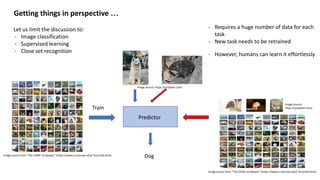
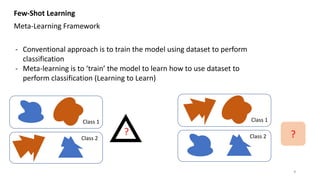
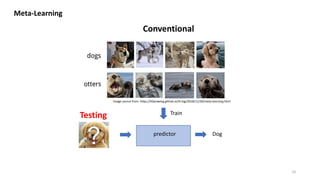
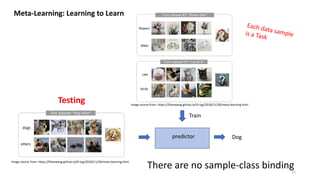
This presentation provides an introduction to few-shot learning. It begins by comparing human and machine learning, noting that humans can learn new tasks from only a few examples while machines typically require large datasets. It then discusses meta-learning as a framework for few-shot learning, where a model is trained to learn from few examples. Finally, it outlines different approaches to meta-learning, including based on similarity, learning algorithms like MAML, and modeling data through Bayesian programs.









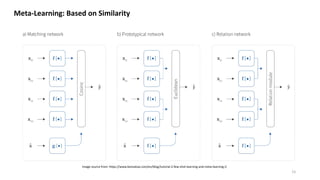
![Meta-Learning: Based on Similarity
0.08 0.02 0.1 0.8
x x x x
sum
Matching
Network
Prototypical
Network
14
[1] Vinyals, O., Blundell, C., Lillicrap, T., & Wierstra, D. (2016). Matching networks for one shot learning. Advances in neural information processing systems, 29, 3630-3638.
[2] Snell, J., Swersky, K., & Zemel, R. S. (2017). Prototypical networks for few-shot learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.05175.
Image source from original paper [1]
Image source from original paper [2]
Image modified from
original paper [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quickintroonfew-shotlearning-en-slideshare-210811095612/85/Introduction-to-Few-shot-learning-14-320.jpg)
![Meta-Learning: Based on Learning Algorithm
Memory Augmented Neural Network (MANN)
Learns the algorithm to store and retrieve memories [1]
16
dog cat dog dog cat
…
NULL
[1] Santoro, A., Bartunov, S., Botvinick, M., Wierstra, D., & Lillicrap, T. (2016, June). Meta-learning with memory-augmented neural networks. In International conference on machine learning (pp.
1842-1850). PMLR.
Image source from original paper [1]
Image source from original paper [1]
Image source: https://unsplash.com/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quickintroonfew-shotlearning-en-slideshare-210811095612/85/Introduction-to-Few-shot-learning-16-320.jpg)
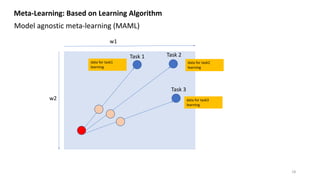
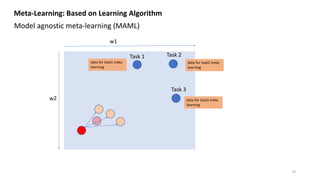
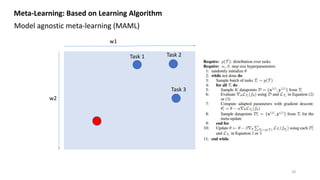
![w1
w2
Meta-Learning: Based on Learning Algorithm
Model agnostic meta-learning (MAML) [1]
17
Task 1 Task 2
Task 3
Init
[1] Finn, C., Abbeel, P., & Levine, S. (2017, July). Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks. In International Conference on Machine Learning (pp. 1126-1135). PMLR.
Image source modified from:
https://lilianweng.github.io/lil-log/2018/11/30/meta-learnin
g.html
Image source modified from:
https://lilianweng.github.io/lil-log/2018/11/30/meta-learnin
g.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quickintroonfew-shotlearning-en-slideshare-210811095612/85/Introduction-to-Few-shot-learning-17-320.jpg)
![Meta-Learning: Based on Data
Modeling through Bayesian Programs
21
…
- Structure of the model contains information
on how the output is created (prior)
- Meta-learning learns a way for various
Bayesian program modules to combine to
express unseen data
- Remember probabilistic programming with
Pyro?
[1] Lake, B. M., Salakhutdinov, R., & Tenenbaum, J. B. (2015). Human-level concept learning through probabilistic program induction. Science, 350(6266), 1332-1338.
Image source from original paper [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quickintroonfew-shotlearning-en-slideshare-210811095612/85/Introduction-to-Few-shot-learning-21-320.jpg)
