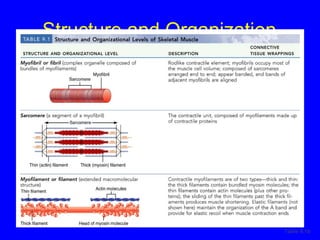
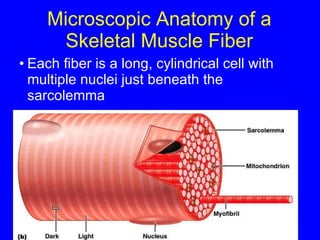
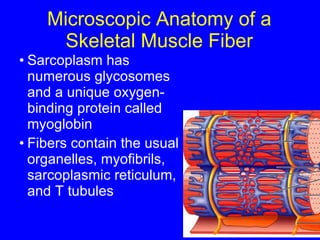
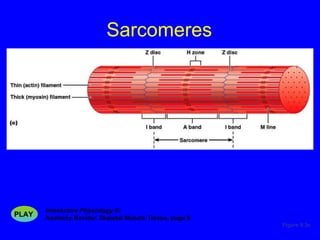
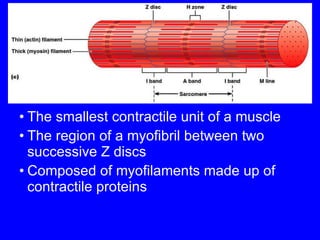
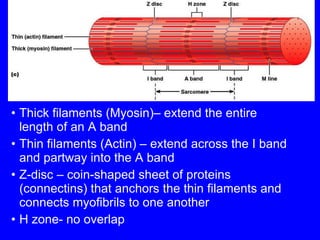
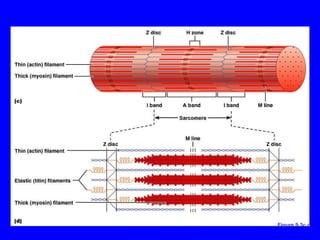
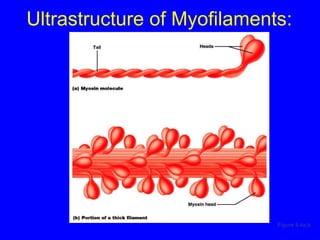
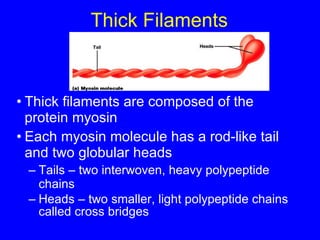
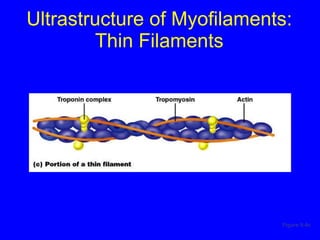
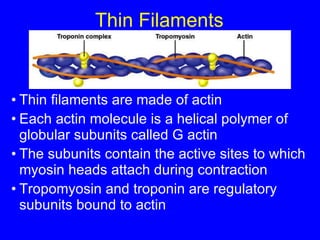
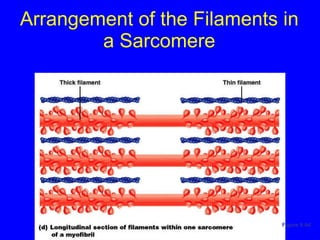
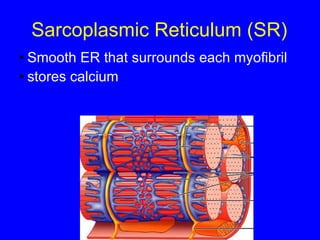
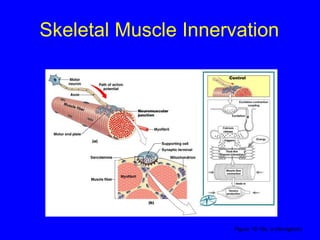
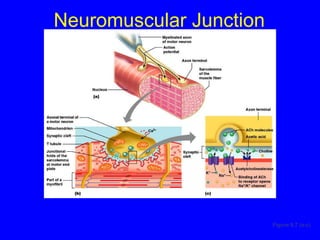
1. The document discusses the structure and function of skeletal muscle tissue. It describes the microscopic anatomy of skeletal muscle fibers and their myofibrils, sarcomeres, and filaments.
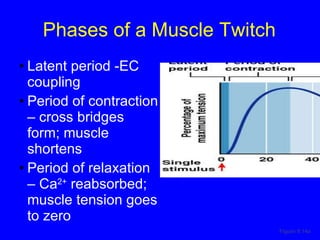
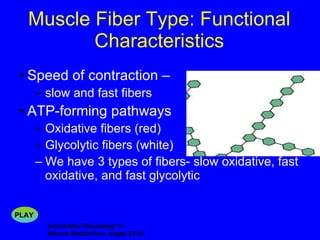
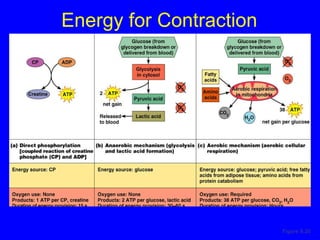
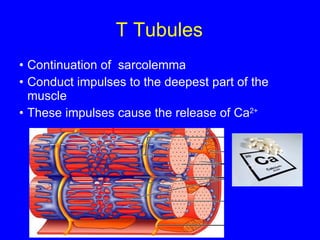
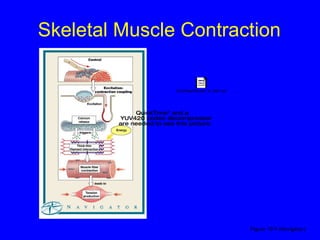
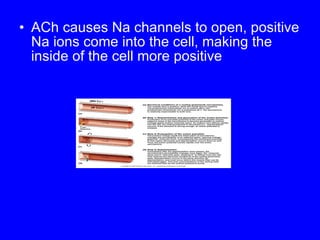
2. The contraction process is summarized, from the generation of an action potential to the sliding filament model. Key steps include calcium release, troponin/tropomyosin interaction, cross-bridge cycling powered by ATP hydrolysis.
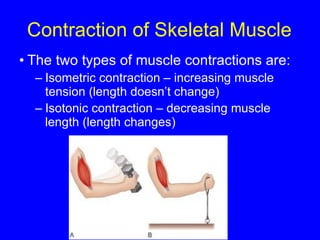
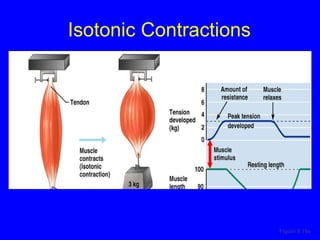
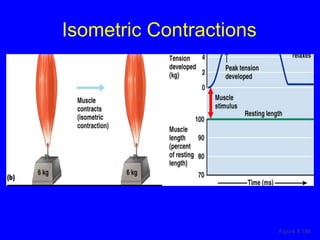
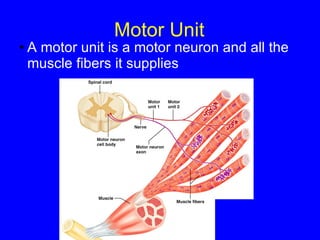
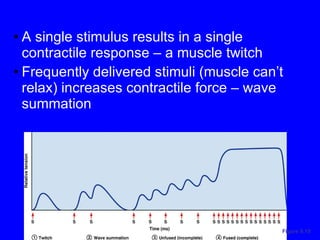
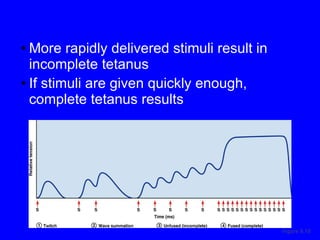
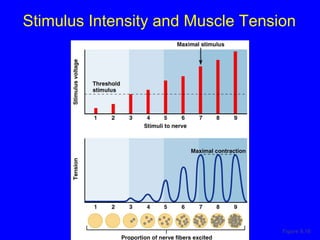
3. Different types of muscle contractions - isometric, isotonic - and motor unit activation patterns - twitch, tetanus - are defined. Stimulus intensity controls muscle force through graded motor unit recruitment.



























![Role of (Ca 2+ ) At low [Ca 2+ ] Tropomyosin blocks the binding sites on actin Myosin cross bridges cannot attach Figure 9.11a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/muscle-100224103545-phpapp01/85/Muscle-52-320.jpg)
![At high [Ca 2+ ] Calcium binds to troponin Troponin changes shape tropomyosin moves away from actin’s binding sites Figure 9.11b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/muscle-100224103545-phpapp01/85/Muscle-53-320.jpg)