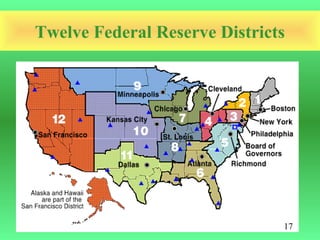
The document discusses the functions of money and monetary policy. It defines money as a medium of exchange, unit of account, store of value, and standard for deferred payment. It also outlines the four functions of money, different items historically used as money, how the price level is determined, requirements for an effective currency, components of the money supply, and the quantity theory of money. It introduces the Federal Reserve as the central bank that implements monetary policy in the US to maintain price stability and full employment through tools like open market operations and setting the federal funds rate.