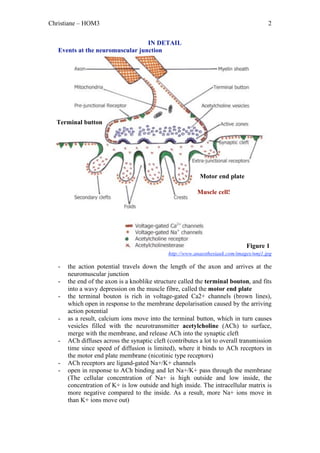
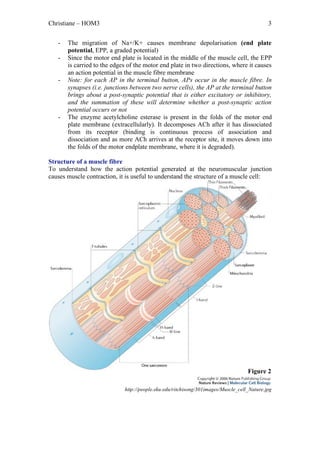
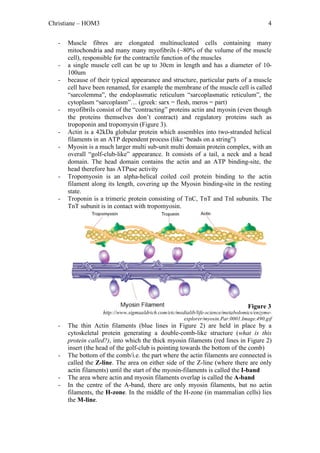
The document outlines the process of skeletal muscle contraction initiated by an action potential at the axon terminal, leading to calcium influx, acetylcholine release, and receptor activation at the neuromuscular junction. This triggers a series of events that culminate in the binding of actin and myosin, resulting in muscle fiber shortening and contraction through power strokes powered by ATP. Once the stimulus ends, calcium levels return to normal, halting muscle contraction.