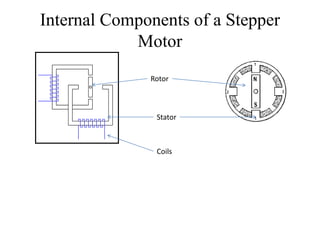
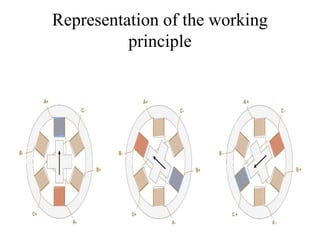
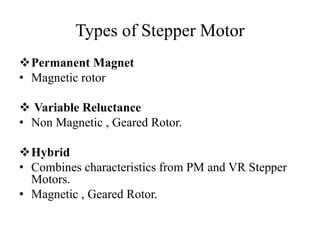
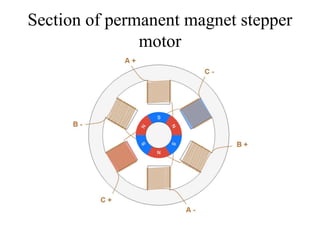
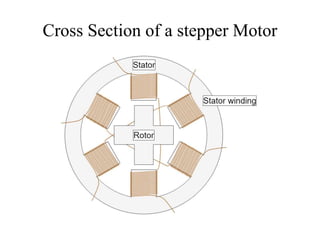
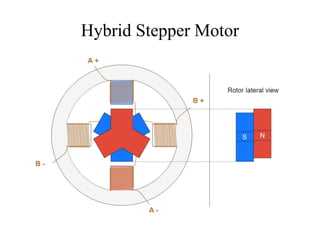
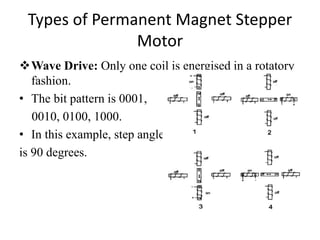
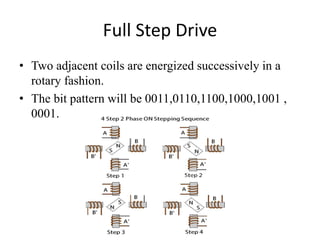
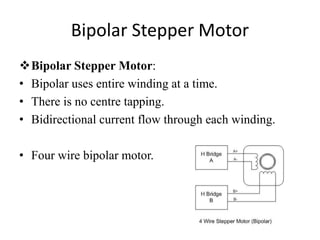
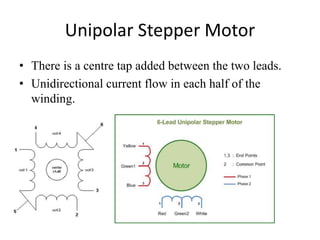
Stepper motors are used for precision position control. They rotate in discrete steps by energizing coils in a specific sequence without position sensors. There are three main types - permanent magnet, variable reluctance, and hybrid stepper motors. Permanent magnet steppers have strong torque but lower speed/resolution, while variable reluctance steppers have higher speed/resolution but lower torque. Hybrid steppers combine benefits of both for high performance. Full, half, and wave drive modes determine step angle and sequence of coil energization. Bipolar steppers use entire windings bidirectionally, while unipolar steppers have center taps for unidirectional current flow.