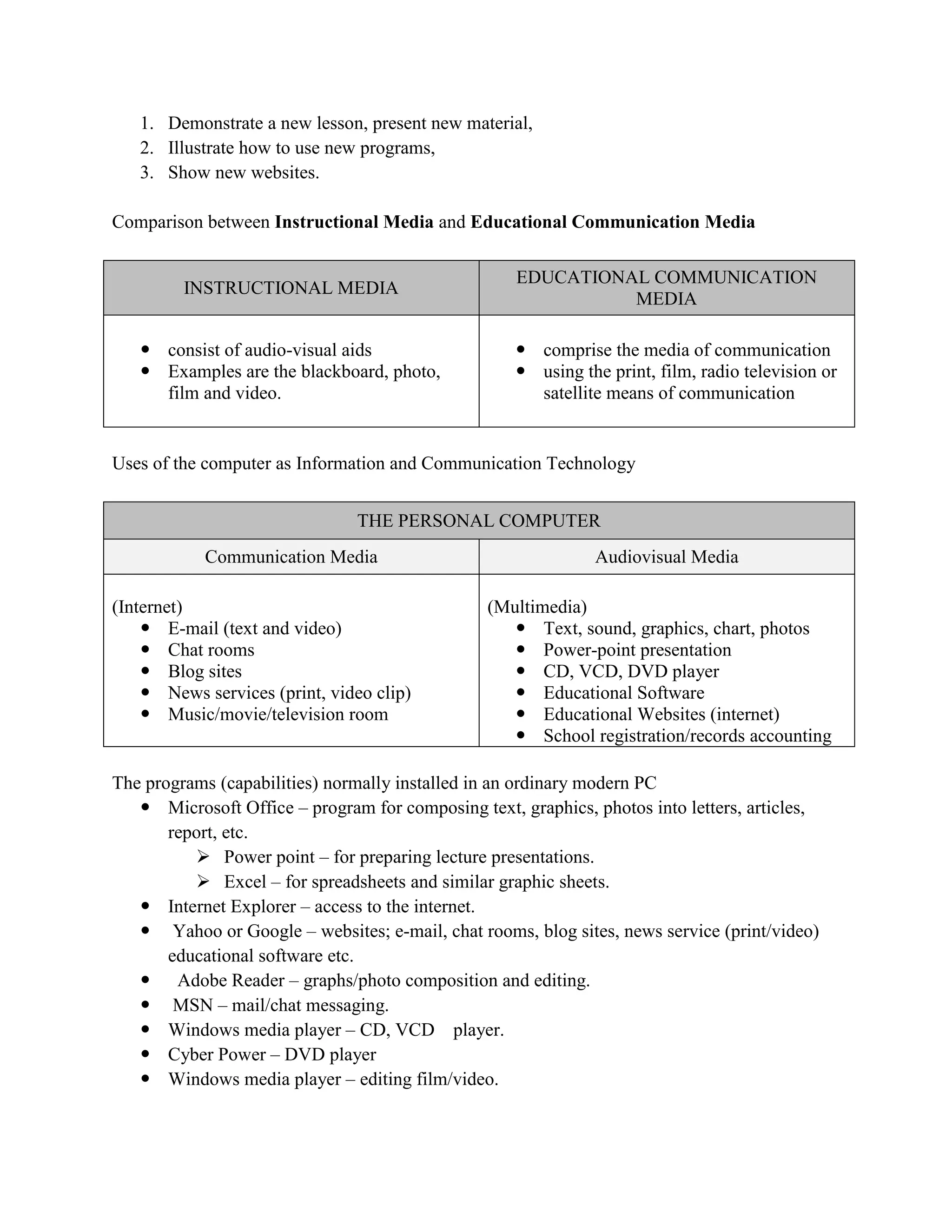
The document discusses how computer technology has transformed into an information and communication technology (ICT) that can be used in education to enhance learning experiences. It provides examples of how computers and the internet can be utilized for communication, multimedia presentations, and interactive learning activities. The uses of different ICT tools like radio, television, and computers in education are also examined.