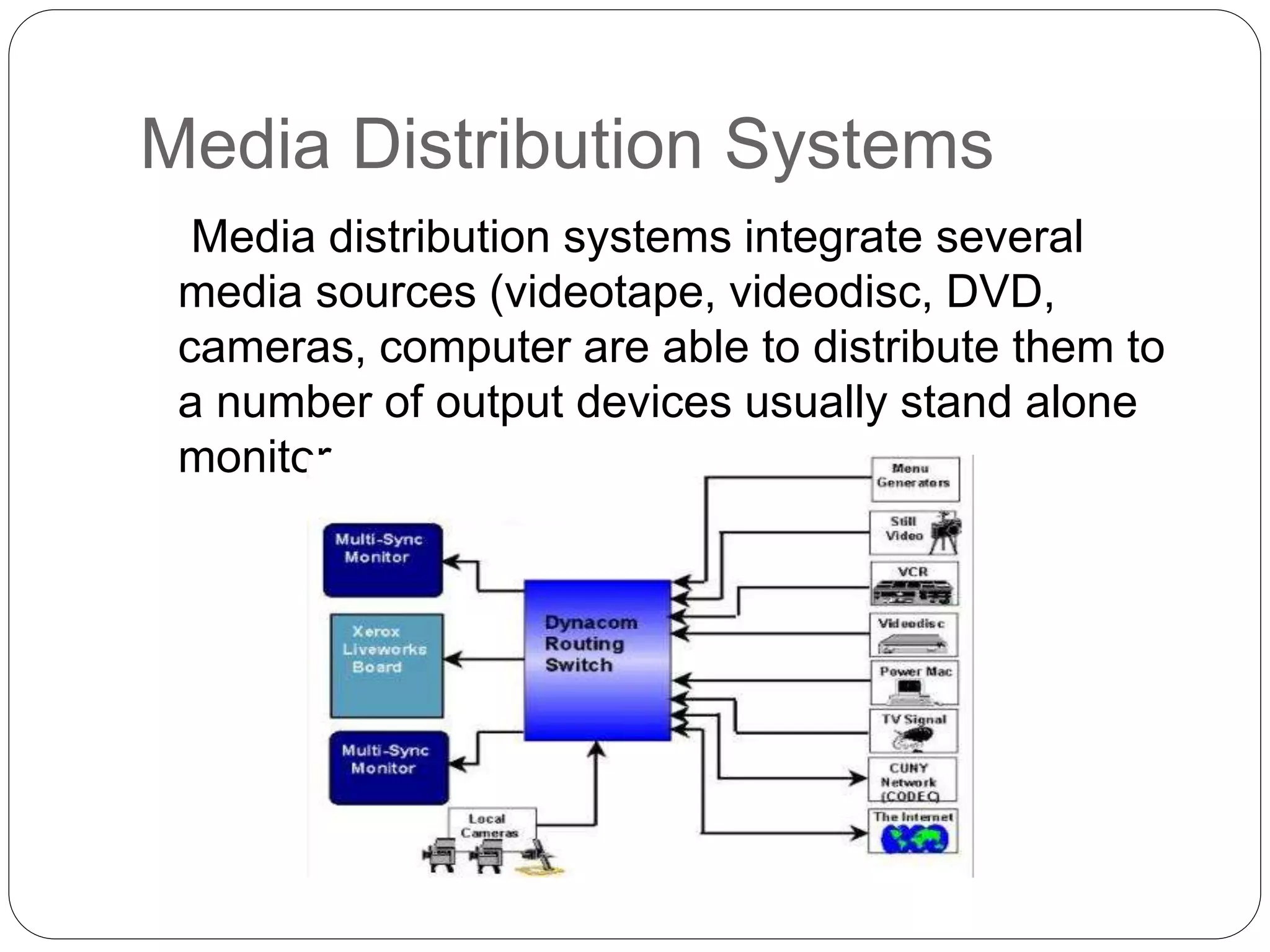
This document discusses multimedia in education. It defines multimedia as any combination of two or more media such as sound, images, text, animation and video. Multimedia allows for associative linkages that let users navigate and retrieve stored information. It also discusses how multimedia can support multiple intelligences and literacy. The document outlines multimedia systems, software, and its use for teaching and learning. It notes the importance of copyright for multimedia resources and describes media distribution systems.