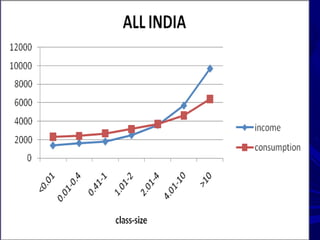
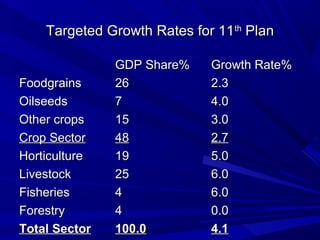
This document summarizes the role of agriculture in India. It notes that agriculture is important to the Indian economy, employing over 55% of the population but only contributing 15% to GDP. Most farmers are small holders on less than 2 hectares of land, with 60% of cultivation being rainfed. The document outlines India's historical agricultural growth rates and discusses the importance of technological and institutional innovations as well as high-value crops and linking small farmers to markets. It proposes targeted growth rates in the 11th plan and concludes that future strategies need to focus on diversification, small farmers, rainfed areas, and rural development to support sustainable agricultural transformation.