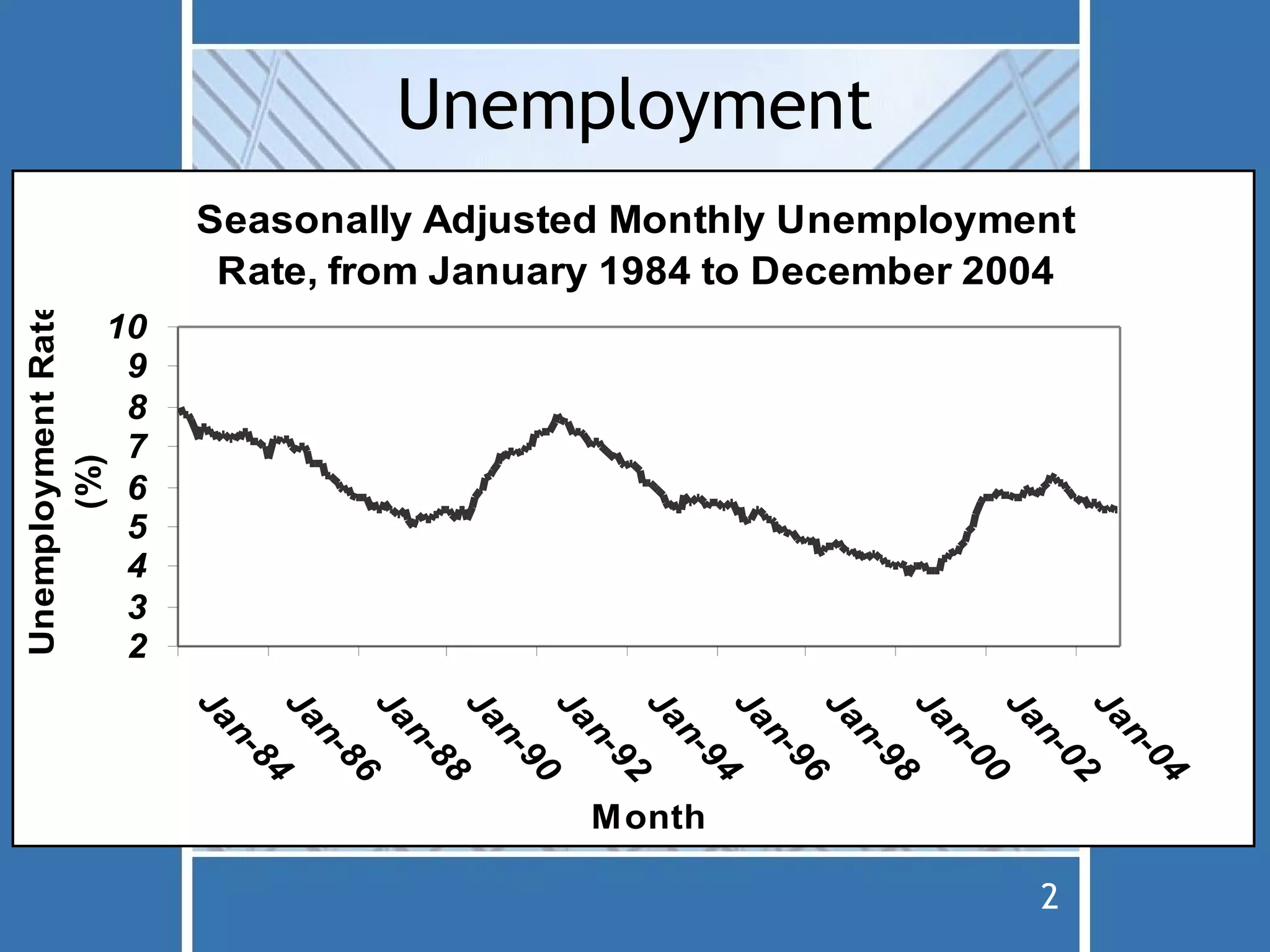
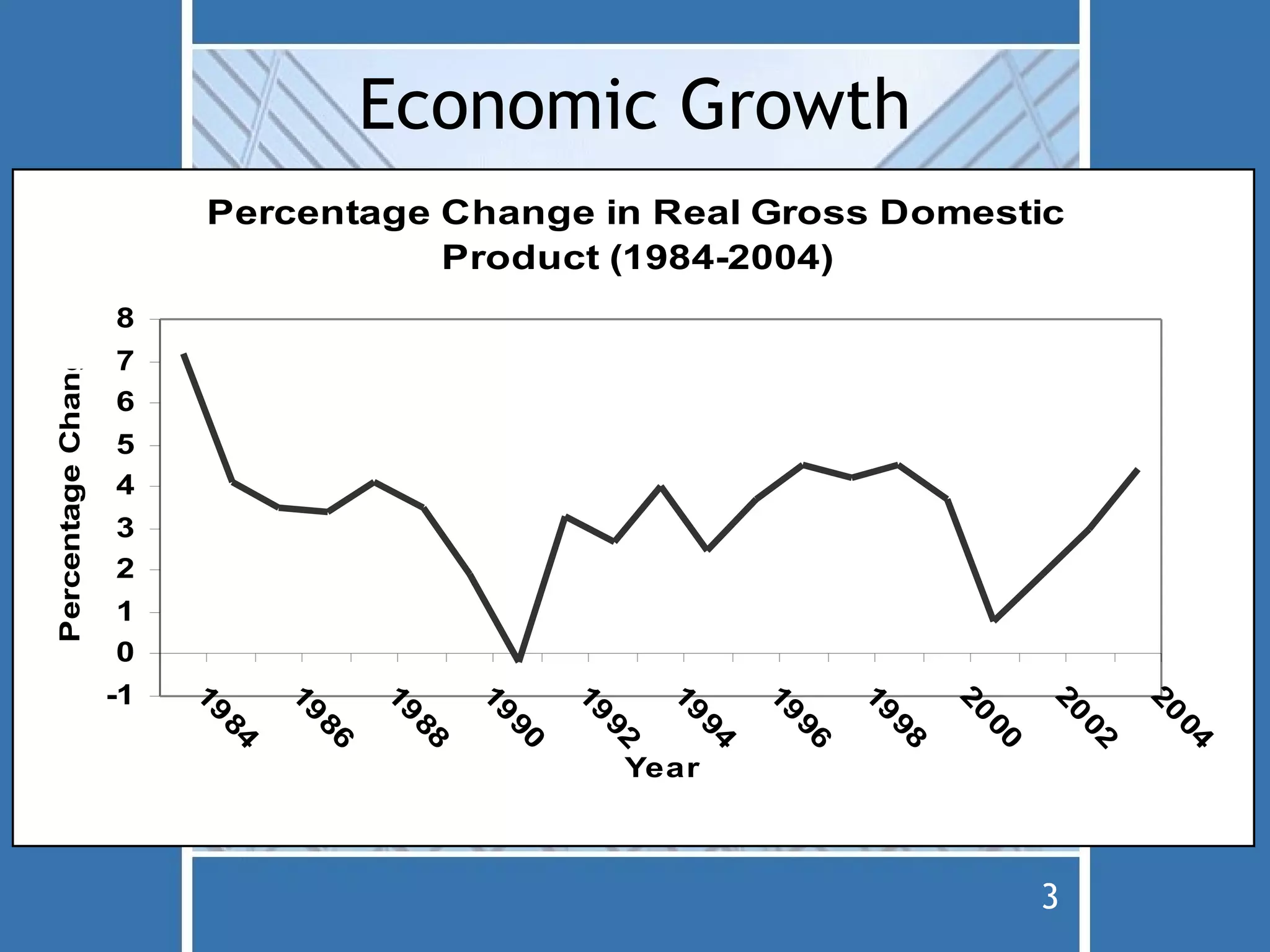
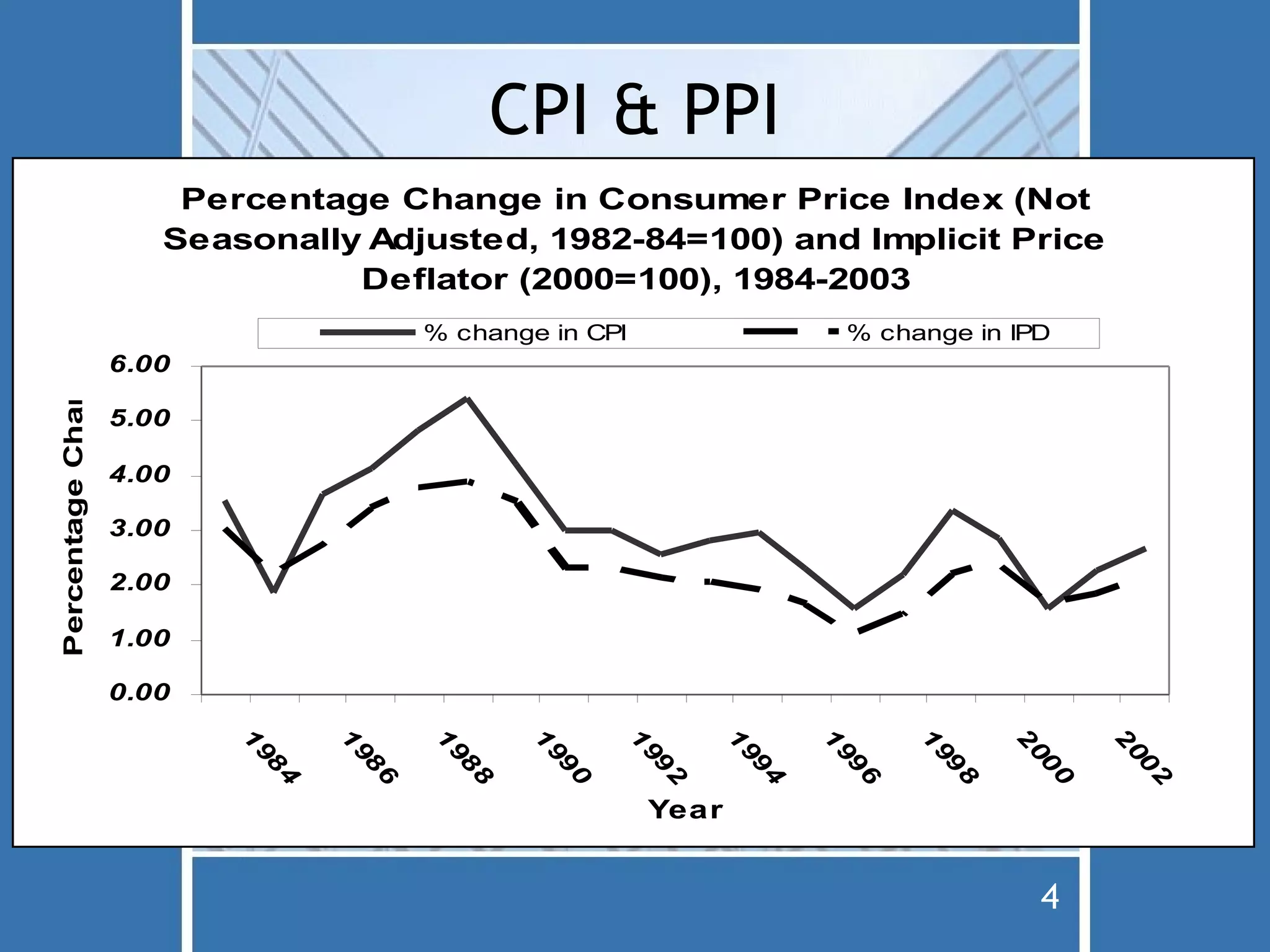
The document discusses fiscal policy and the expenditure multiplier. It explains that fiscal policy uses changes in government spending and taxation to influence the level of economic activity. It also discusses how the expenditure multiplier effect causes an initial change in spending to be multiplied through subsequent rounds of spending. Government spending is more directly impactful on the economy than taxation due to how consumers respond to tax changes. The document also covers crowding out, which occurs when government borrowing to finance spending bids up interest rates and reduces private investment.