Embed presentation
Downloaded 217 times













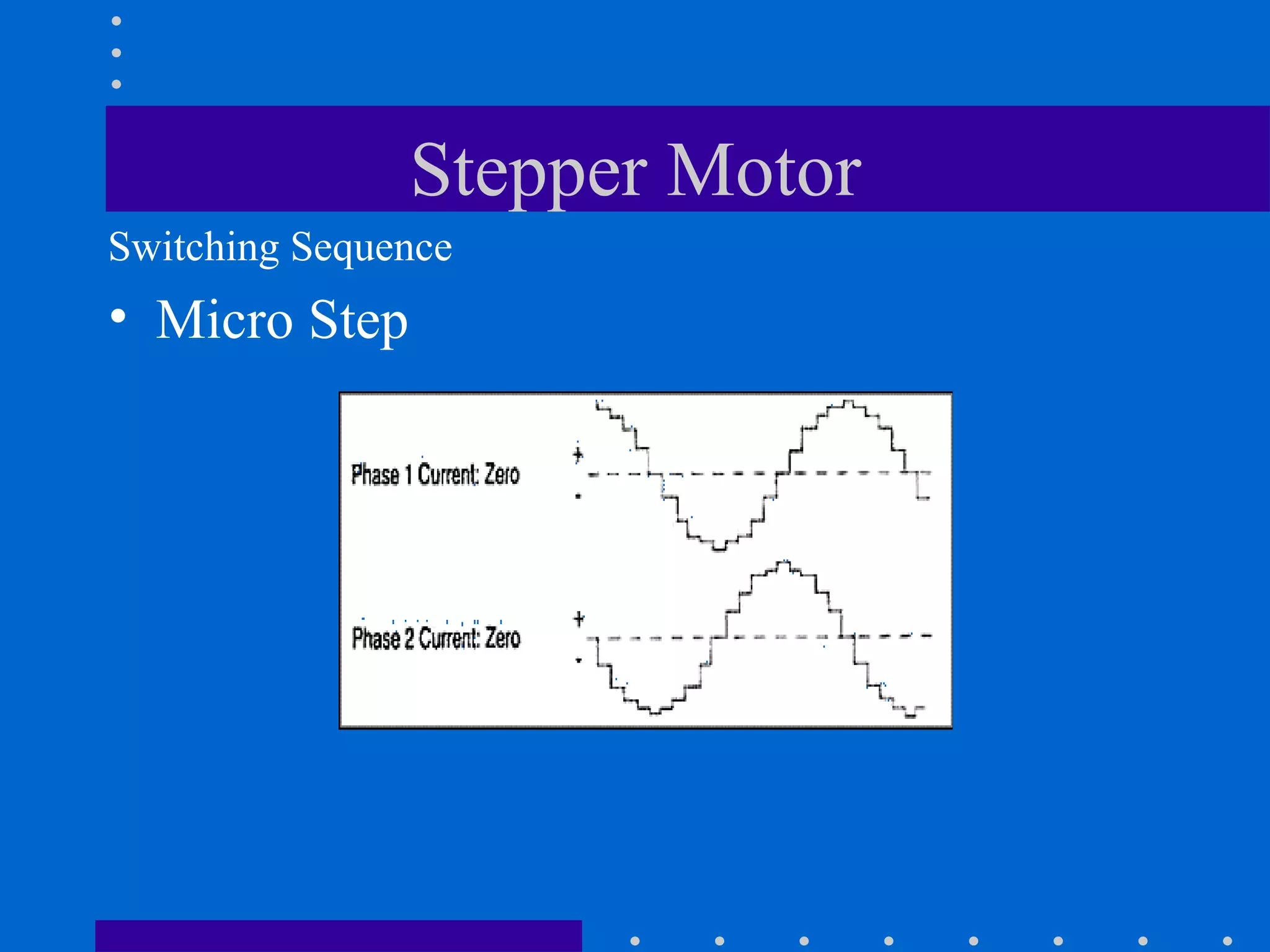





This document provides an overview of different types of motors, including stepper motors and servos. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of stepper motors, describes different types of stepper motors including permanent magnet, variable reluctance, and hybrid steppers. It also covers the theory of operation, switching sequences for full, half, and microstepping, and some applications of stepper motors such as in printers, transport, and wafer slicing. Servo motors are also briefly mentioned.



















