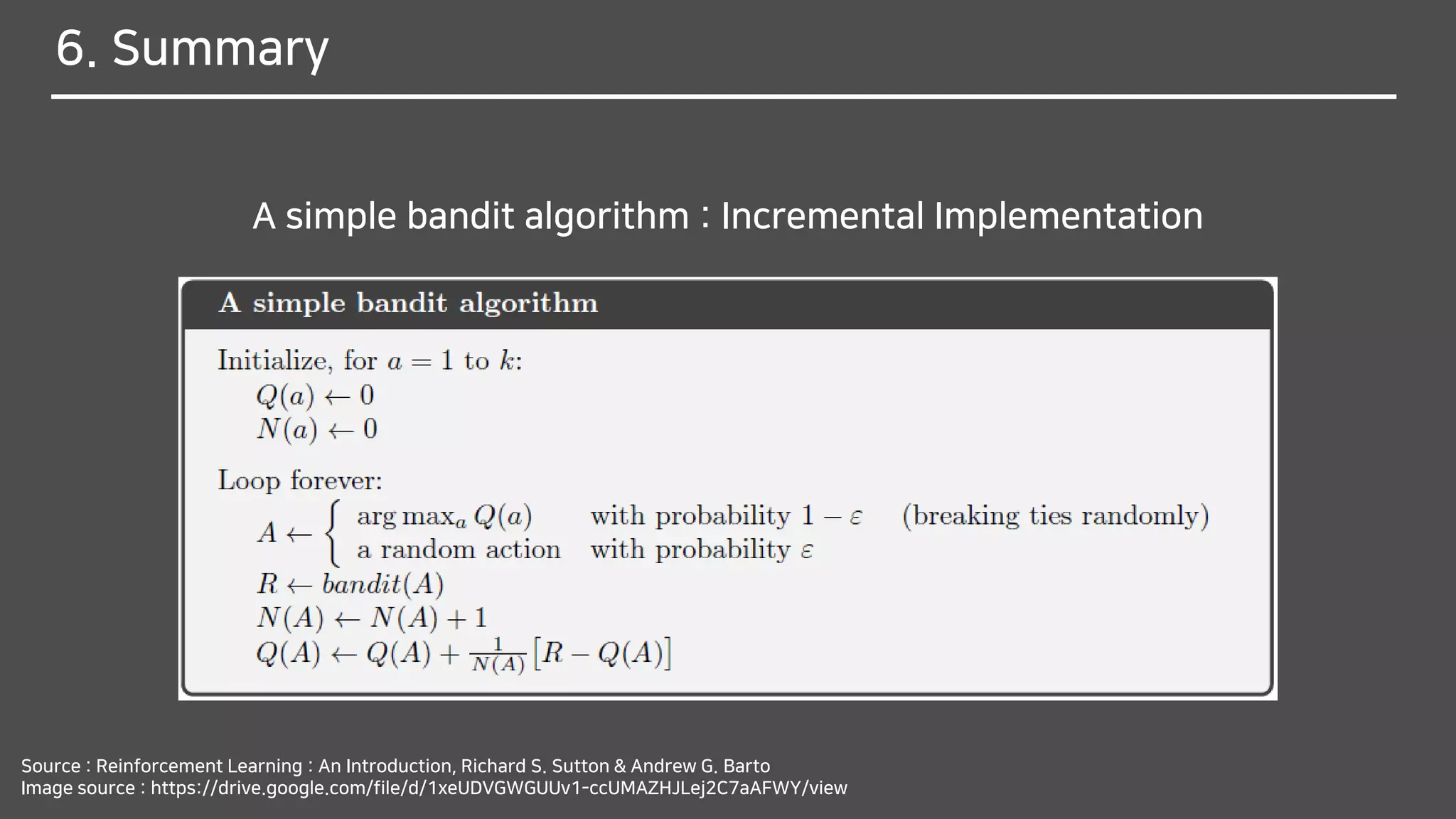
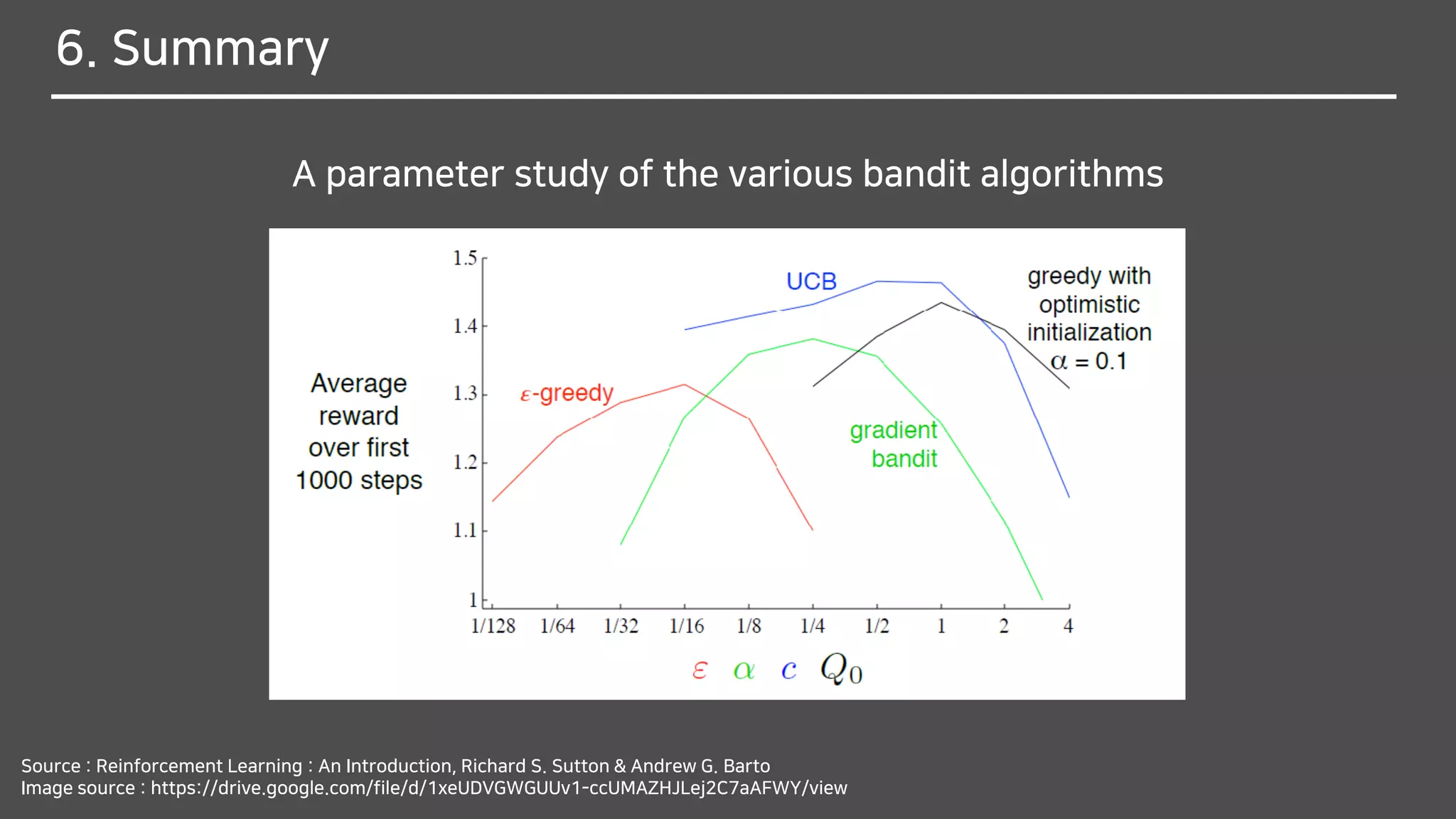
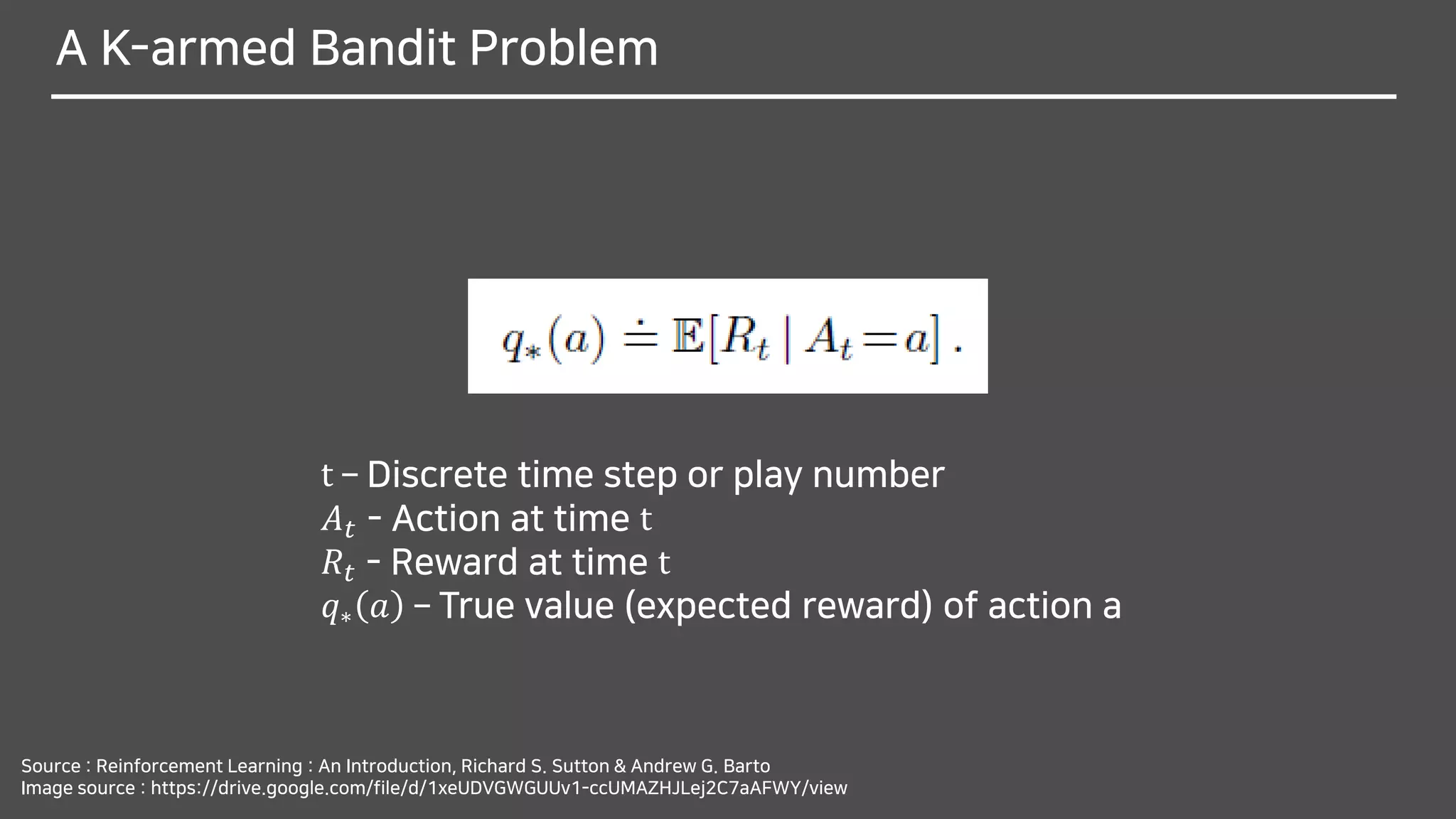
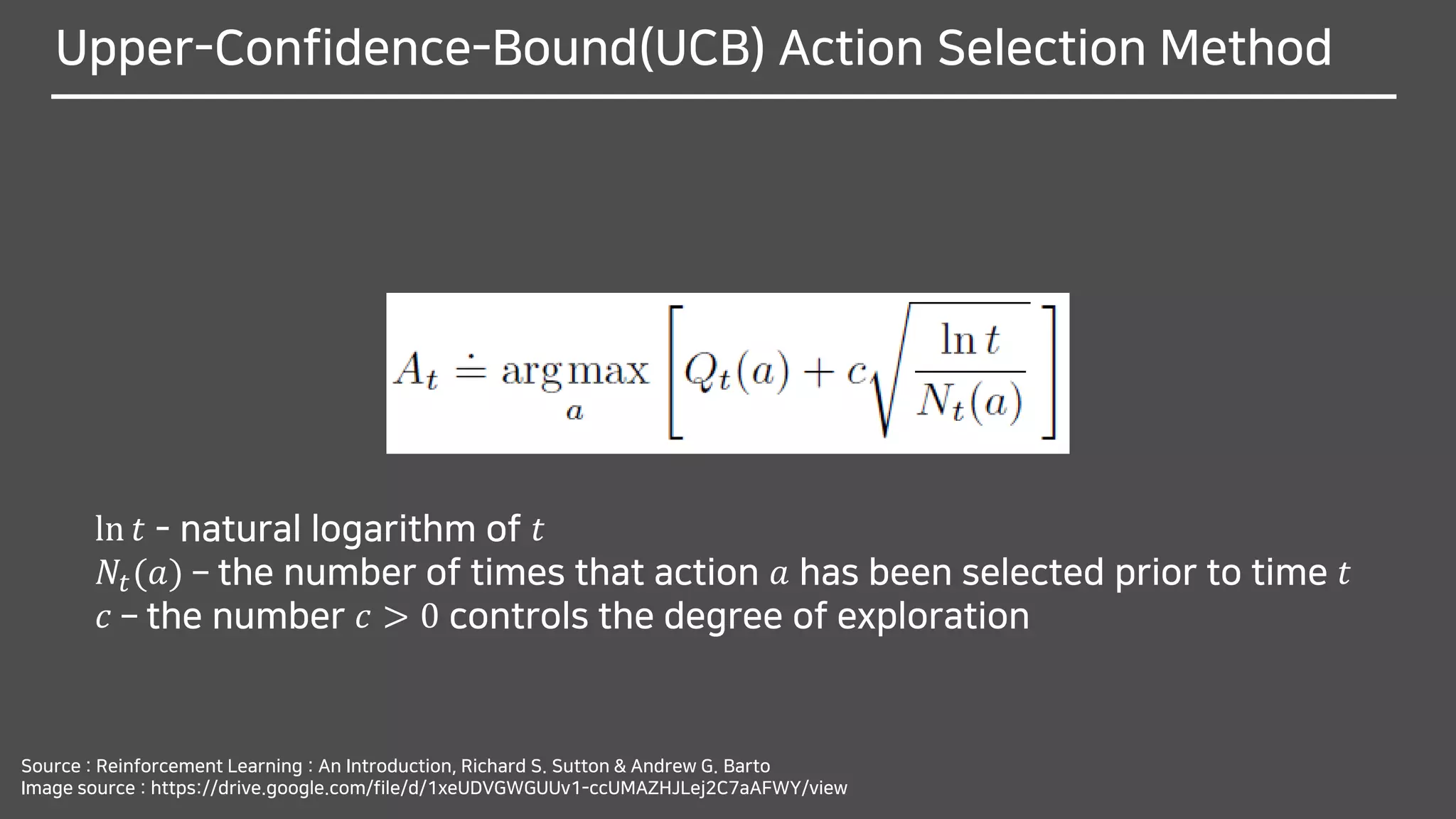
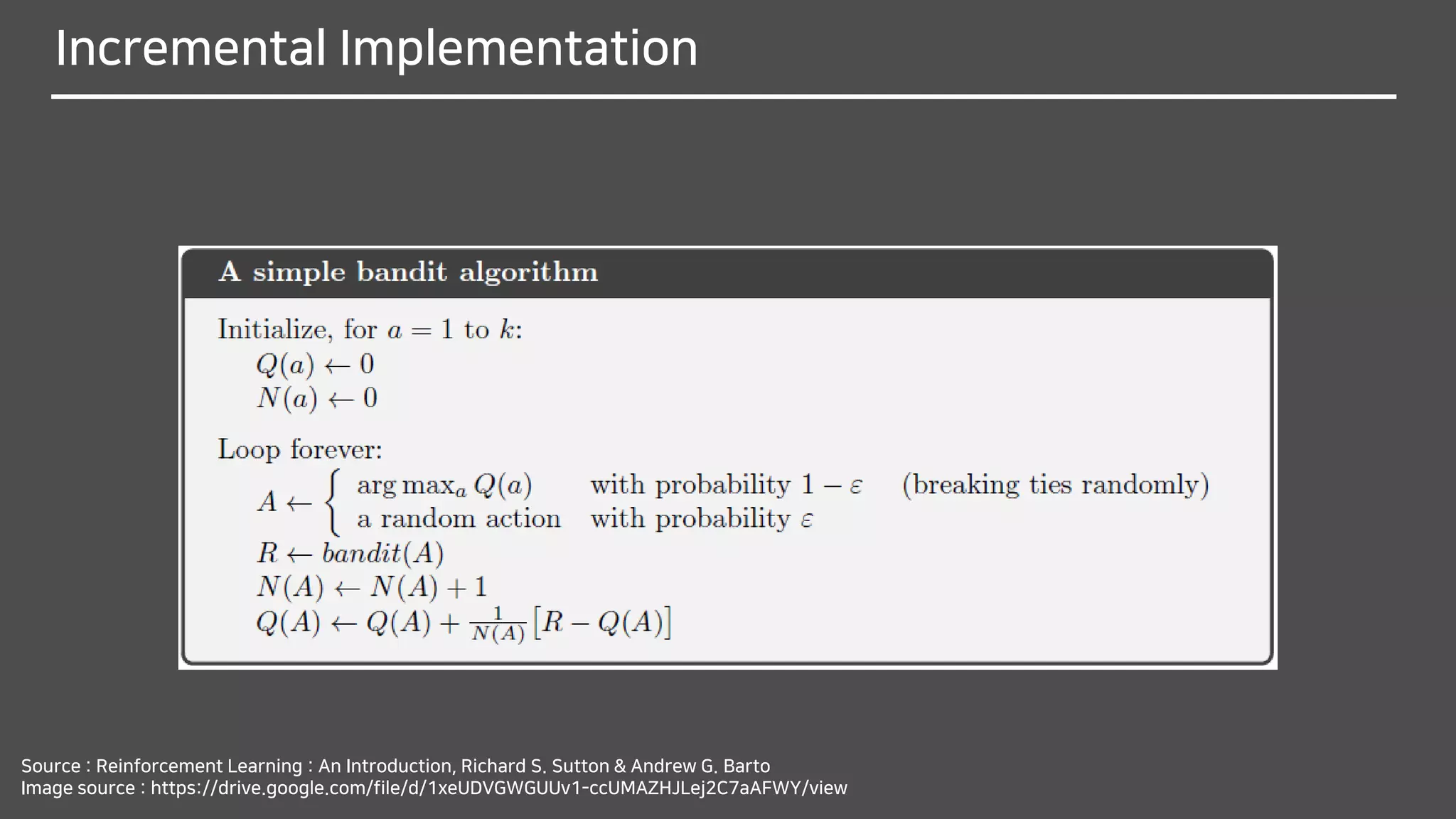
The document discusses multi-armed bandits (MAB), a foundational concept in reinforcement learning (RL) which involves balancing exploitation and exploration to optimize decision-making. It outlines various methods for solving MAB problems including simple-average action-value methods, ε-greedy, and upper-confidence-bound methods. Additionally, it covers simple bandit algorithms and gradient bandit algorithms that adaptively learn preferences and optimize rewards based on historical performance.

































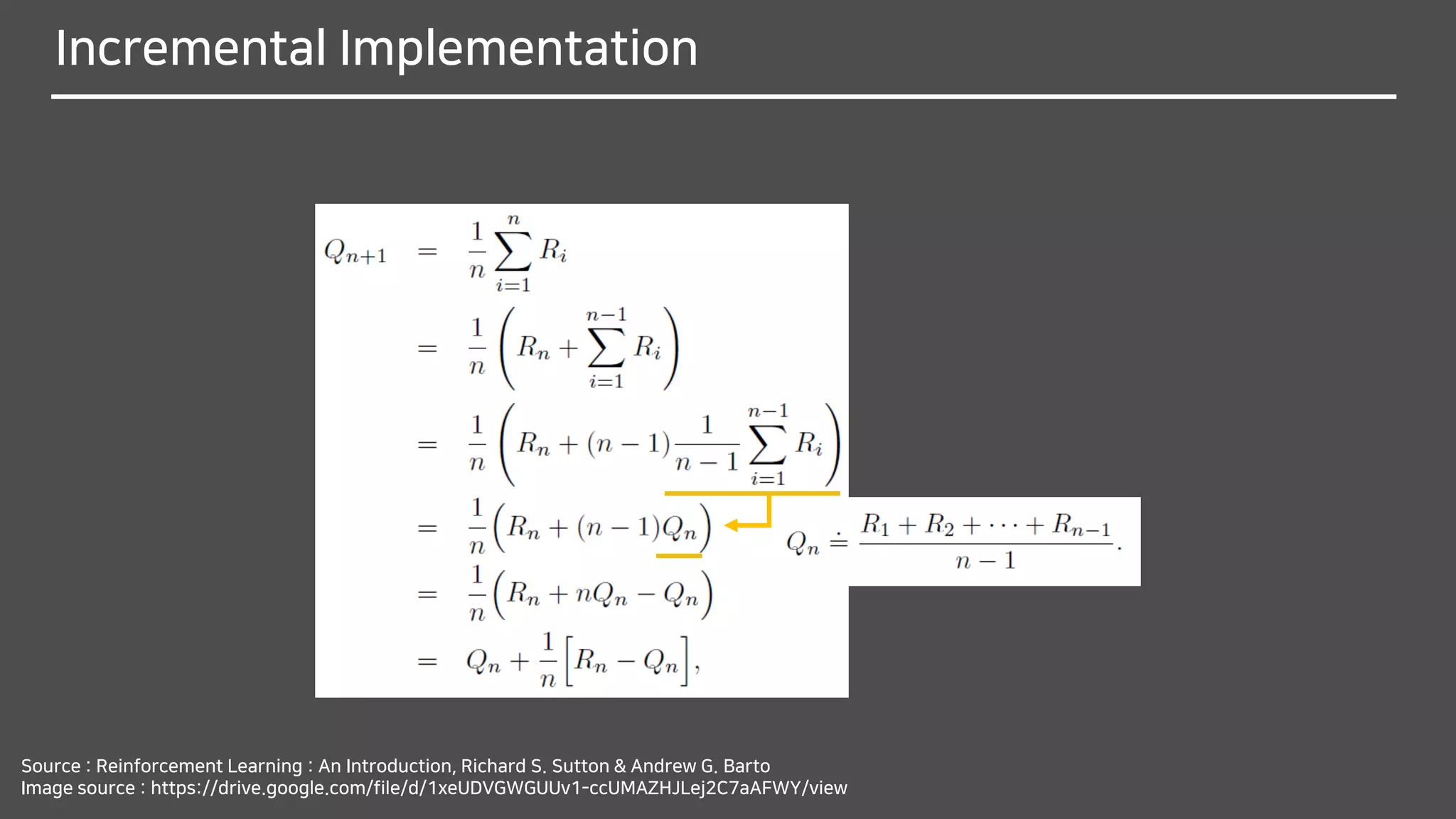
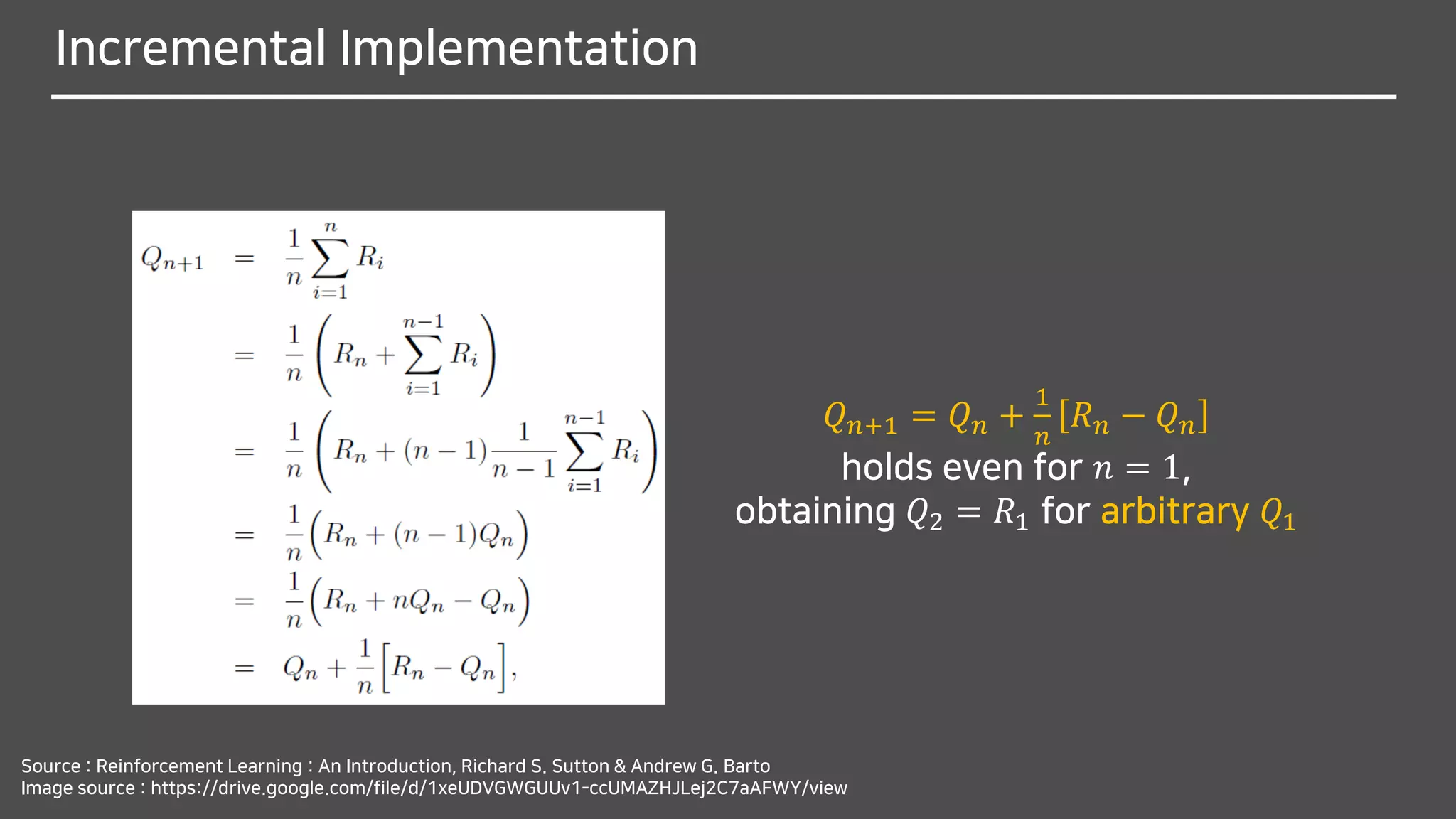







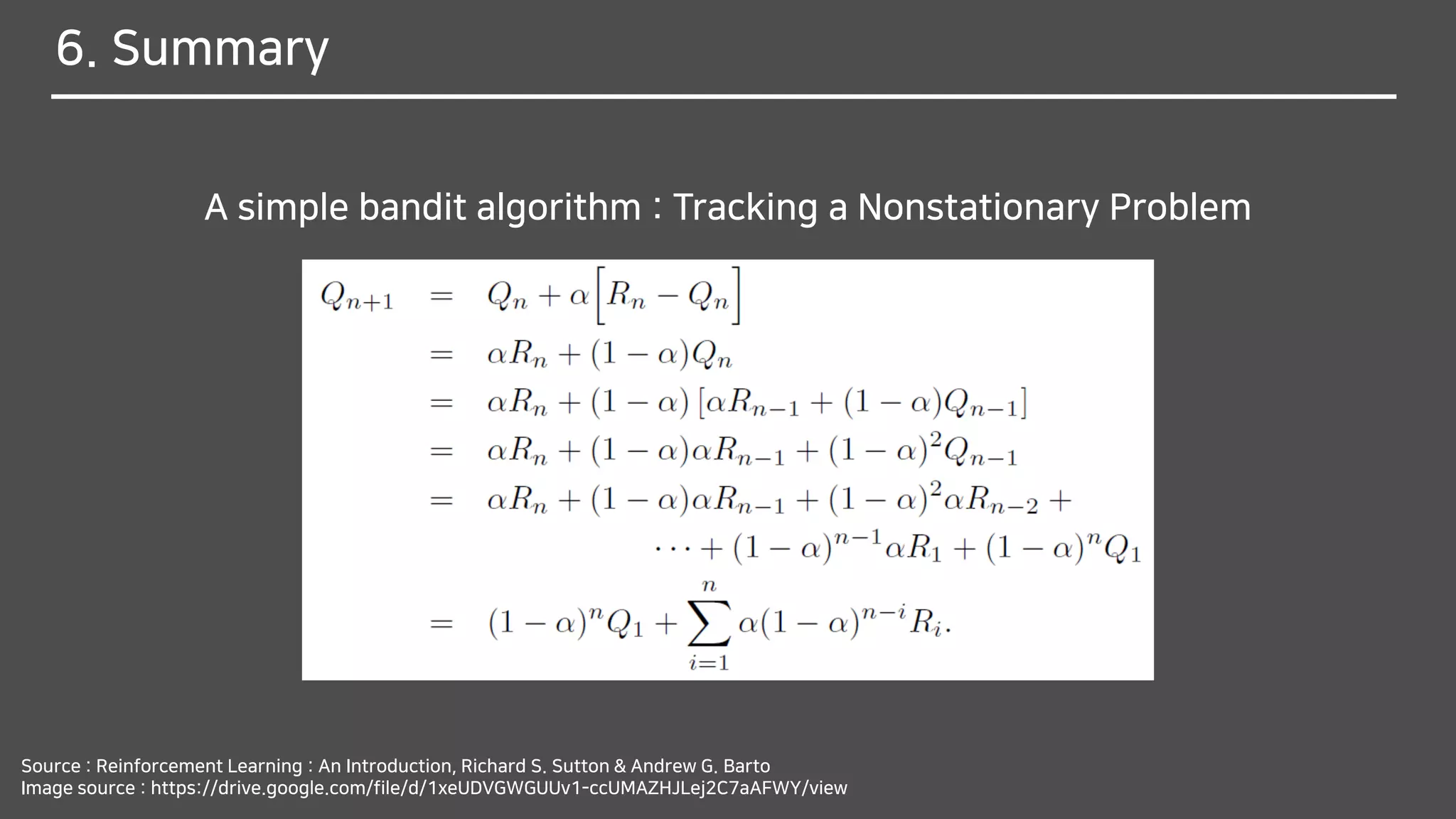
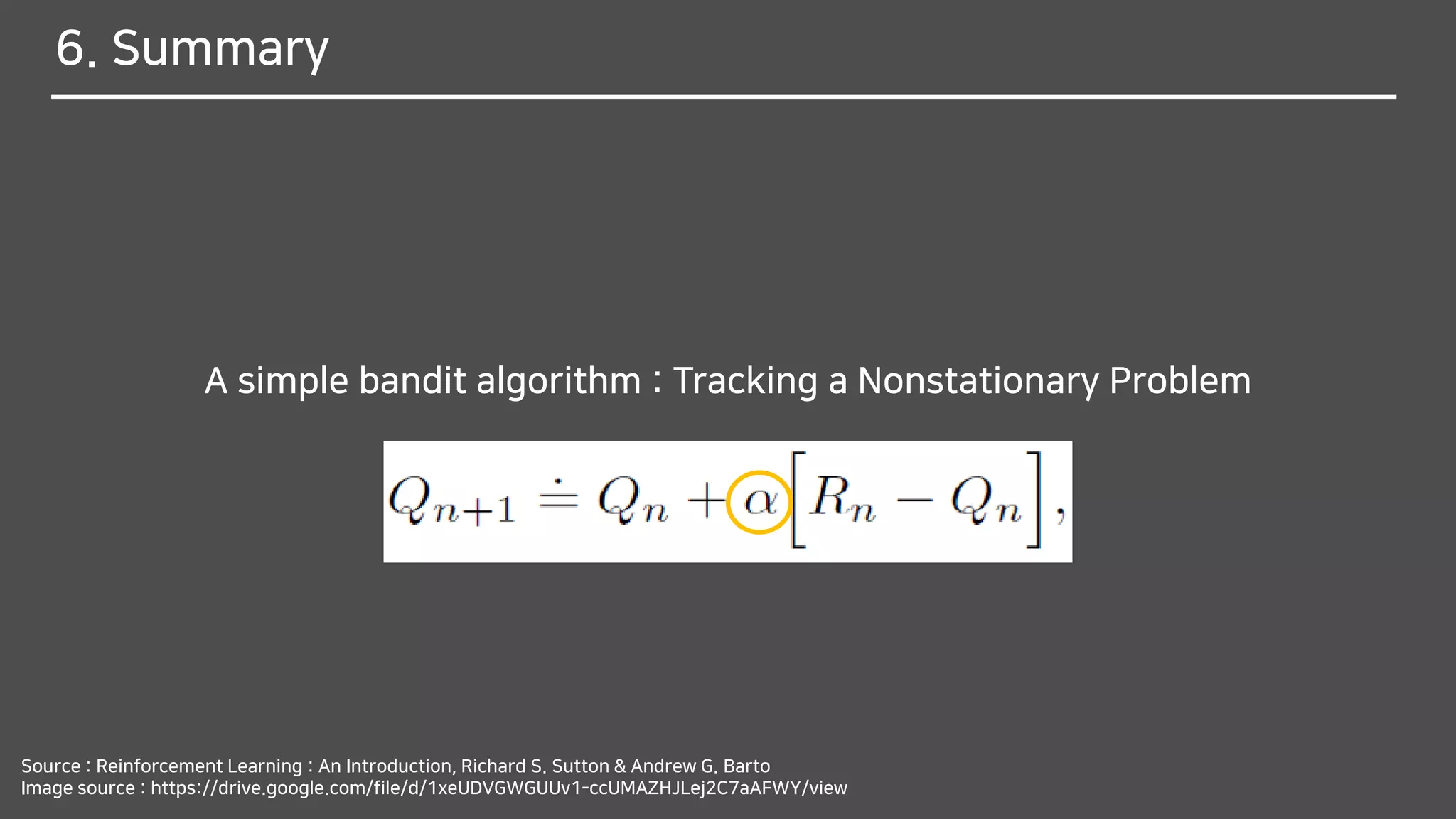
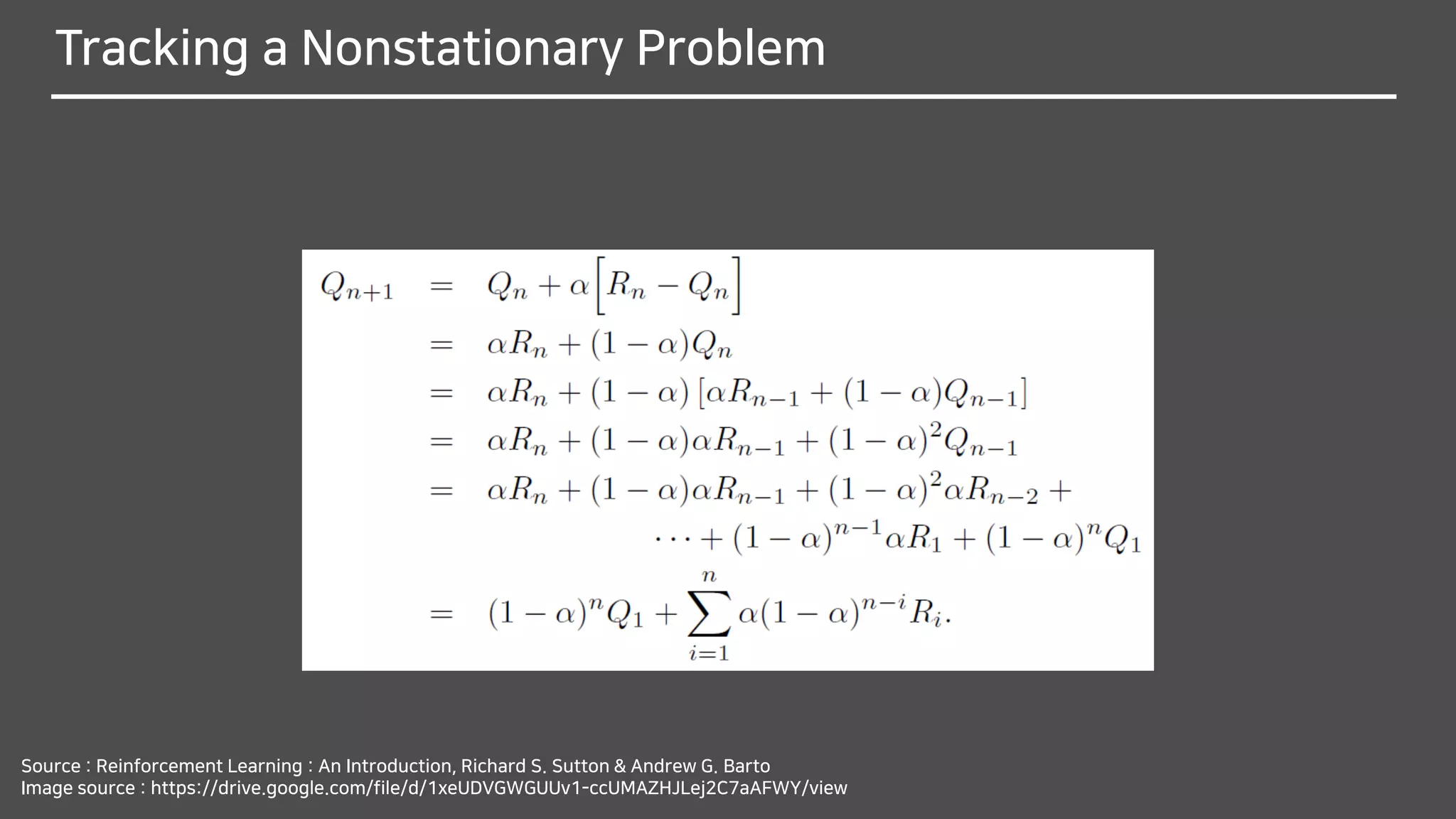
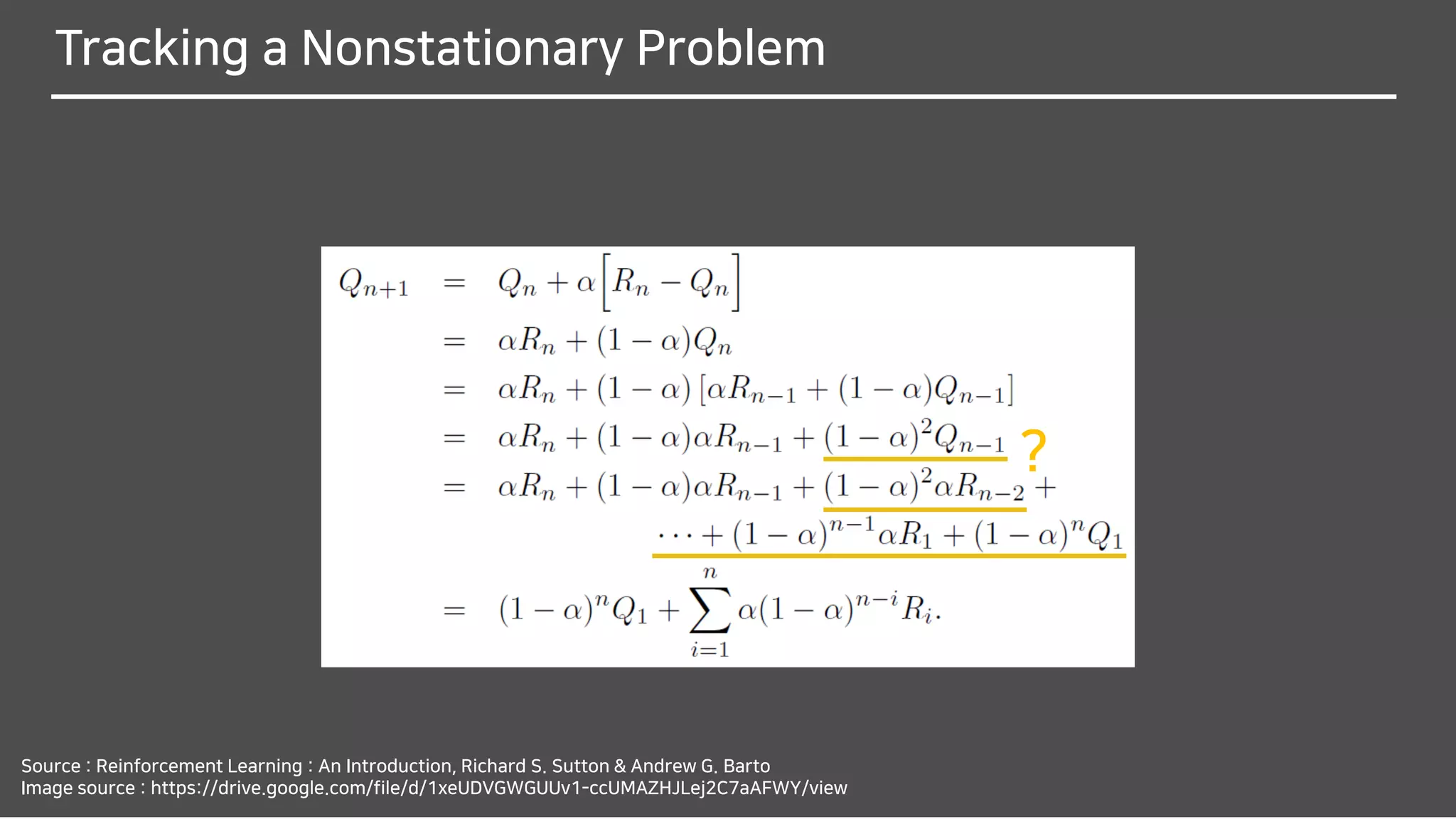
![Tracking a Nonstationary Problem
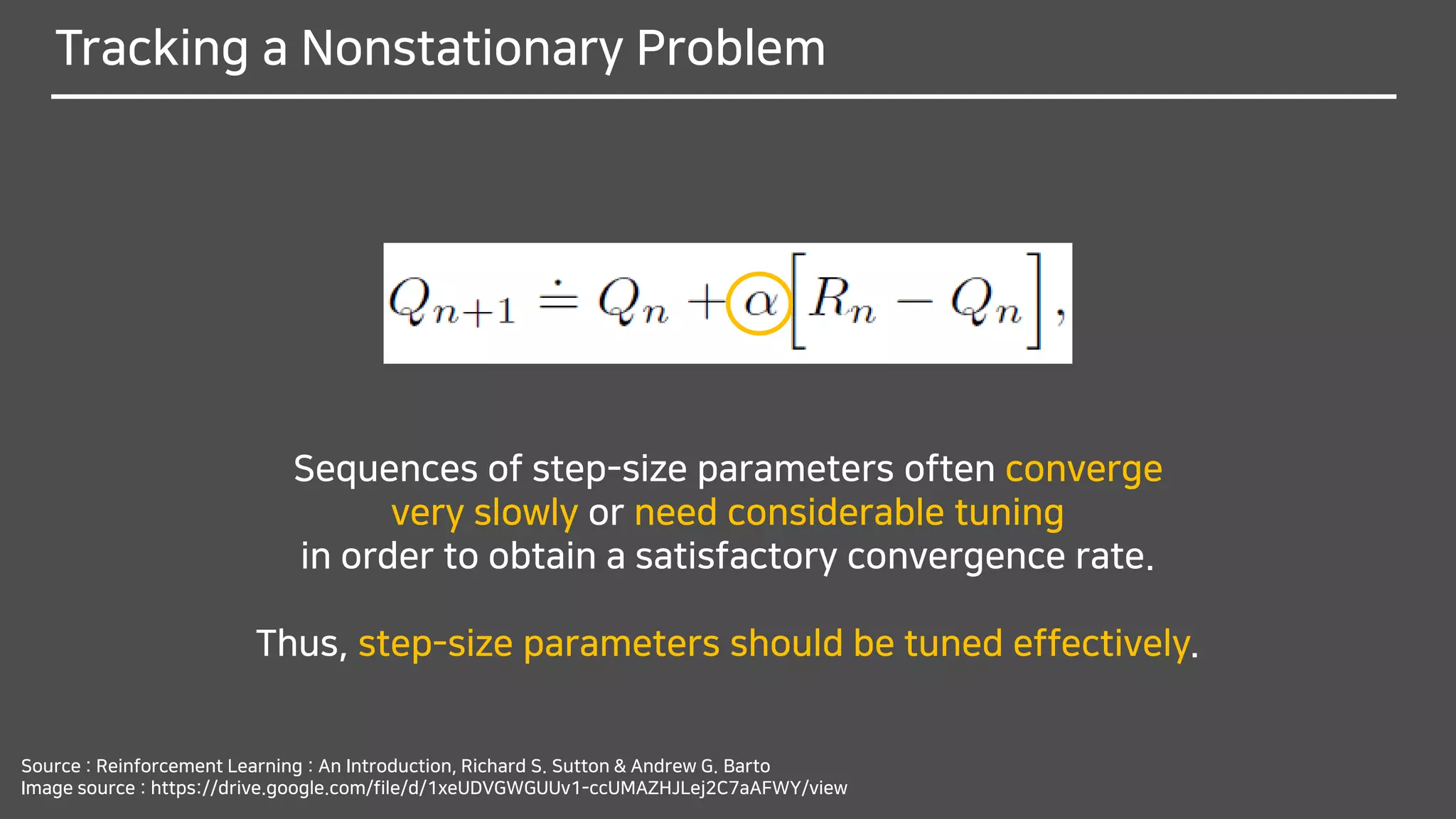
Why do you think it should be changed from
1
𝑛
to 𝛼?
We often encounter RL problems that are effectively nonstationary.
In such cases it makes sense to give more weight
to recent rewards than to long-past rewards.
One of the most popular ways of doing this is to use
a constant step-size parameter.
The step-size parameter 𝛼 ∈ (0,1] is constant.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multi-armedbandits-180409074129/75/Multi-armed-Bandits-47-2048.jpg)







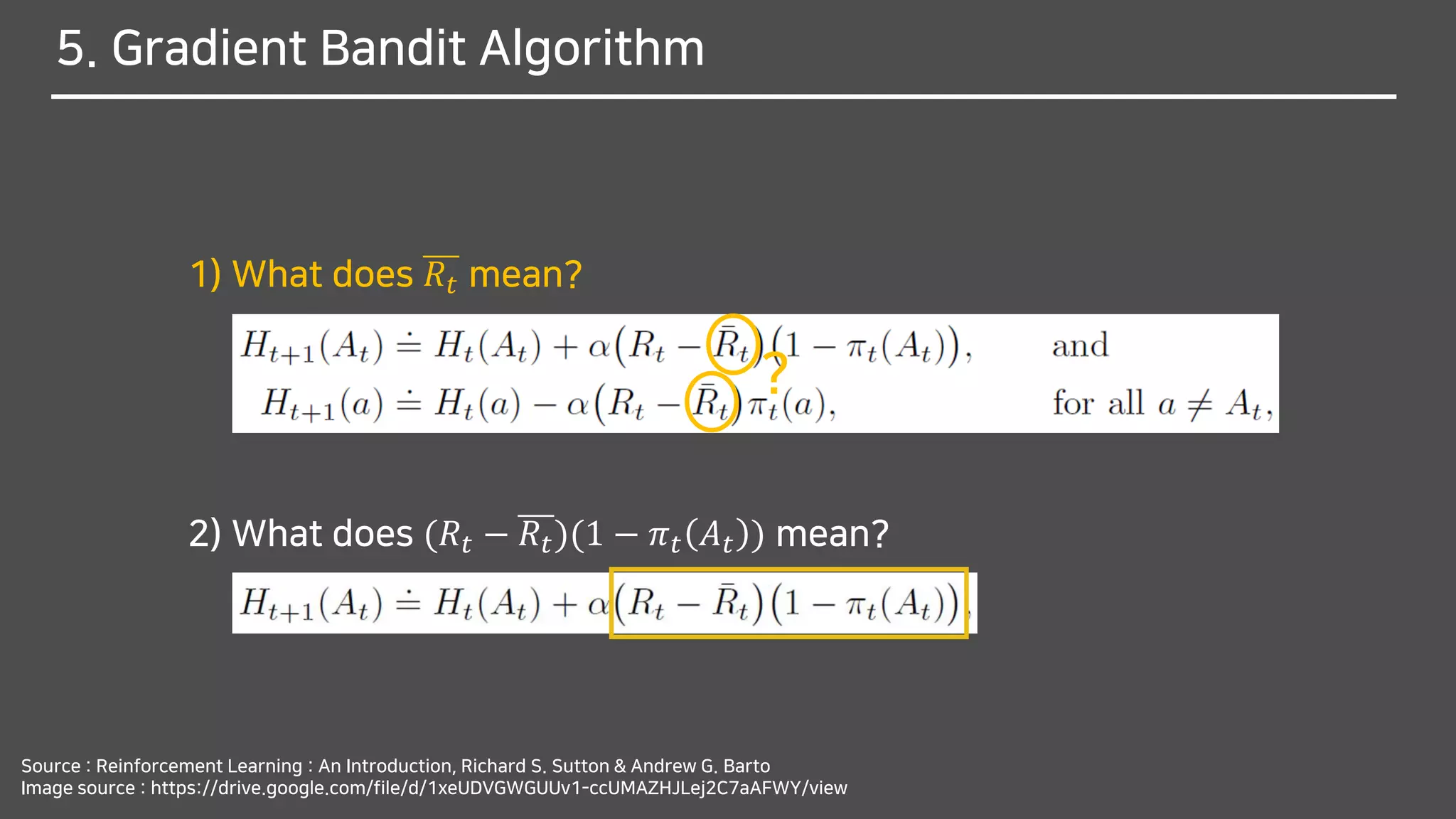
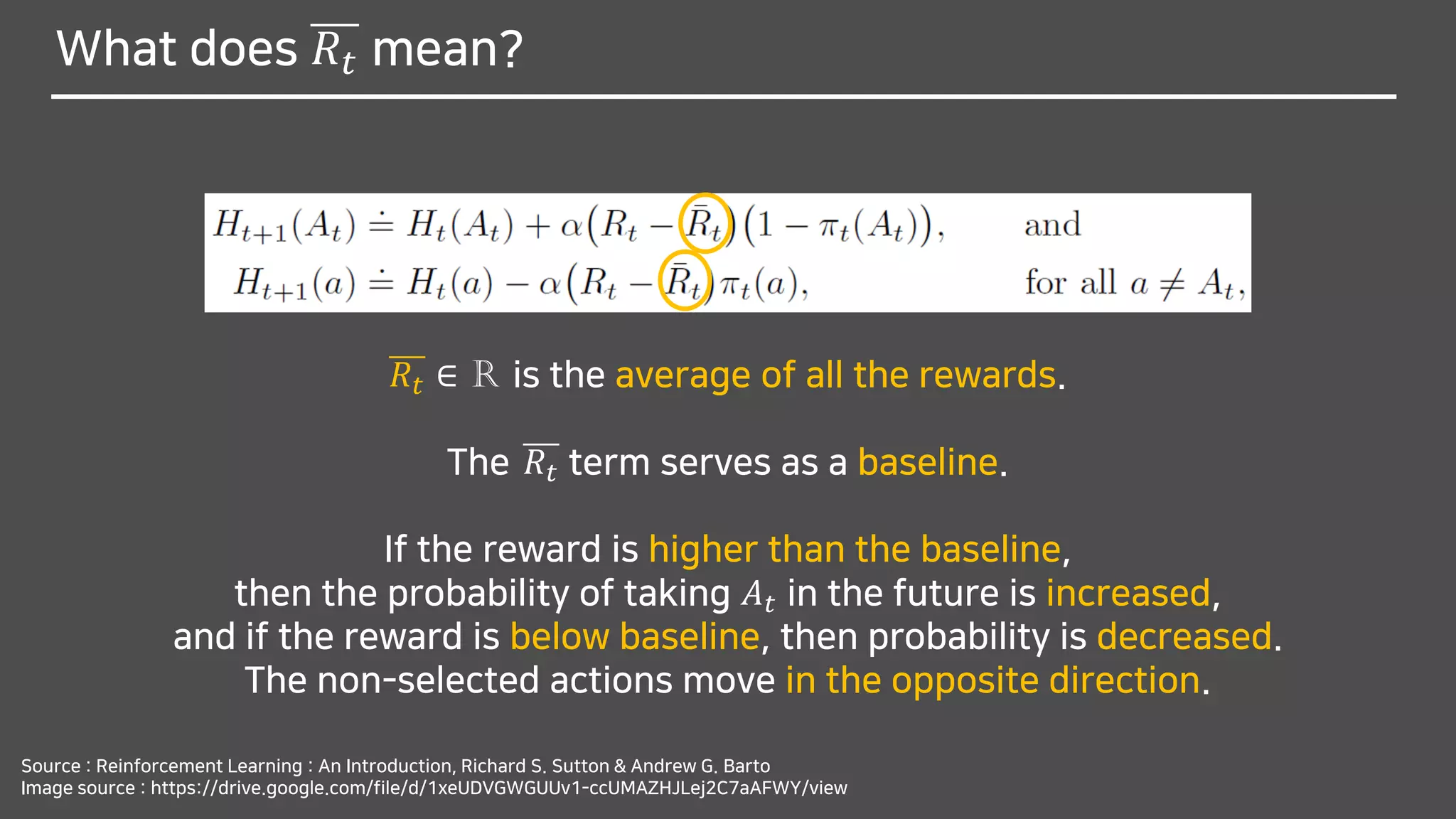
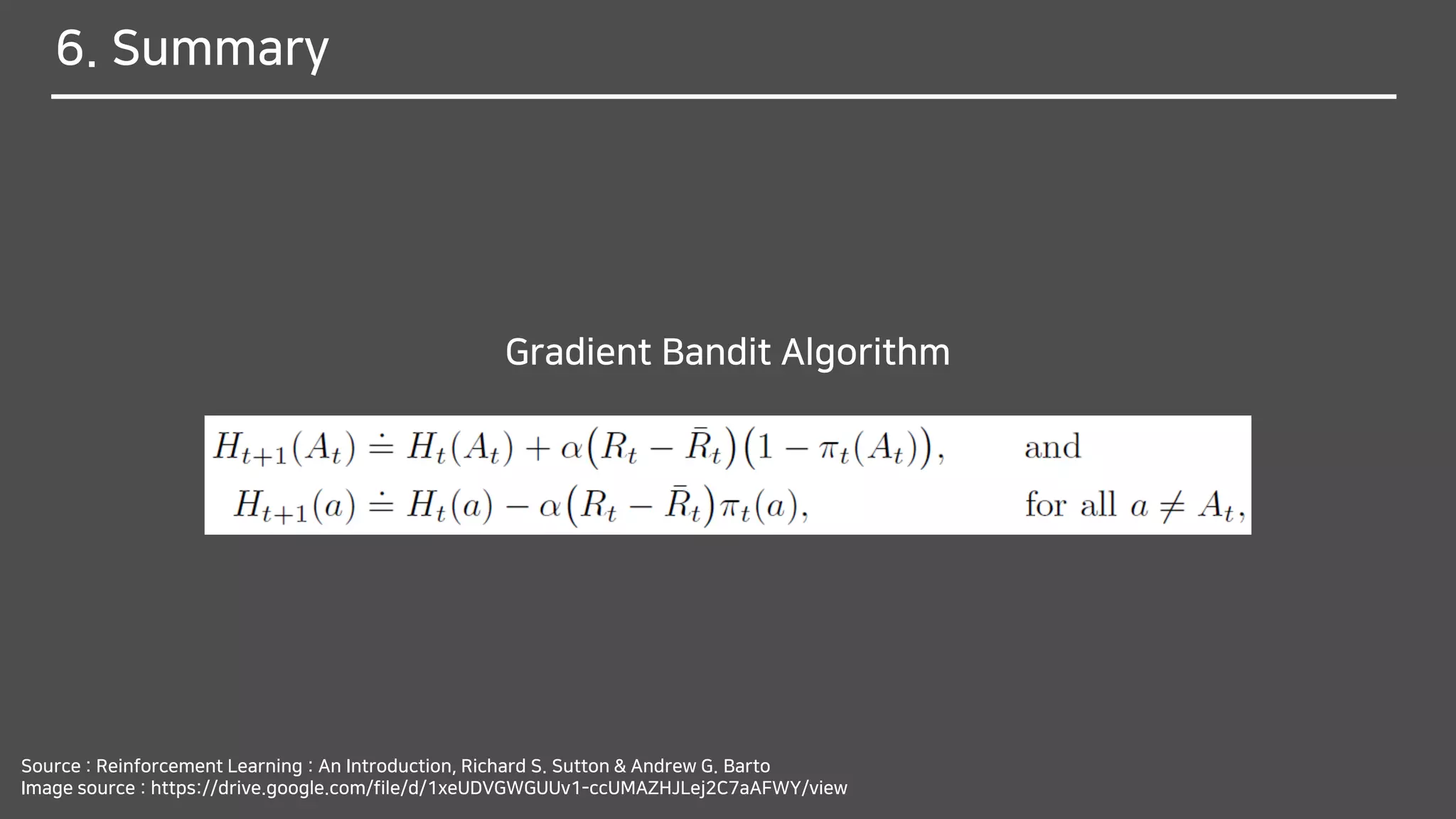
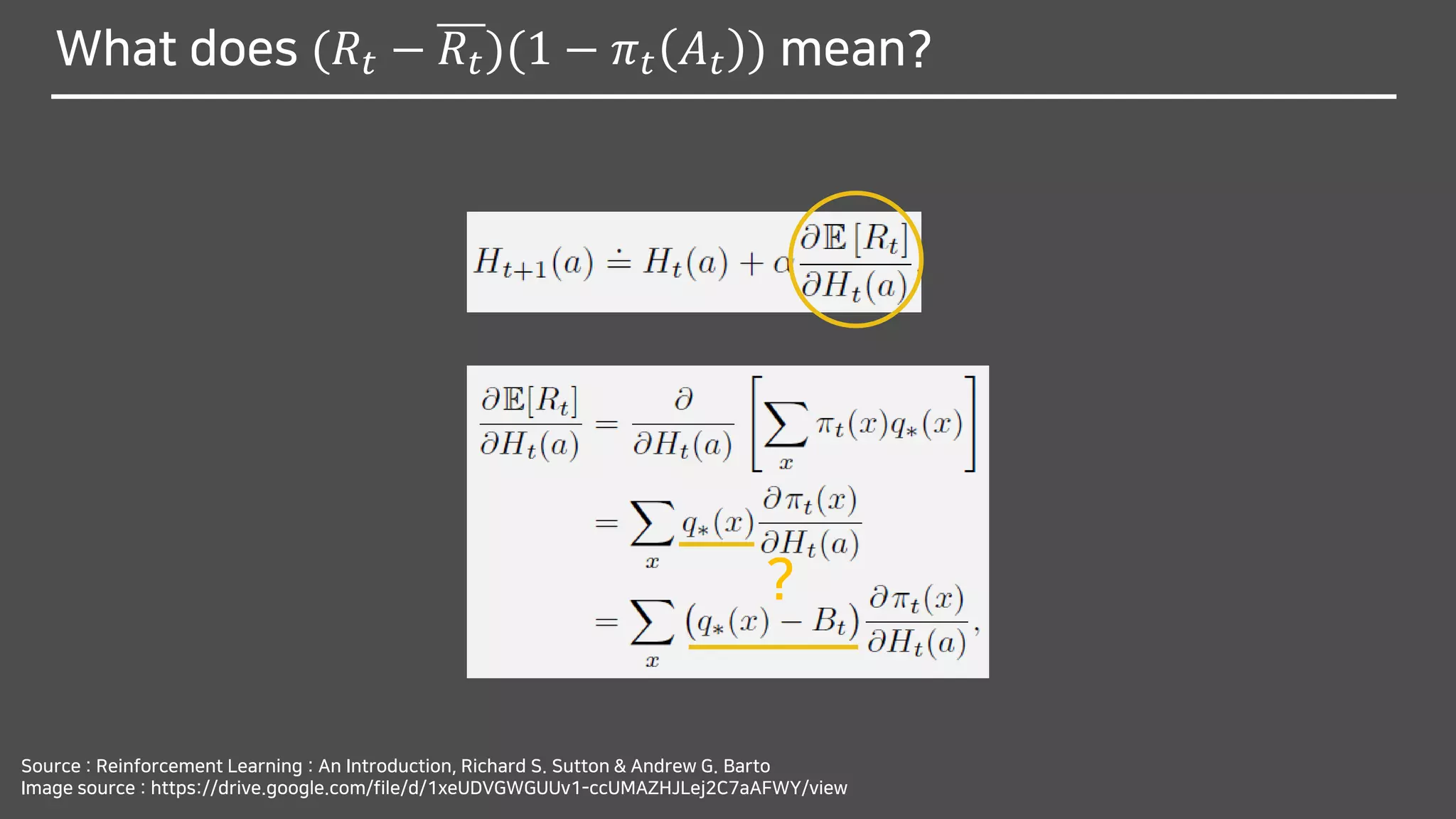
![What does (𝑅𝑡 − 𝑅𝑡)(1 − 𝜋 𝑡 𝐴 𝑡 ) mean?
Source : Reinforcement Learning : An Introduction, Richard S. Sutton & Andrew G. Barto
Image source : https://drive.google.com/file/d/1xeUDVGWGUUv1-ccUMAZHJLej2C7aAFWY/view
- Stochastic approximation to gradient ascent
in Bandit Gradient Algorithm
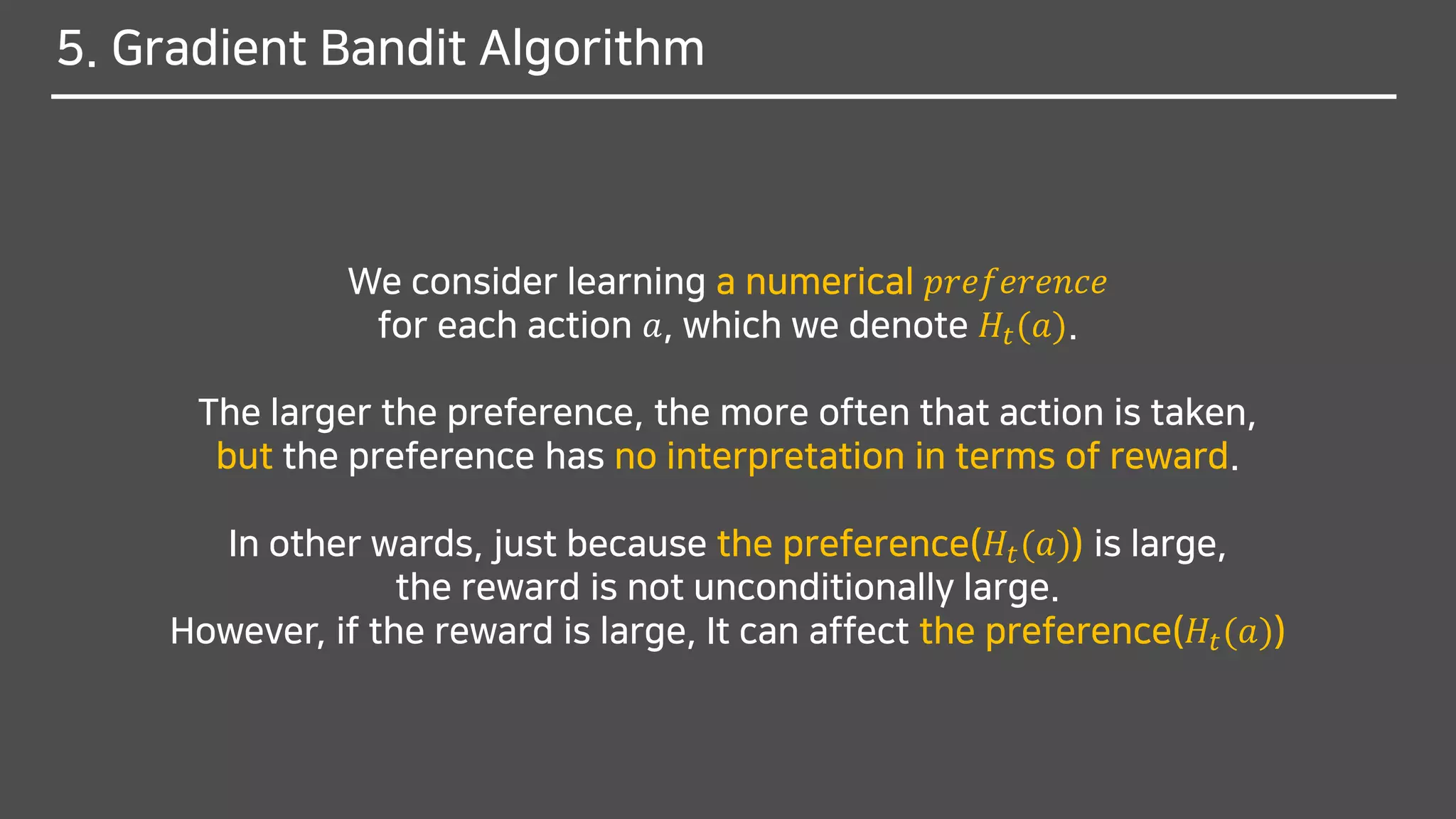
- Expected reward
- Expected reward by Low of total expectationE[𝑅𝑡] = E[ E 𝑅𝑡 𝐴 𝑡 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multi-armedbandits-180409074129/75/Multi-armed-Bandits-63-2048.jpg)
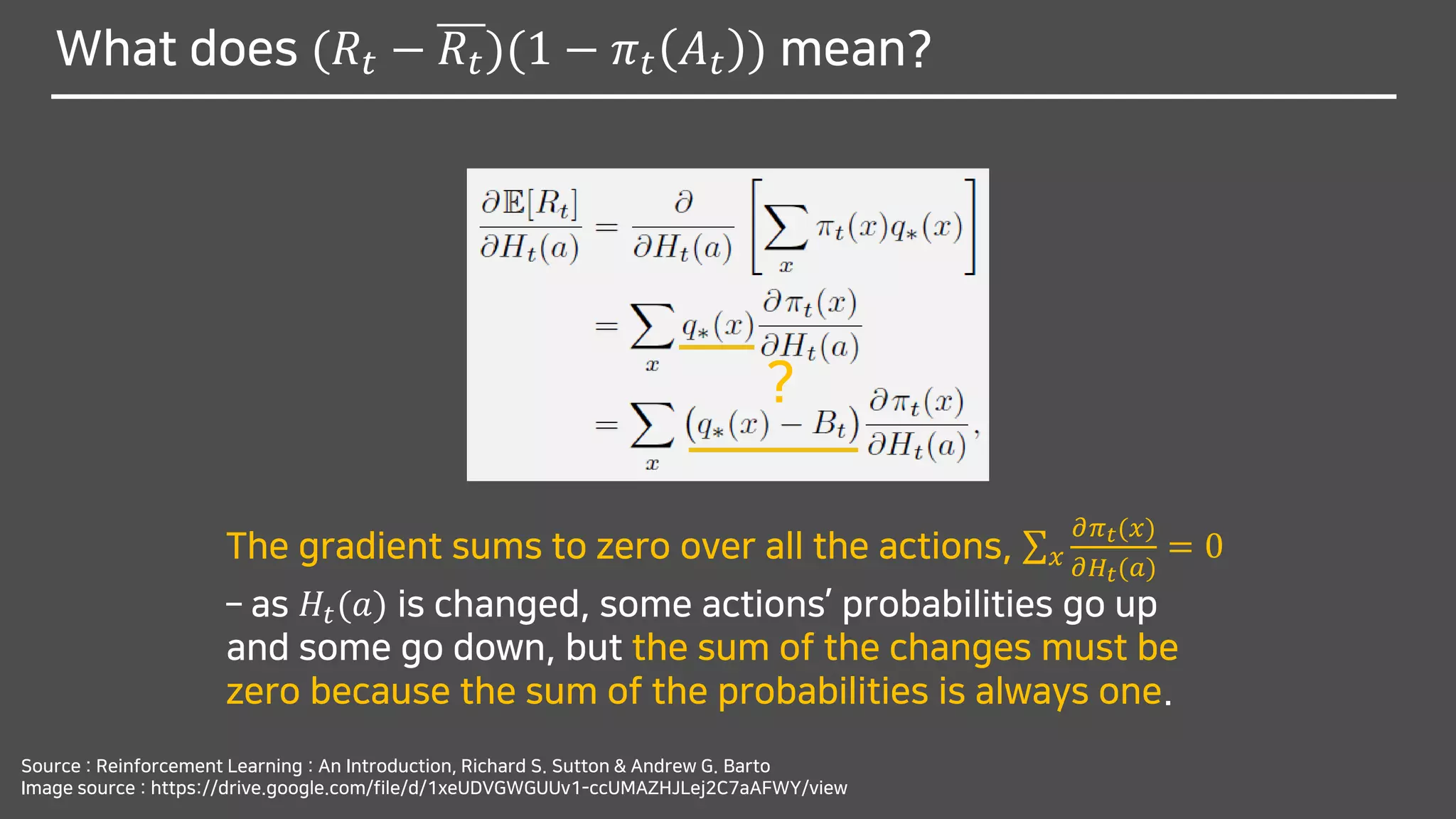
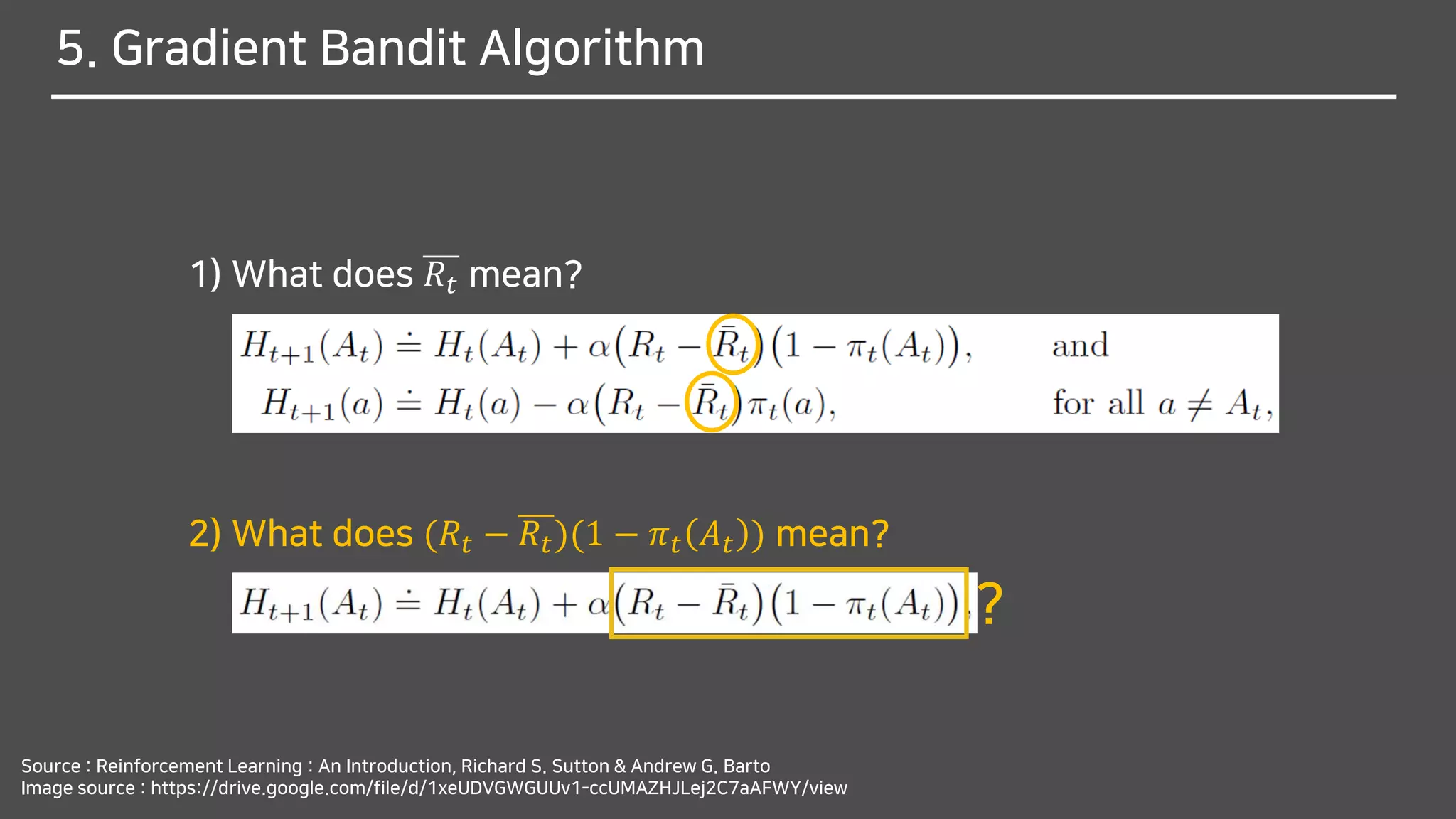
![What does (𝑅𝑡 − 𝑅𝑡)(1 − 𝜋 𝑡 𝐴 𝑡 ) mean?
Source : Reinforcement Learning : An Introduction, Richard S. Sutton & Andrew G. Barto
Image source : https://drive.google.com/file/d/1xeUDVGWGUUv1-ccUMAZHJLej2C7aAFWY/view
?
E[𝑅𝑡] = E[ E 𝑅𝑡 𝐴 𝑡 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multi-armedbandits-180409074129/75/Multi-armed-Bandits-68-2048.jpg)
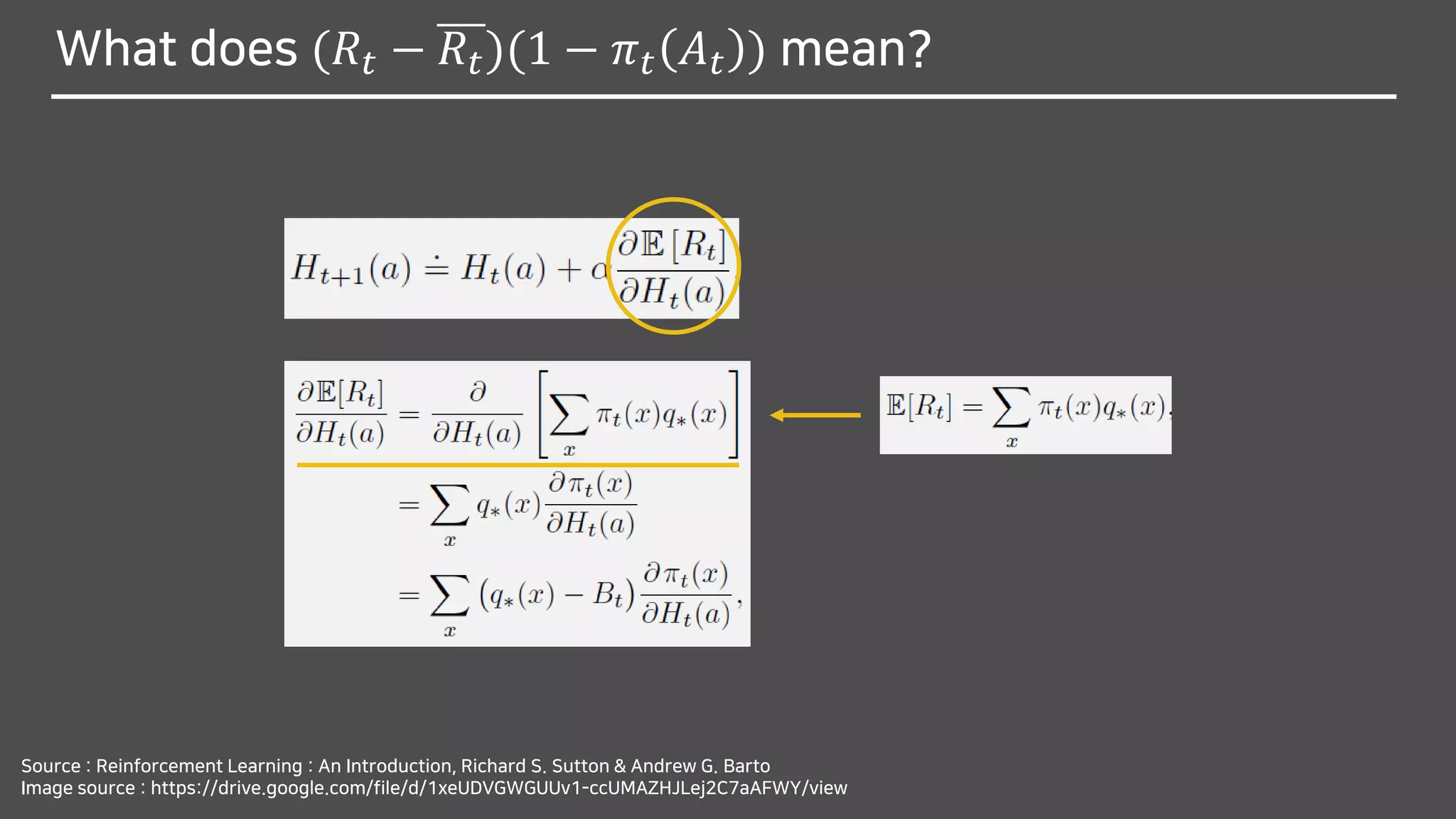
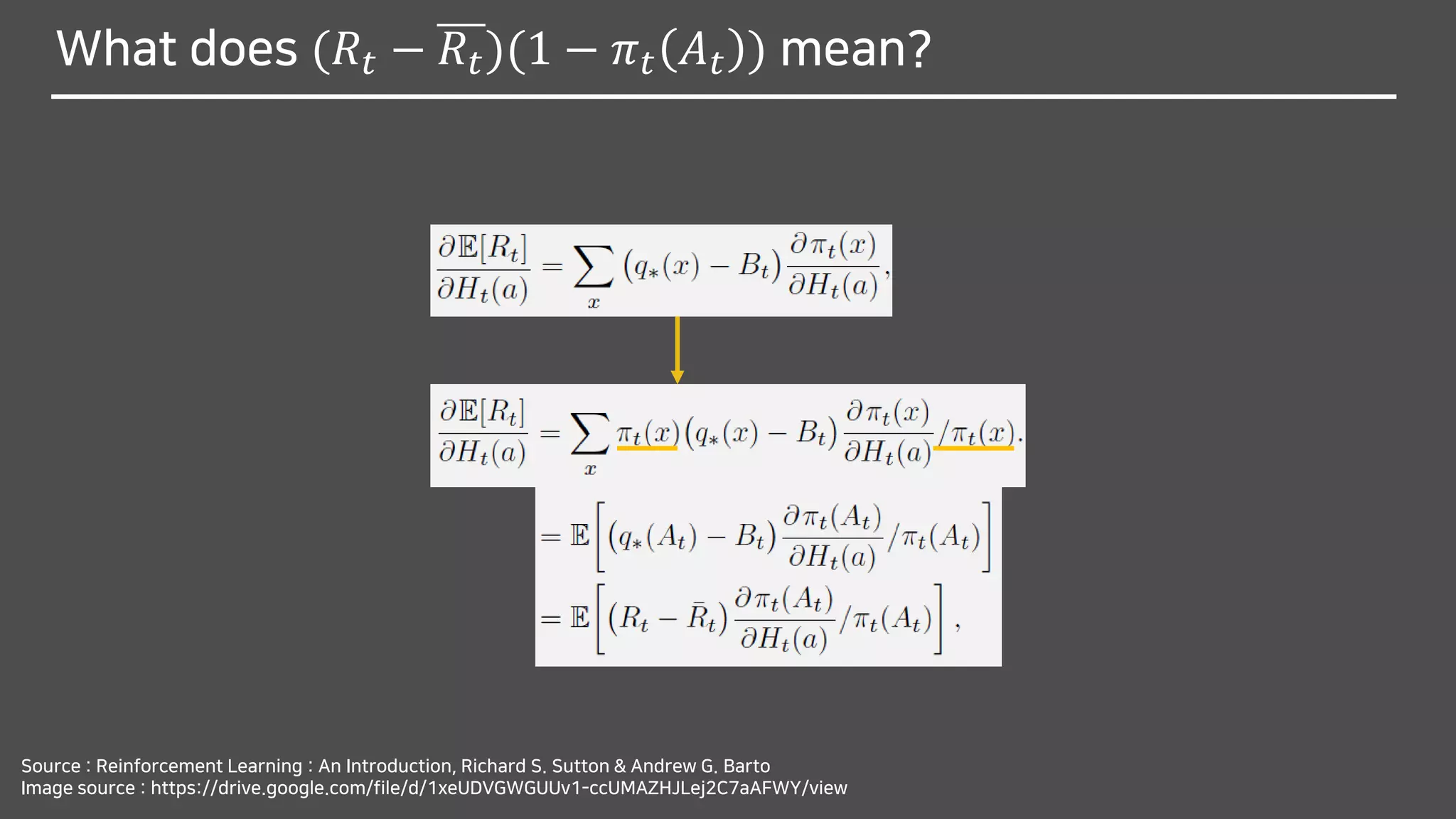
![What does (𝑅𝑡 − 𝑅𝑡)(1 − 𝜋 𝑡 𝐴 𝑡 ) mean?
Source : Reinforcement Learning : An Introduction, Richard S. Sutton & Andrew G. Barto
Image source : https://drive.google.com/file/d/1xeUDVGWGUUv1-ccUMAZHJLej2C7aAFWY/view
∴
We can substitute a sample of the expectation above
for the performance gradient in 𝐻𝑡+1 𝑎 ≅ 𝐻𝑡 𝑎 + 𝛼
𝜕E[𝑅 𝑡]
𝜕𝐻𝑡(𝑎)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multi-armedbandits-180409074129/75/Multi-armed-Bandits-70-2048.jpg)