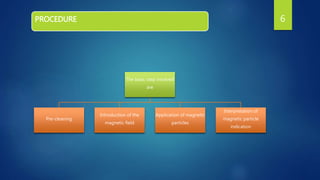
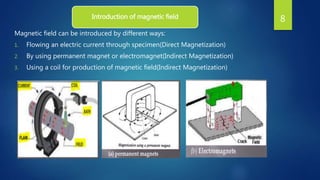
Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI) is a non-destructive testing method that uses magnetic fields and particles to detect surface and near-surface flaws in ferromagnetic materials, commonly employed in industries such as automotive and aerospace. The process involves magnetizing the component, applying iron particles, and interpreting the resulting magnetic indications to identify defects. Despite its advantages like cost-effectiveness and the ability to detect small flaws, MPI has limitations including its ineffectiveness on non-ferrous materials and the requirement for relatively smooth surfaces.