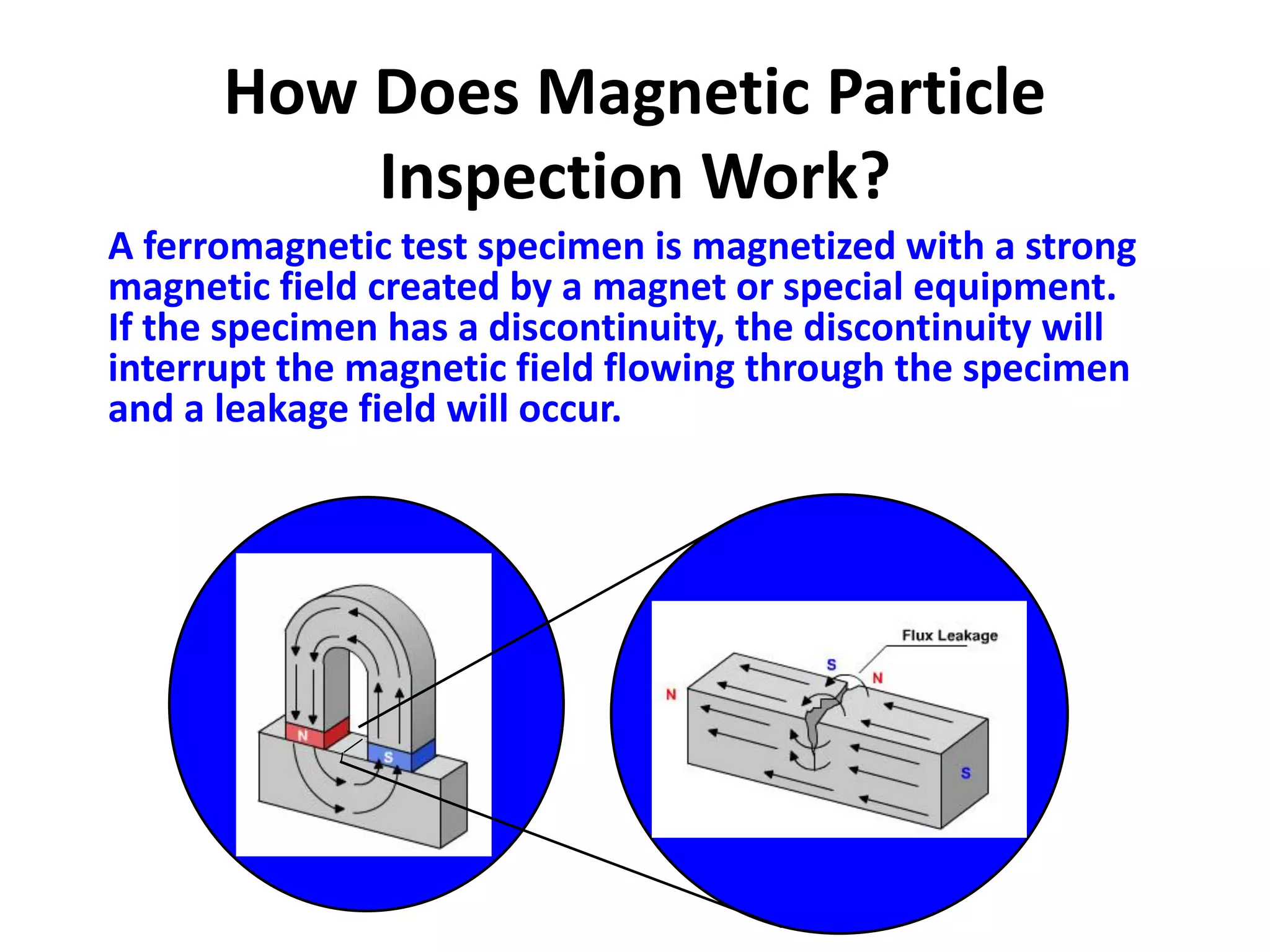
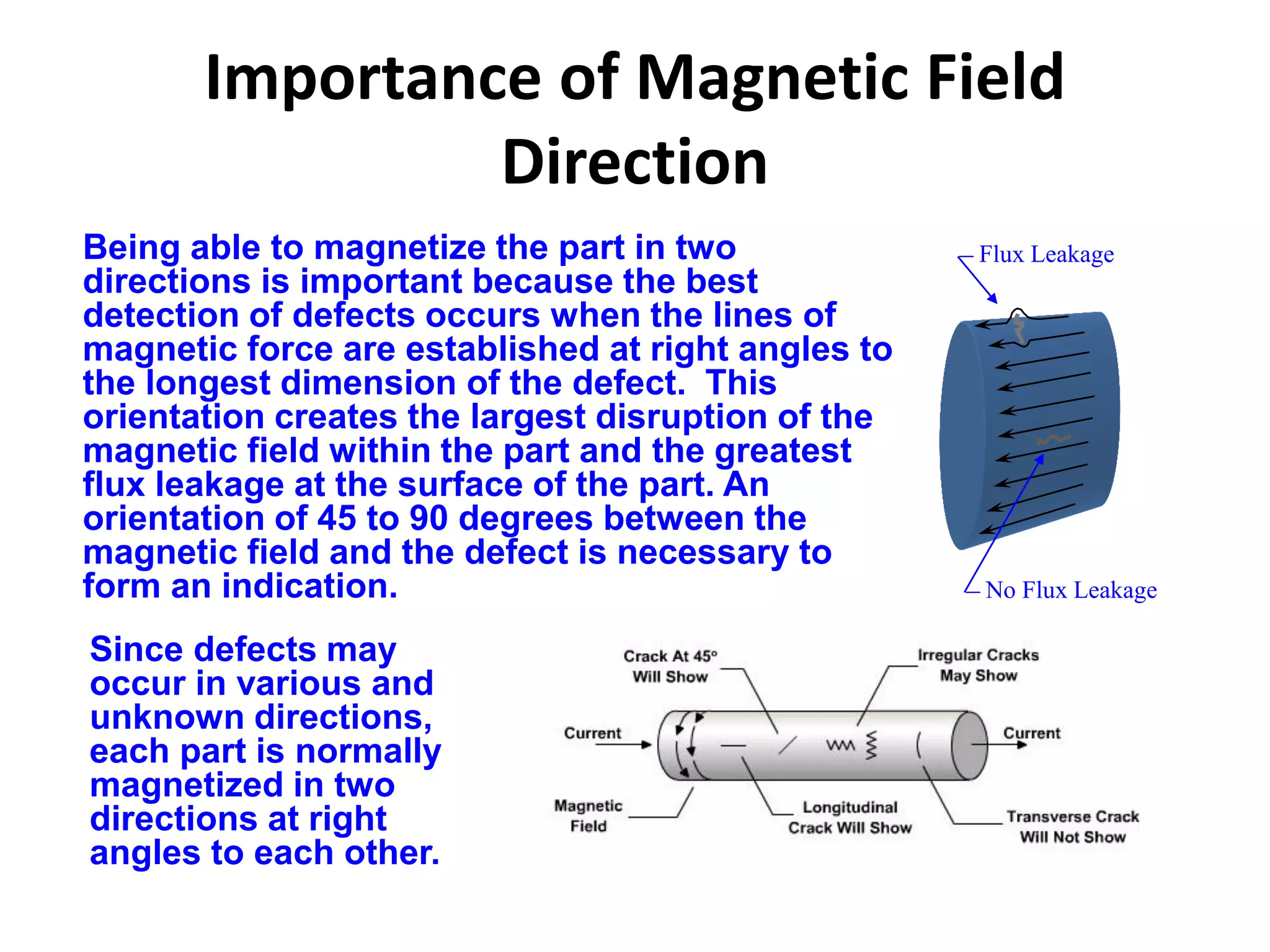
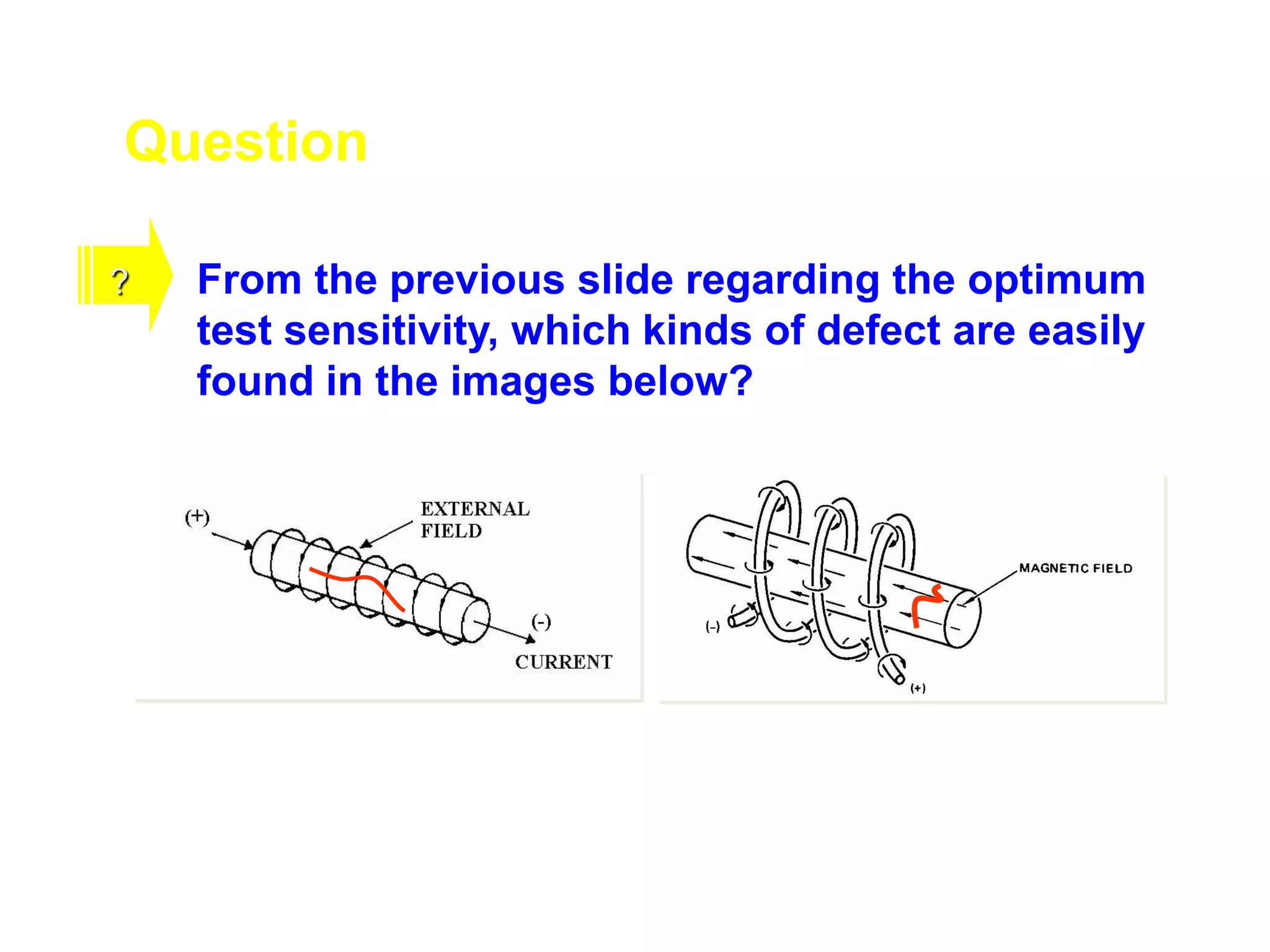
This document provides an overview of magnetic particle inspection (MPI), a non-destructive testing method used to detect surface and near-surface discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials. It describes how MPI works by magnetizing a component and applying iron particles to reveal defects that interrupt the magnetic field. The basic procedure involves pre-cleaning, introducing a magnetic field longitudinally or circularly, applying dry or wet magnetic particles, and interpreting any indications. Common MPI techniques are discussed along with the method's advantages of being fast, portable and able to detect a variety of defect types, as well as its limitations in inspecting non-ferrous materials and providing limited subsurface detection.