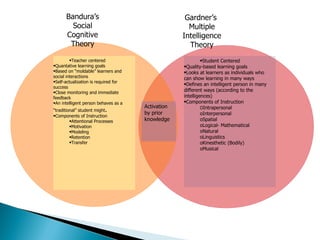
Howard Gardner's Multiple Intelligence Theory proposes that there are seven original domains of intelligence rather than just a single general intelligence. The theory defines intelligence broadly based on a set of skills, talents, or mental abilities. The seven original domains are logical-mathematical, linguistic, musical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, interpersonal, and intrapersonal intelligence. The theory suggests that individuals have unique combinations of these intelligences and can be intelligent in different ways.