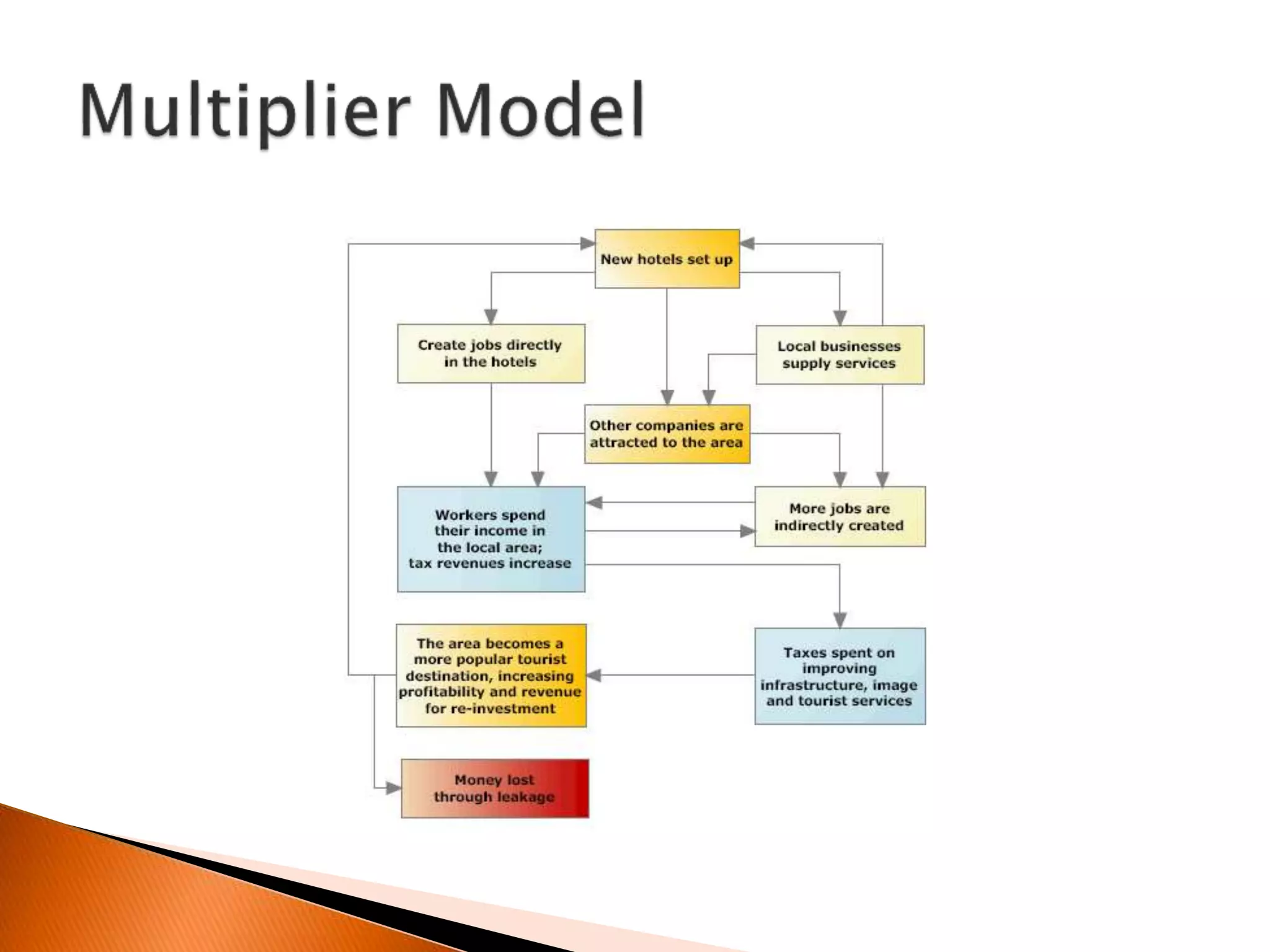
The document discusses the concept of economic multipliers in tourism. It explains that tourist spending generates direct, indirect, and induced economic impacts as money is spent and re-spent in a destination economy. Every transaction provides new income and the multiplier effect results in the initial spending being multiplied across economic sectors. The size of the multiplier depends on factors like leakages from the economy through imports or savings. Different types of multipliers are used to measure the total economic impact in terms of sales, output, income, and employment generated by initial tourist expenditures.